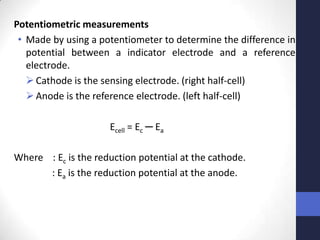
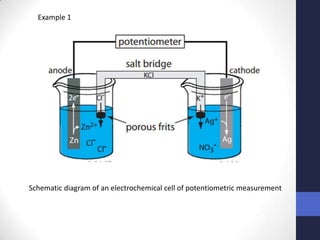
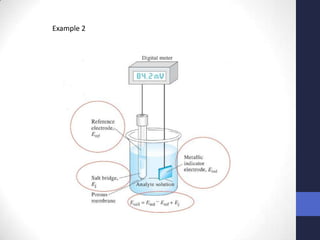
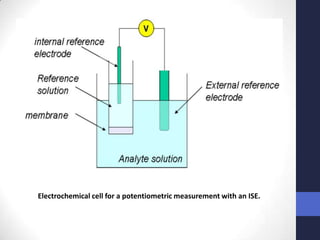
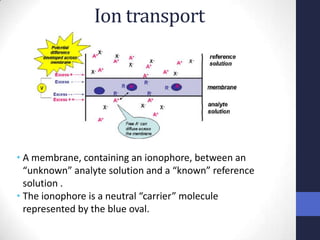
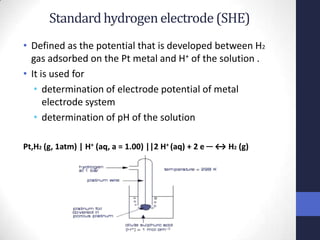
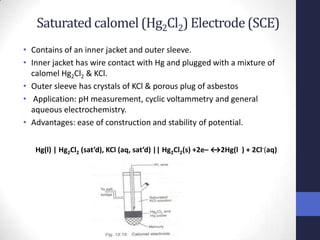
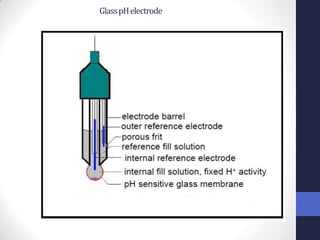
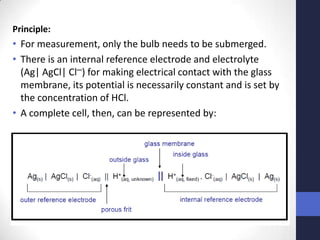
This document discusses the principles of potentiometric measurement. Potentiometry involves measuring the potential of an electrochemical cell under conditions of zero current flow, allowing the cell composition to remain unchanged. The potential is related to analyte concentration by the Nernst equation. Potentiometric cells consist of a sensing electrode and a reference electrode separated by a salt bridge. The potential difference between the electrodes corresponds to analyte levels. Common sensing electrodes include ion-selective electrodes and metallic electrodes like silver or copper that respond to specific ions.





















![Alkaline Error cont.
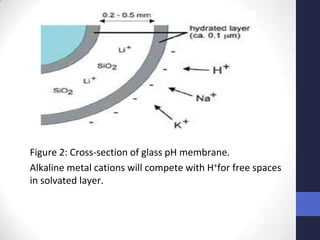
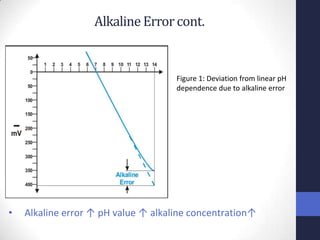
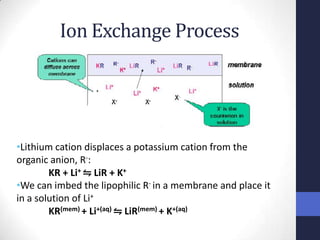
• At high pH where [H+] <<< [Na+], electrode begins to
respond to [Na+].
• Ion exchange reaction occurs at membrane surface
• Alkaline ions will replace H+ ions completely/partially in
outer gel layer of glass membrane.
• Result: pH value measured < actual pH
• Usually noticeable: - pH> 12
- [Li+ /Na+] ≥ 0.1 mol/litre](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sclg6final-121204074642-phpapp01/85/potentiometry-34-320.jpg)