Embed presentation
Downloaded 62 times
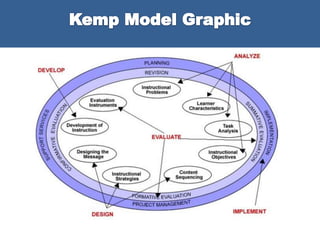



The document describes an instructional design model that has 9 iterative and interdependent steps for developing instructional programs in a systemic and flexible way. It focuses on identifying instructional problems, learner characteristics, objectives, sequencing content, designing strategies, planning delivery, and evaluating objectives. The model allows designers to begin at any point and revise designs concurrently for adaptability. However, constant revision may be time-consuming.



