The document provides an overview of several instructional design models:
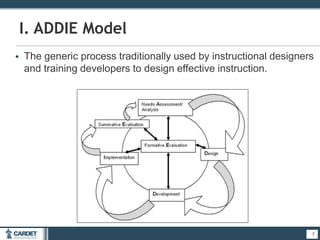
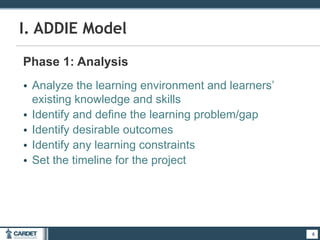
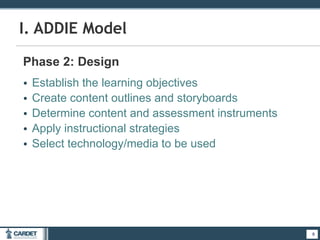
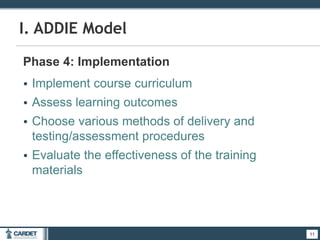
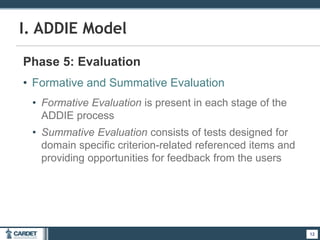
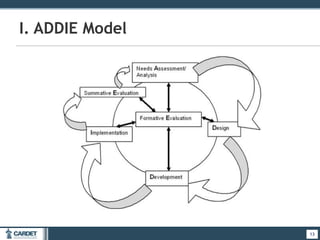
1. The ADDIE model, which is a systematic 5-phase process of analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation. Each phase is described.
2. The Dick and Carey model, which involves learners and subject matter experts interacting continuously to review and revise prototypes.
3. Rapid prototyping, which involves quickly generating mock-ups or physical samples of products to get feedback early in the design process.
4. Merrill's First Principles of Instruction, which proposes learning is most effective when problem-based and involving four phases: activating prior knowledge, demonstrating skills, applying skills, and integrating skills into real-world activities.