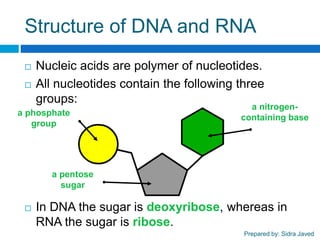
Friedrich Miescher isolated nuclein from white blood cell nuclei in 1868, which showed acidic properties and was renamed nucleic acid. Nucleic acids are present in all living cells and viruses, containing the genetic blueprint and instructions for growth, development, and reproduction. There are two main types: DNA containing deoxyribose and the bases A, G, T, C; and RNA containing ribose and the bases A, G, U, C. Nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides containing a phosphate group, sugar, and nitrogenous base. DNA has a double-stranded structure with bases pairing via hydrogen bonds, while RNA is single-stranded.