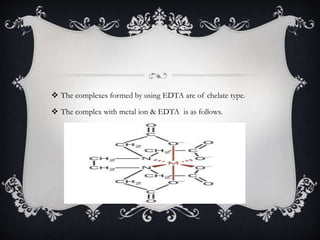
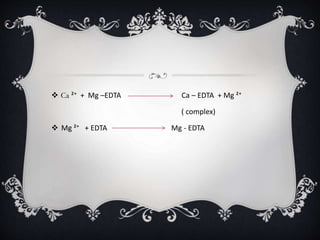
Complexometric titration involves converting simple metal ions into stable, water-soluble complexes via ligand interactions, with examples including unidentate, bidentate, and multidentate ligands like EDTA. Various titration types, such as direct, back, and indirect titrations, are employed based on the stability of the metal-ligand complex. Applications include measuring water hardness and detecting metal ion concentrations in different contexts.