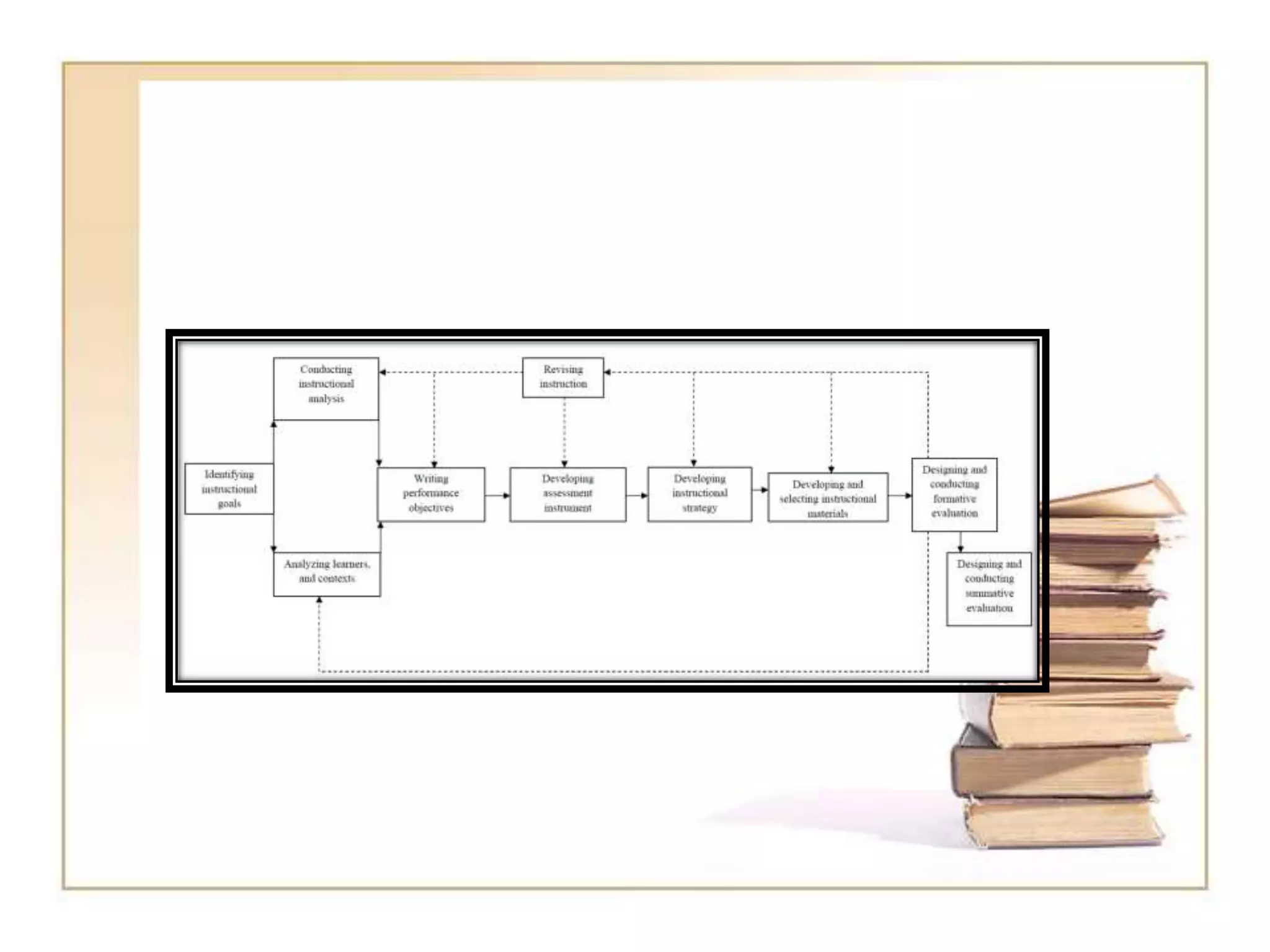
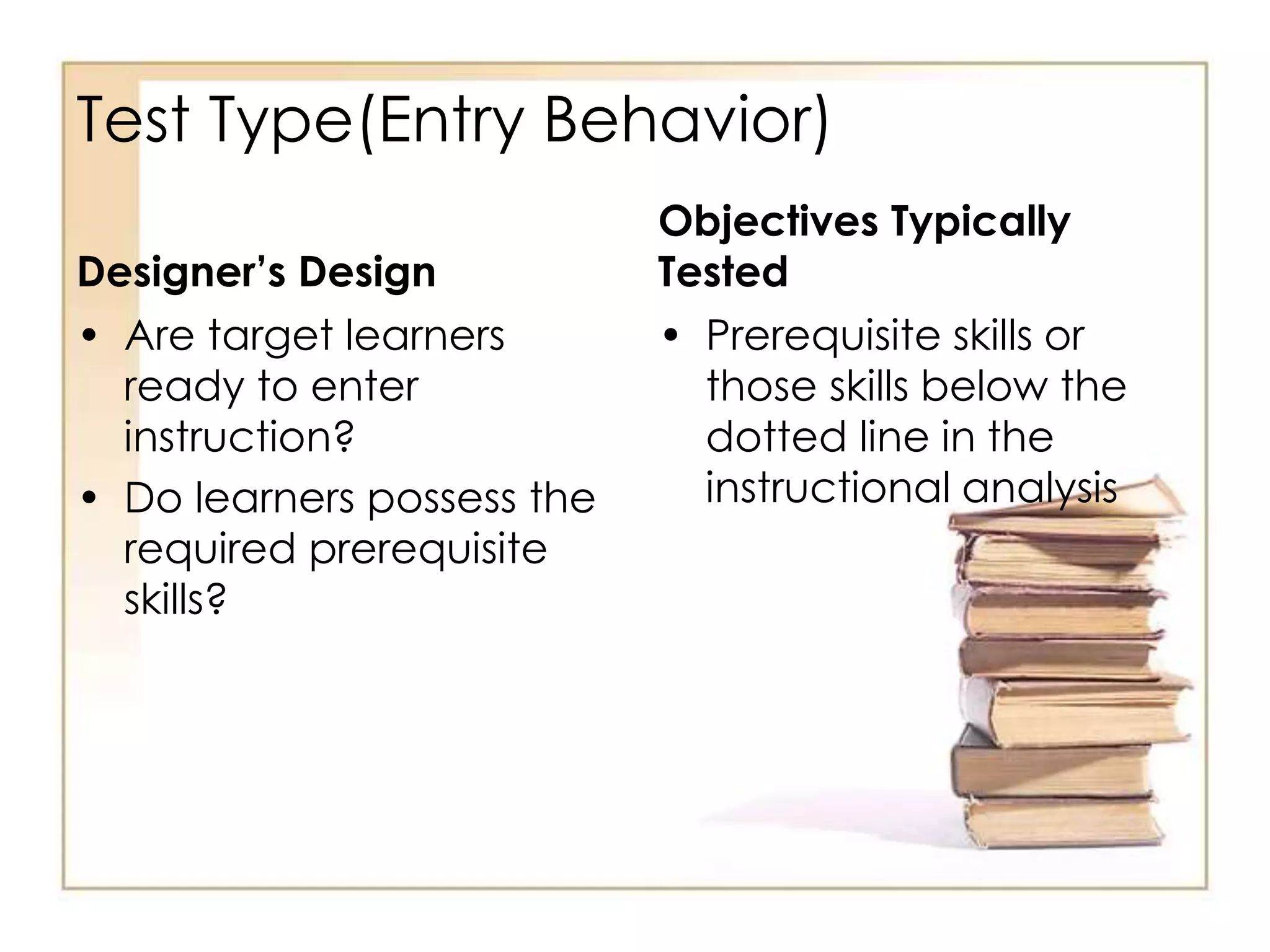
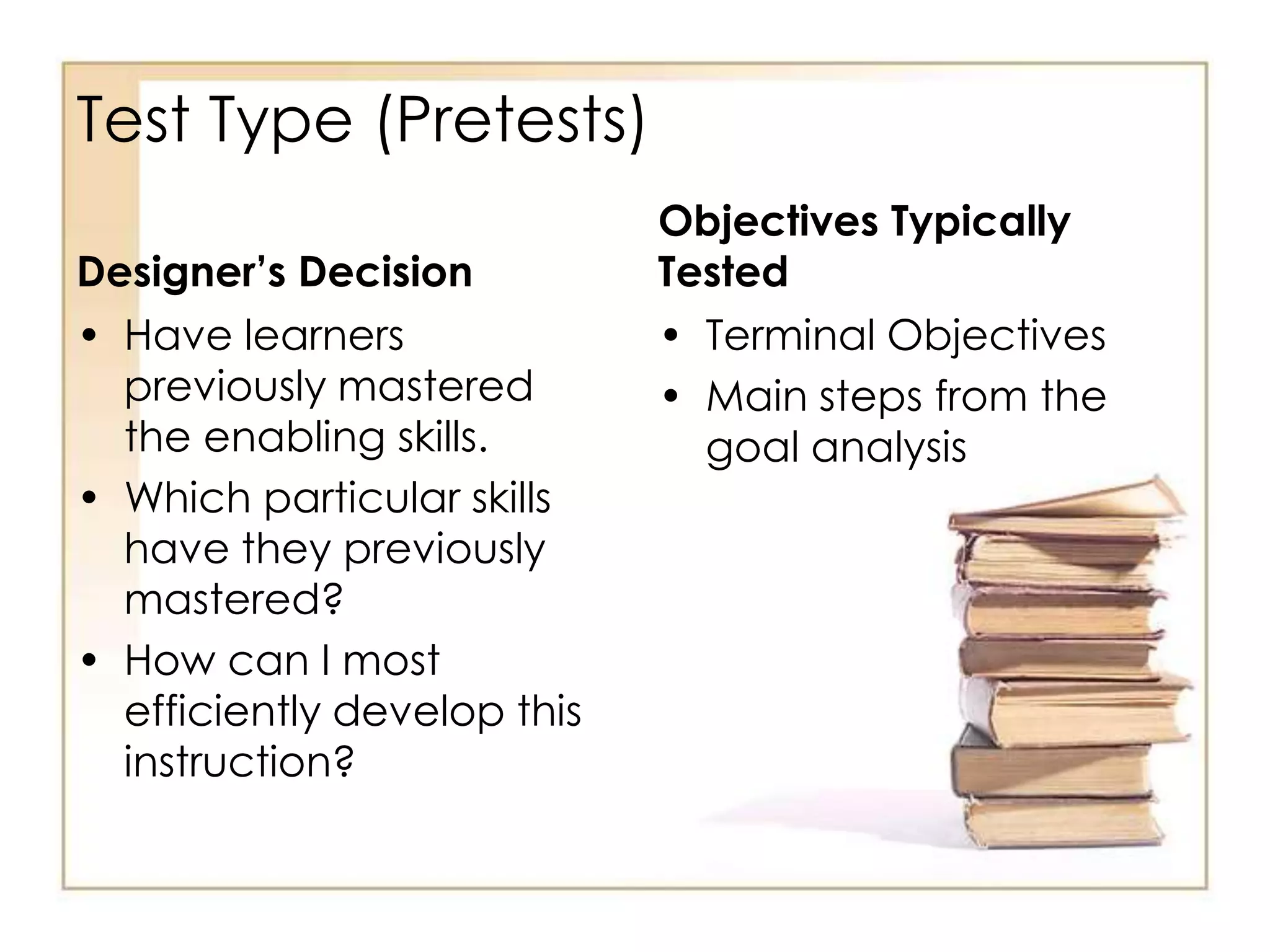
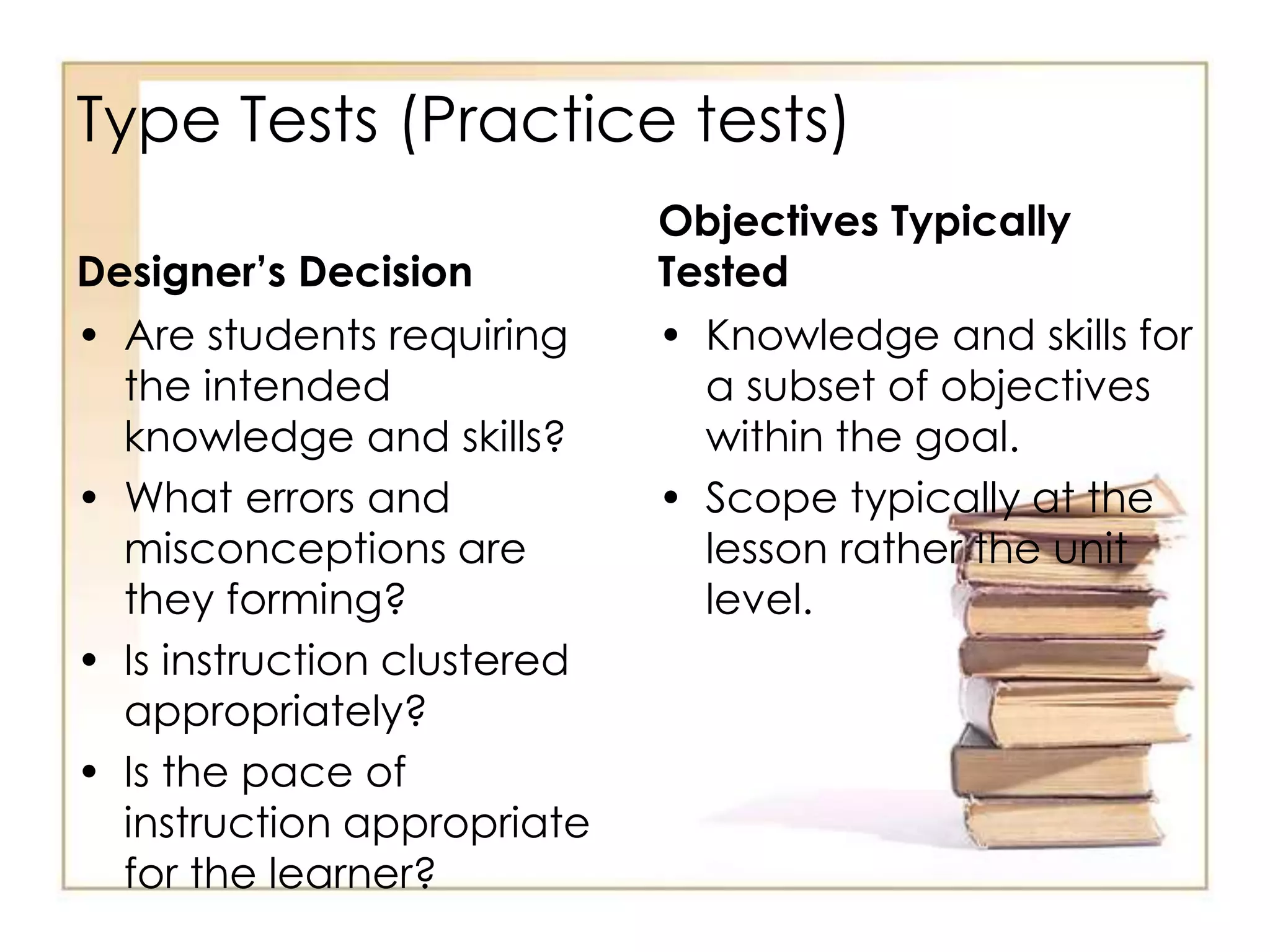
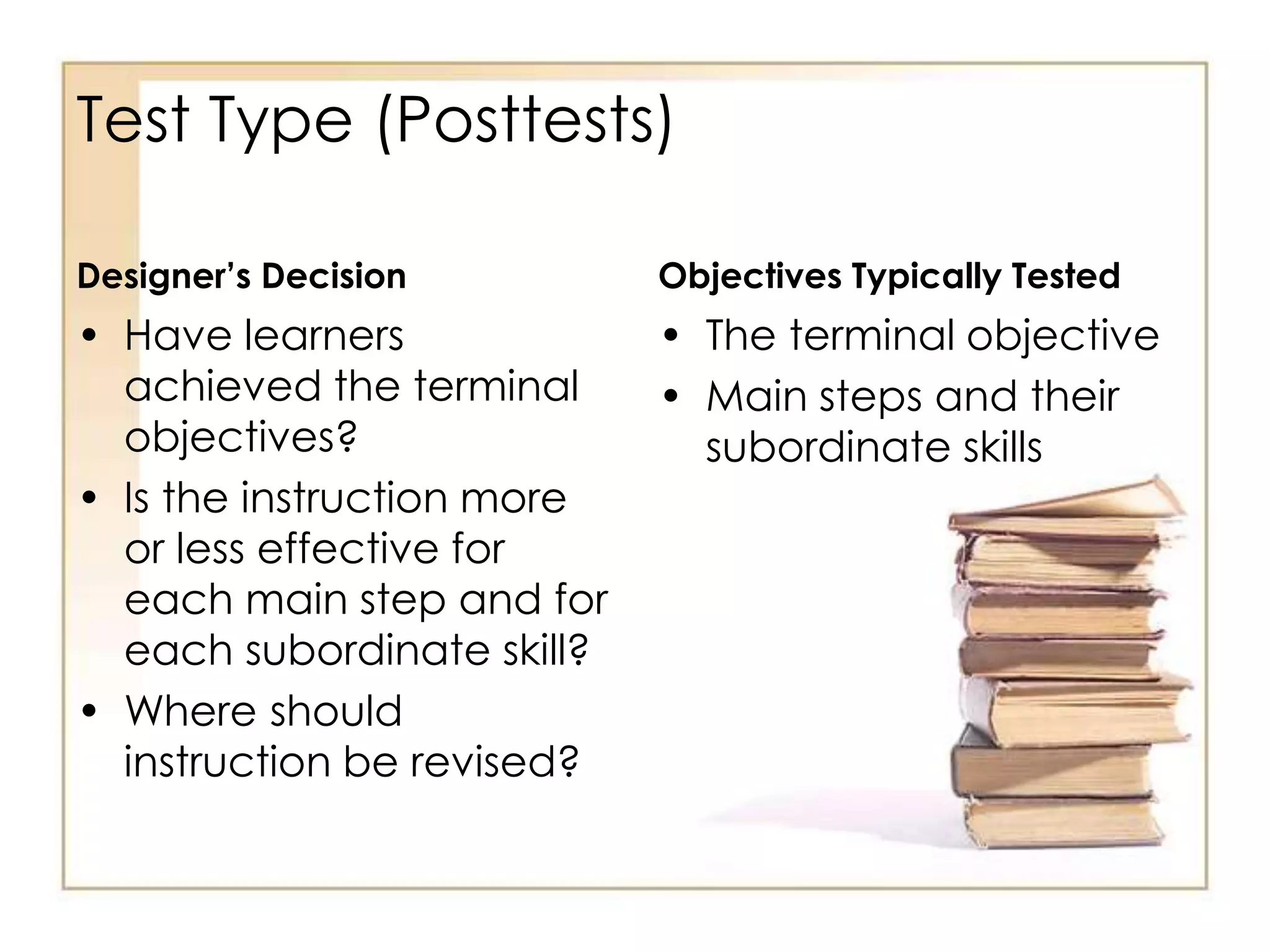
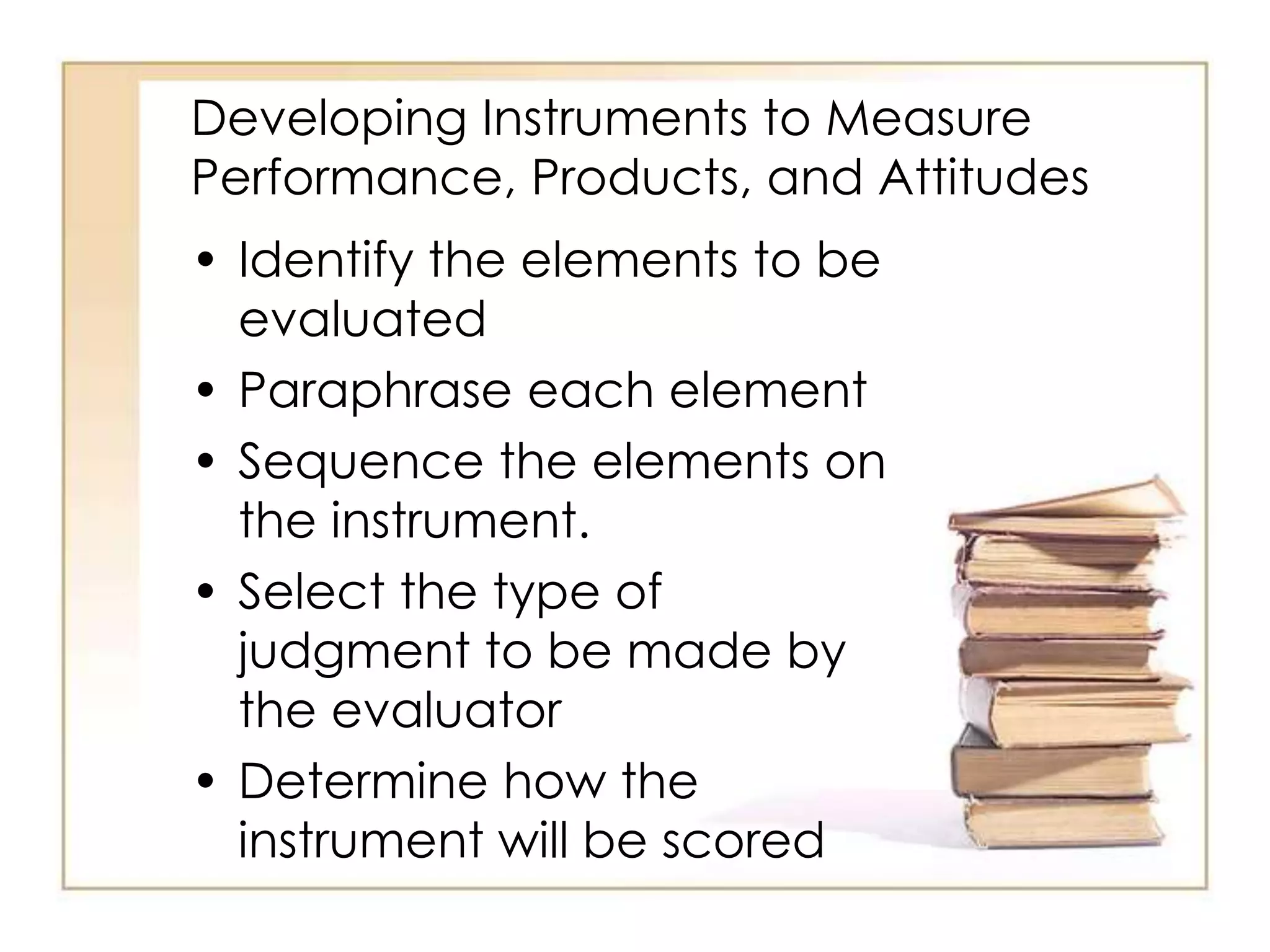
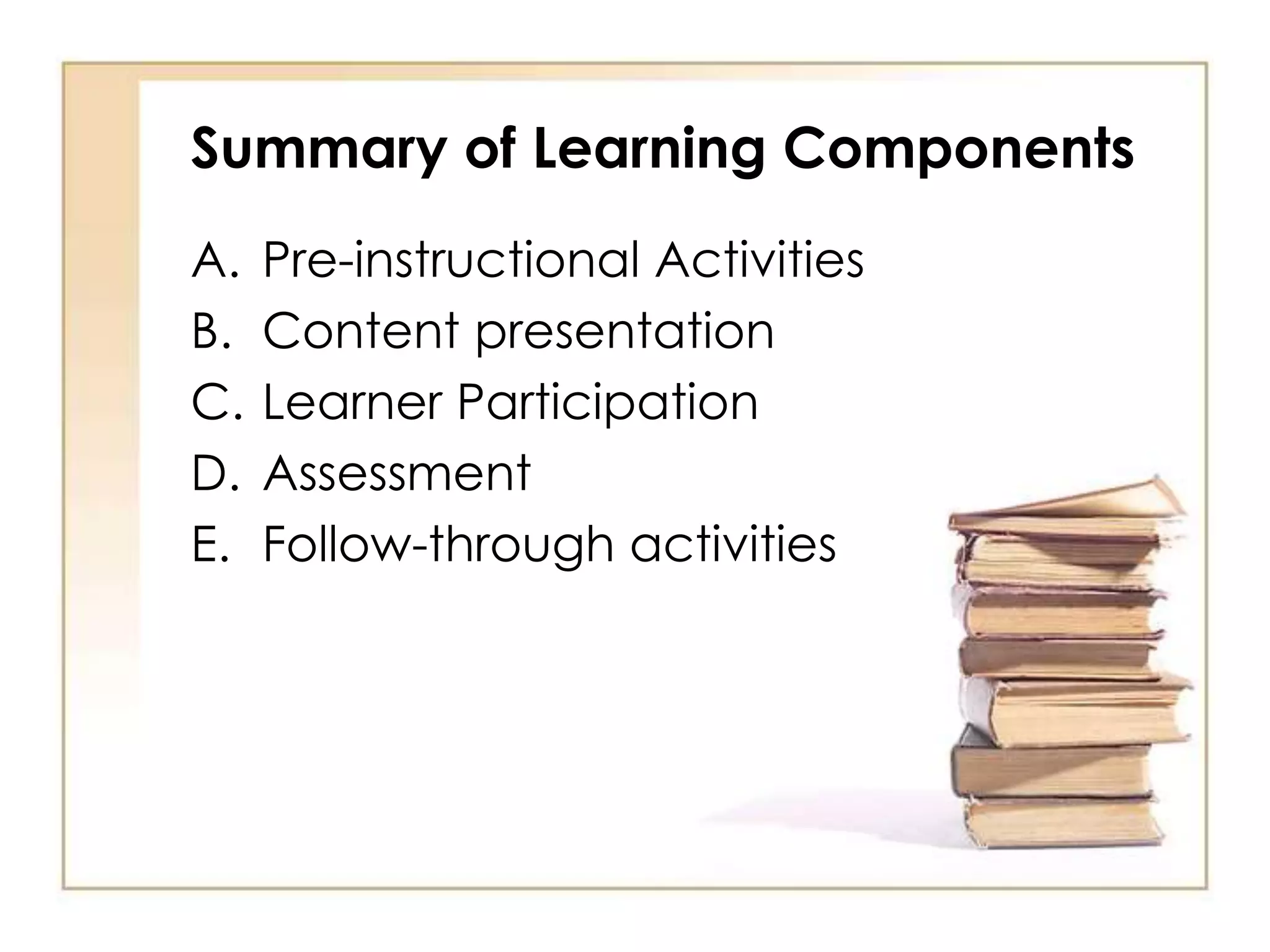
This document outlines the key principles and steps of instructional design according to Dick and Carey's systematic design model. It discusses establishing instructional goals, analyzing the learning context, writing objectives and criterion-referenced tests, developing instructional strategies and materials, and conducting formative evaluations to revise instruction. The goal is to design effective instruction by thoroughly analyzing learning needs and contexts, developing appropriate objectives and assessments, selecting optimal instructional approaches, and refining the design through evaluation and revision.