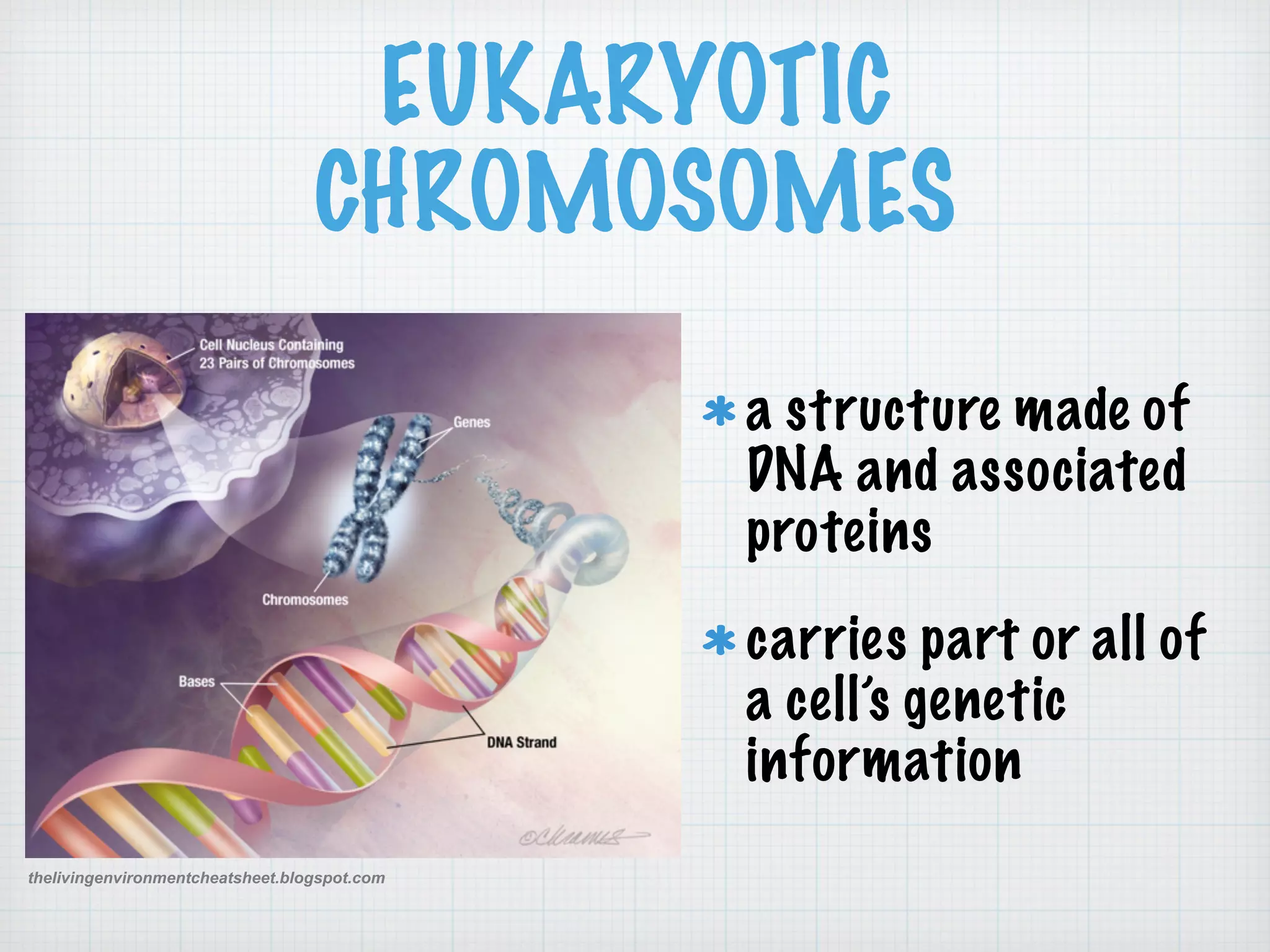
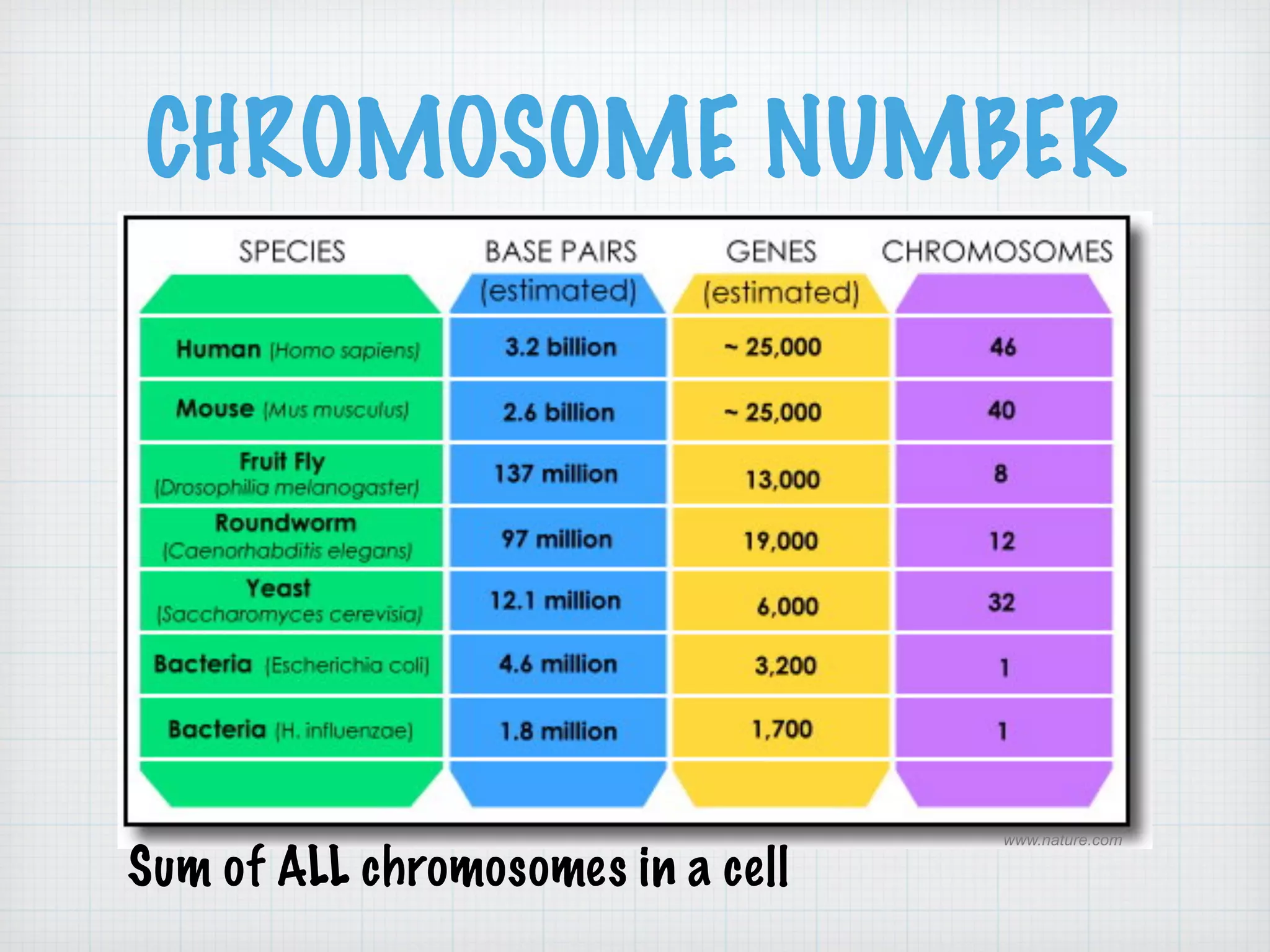
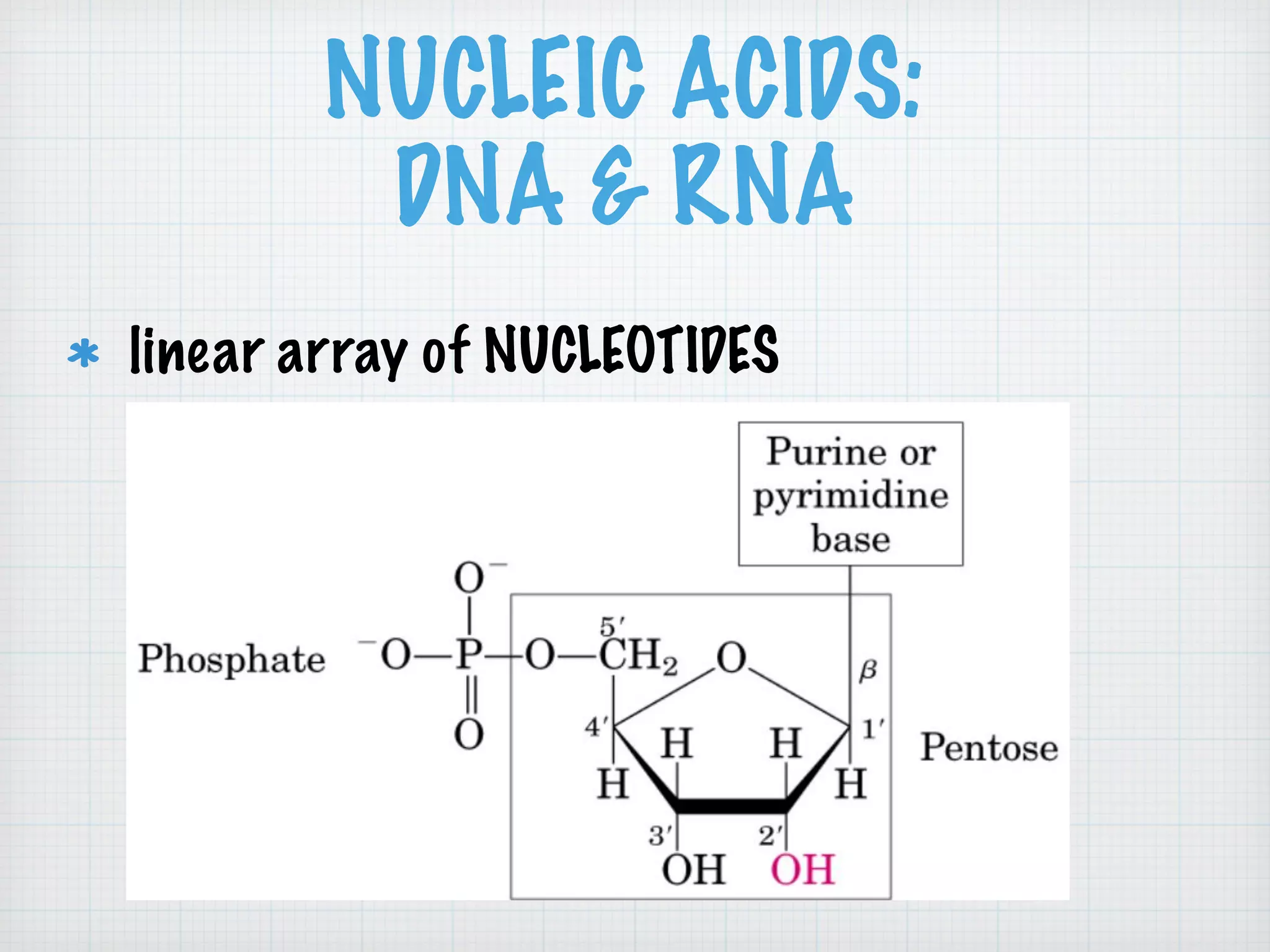
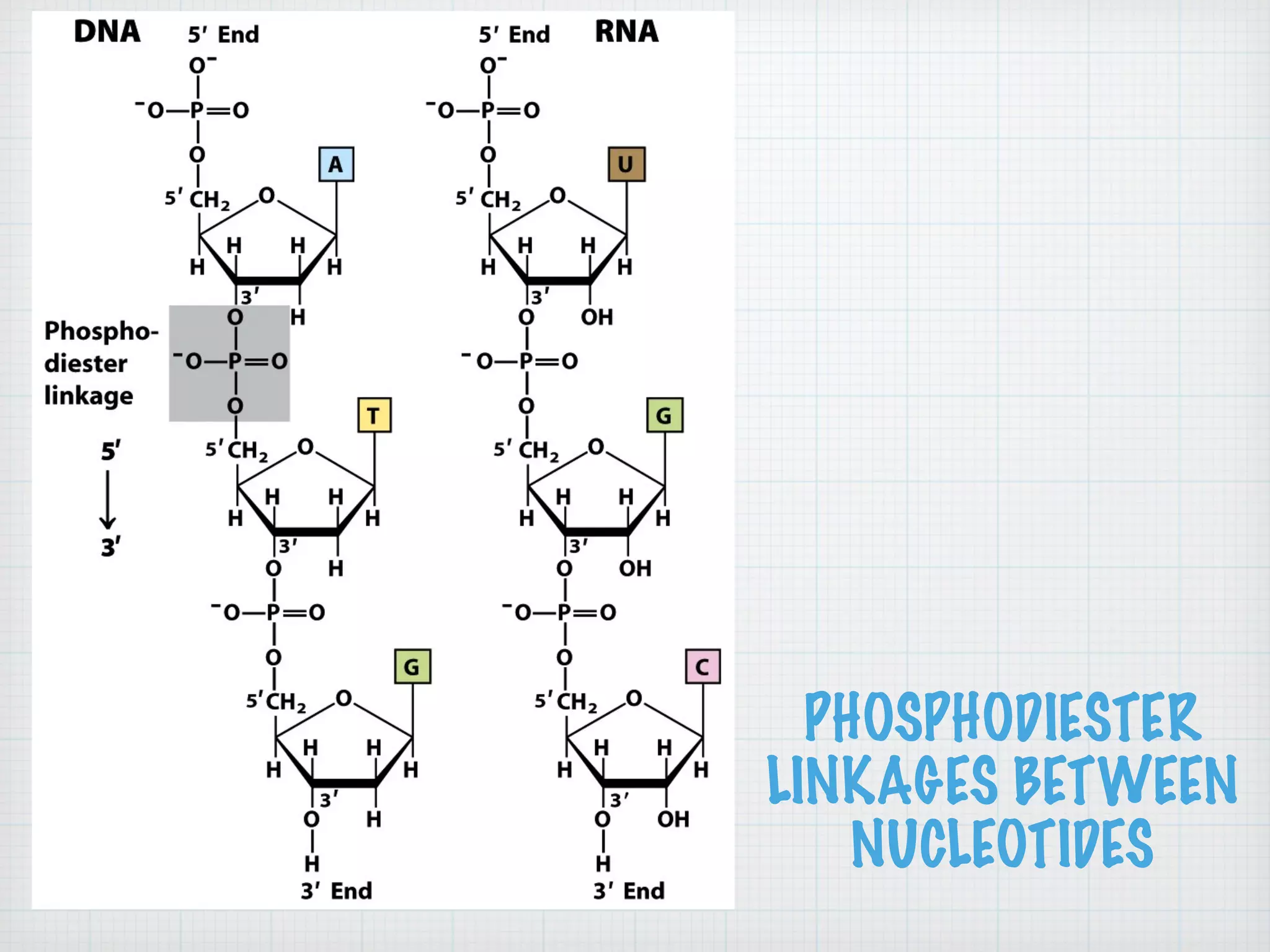
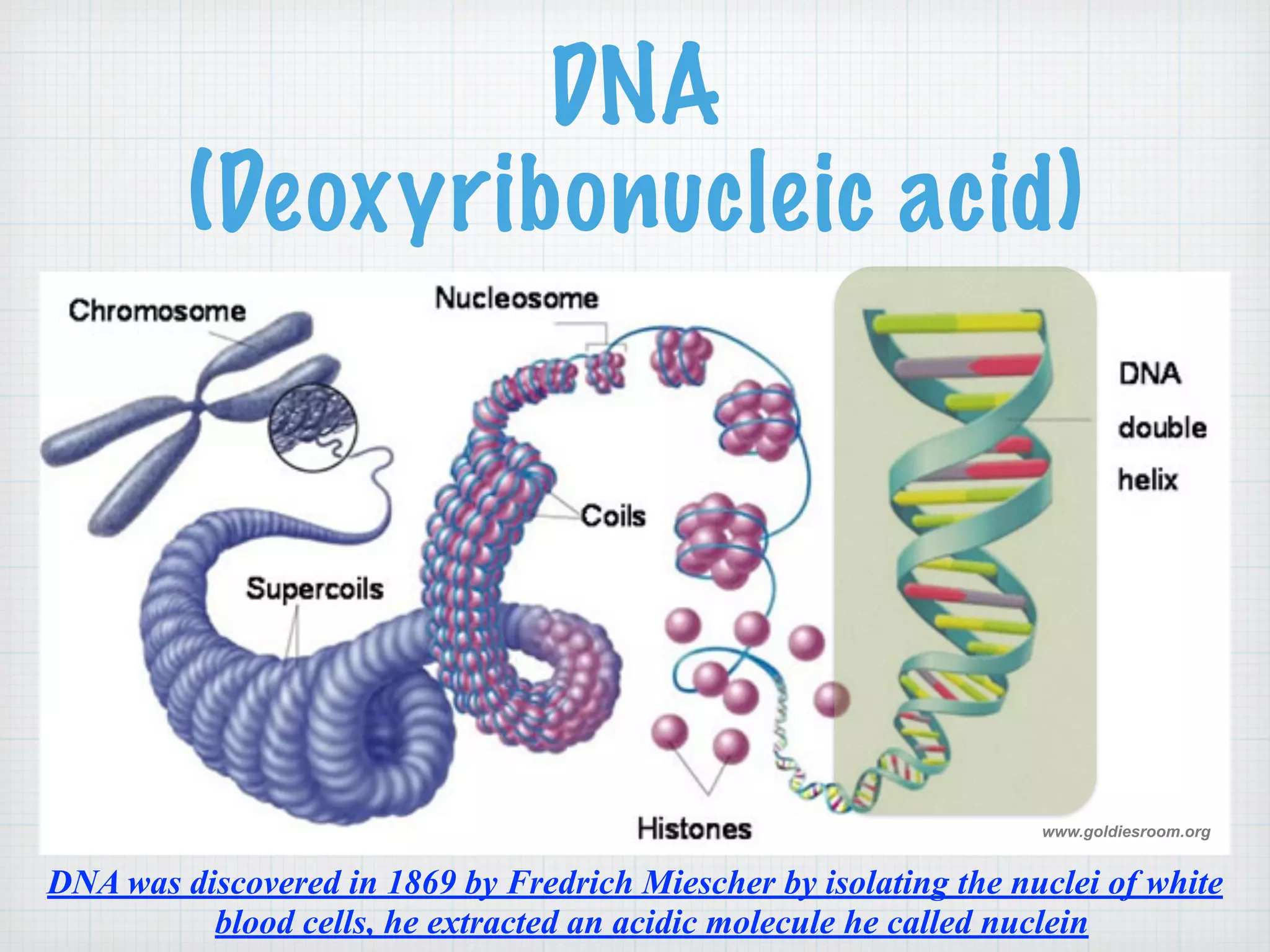
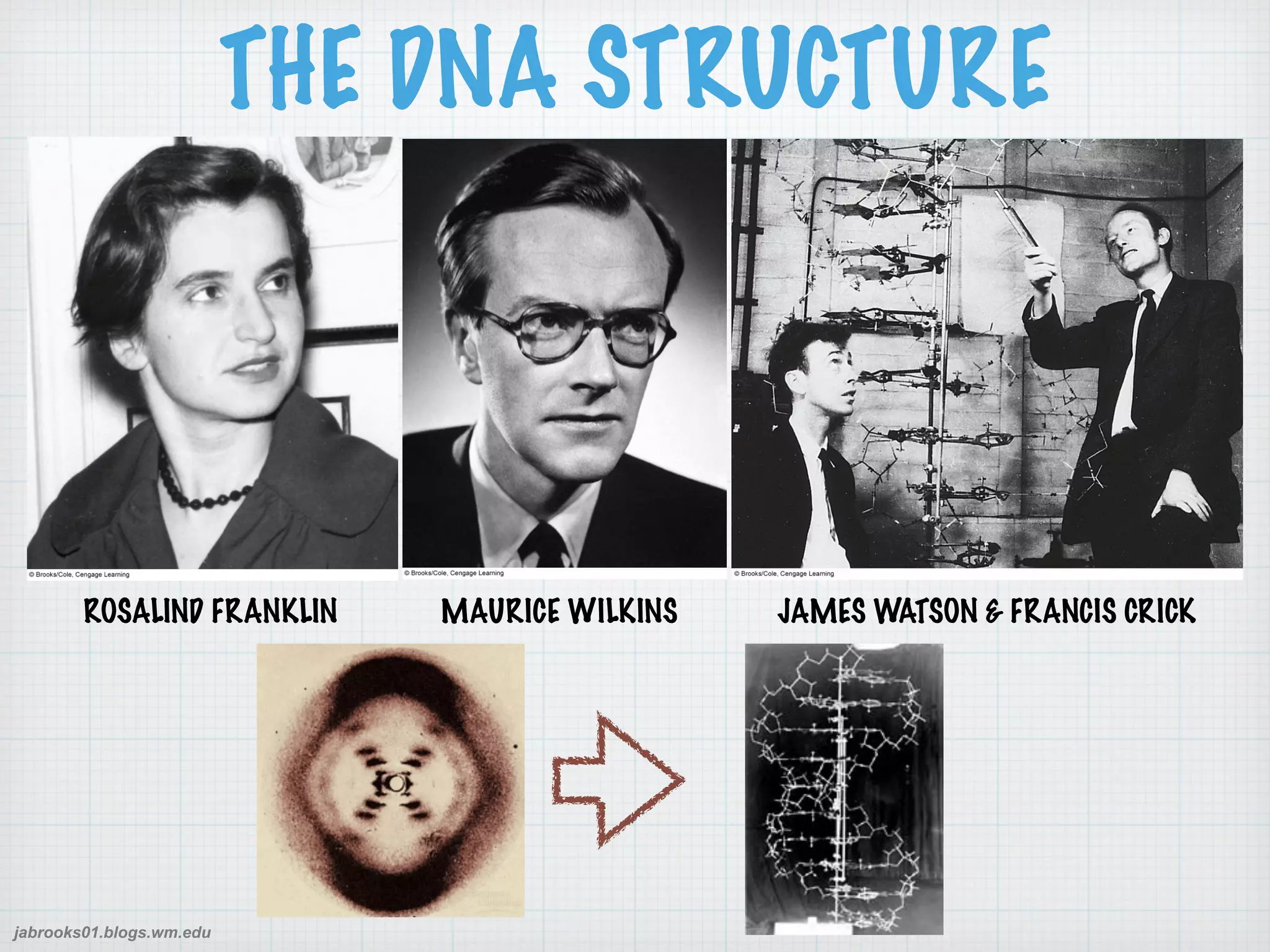
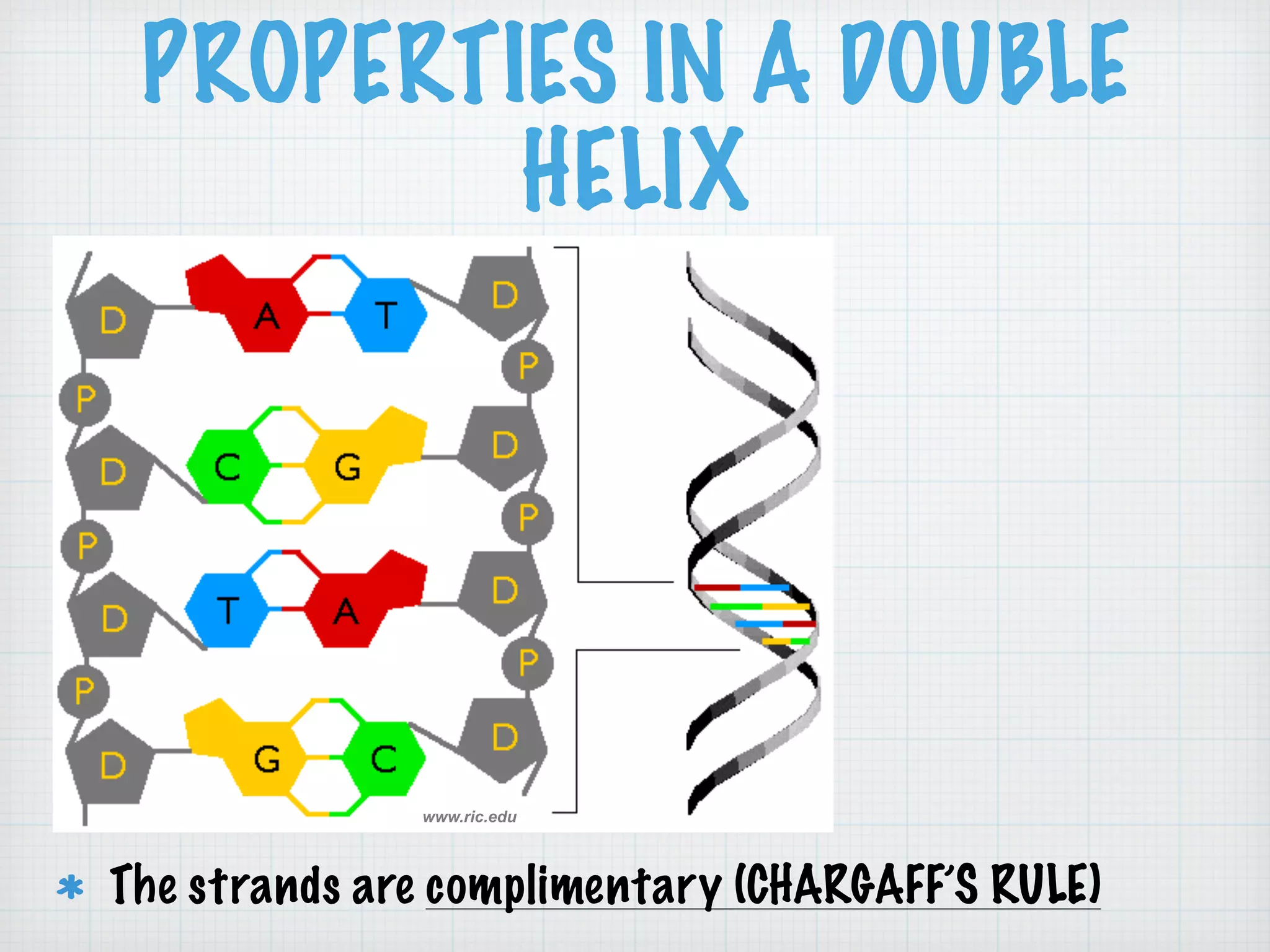
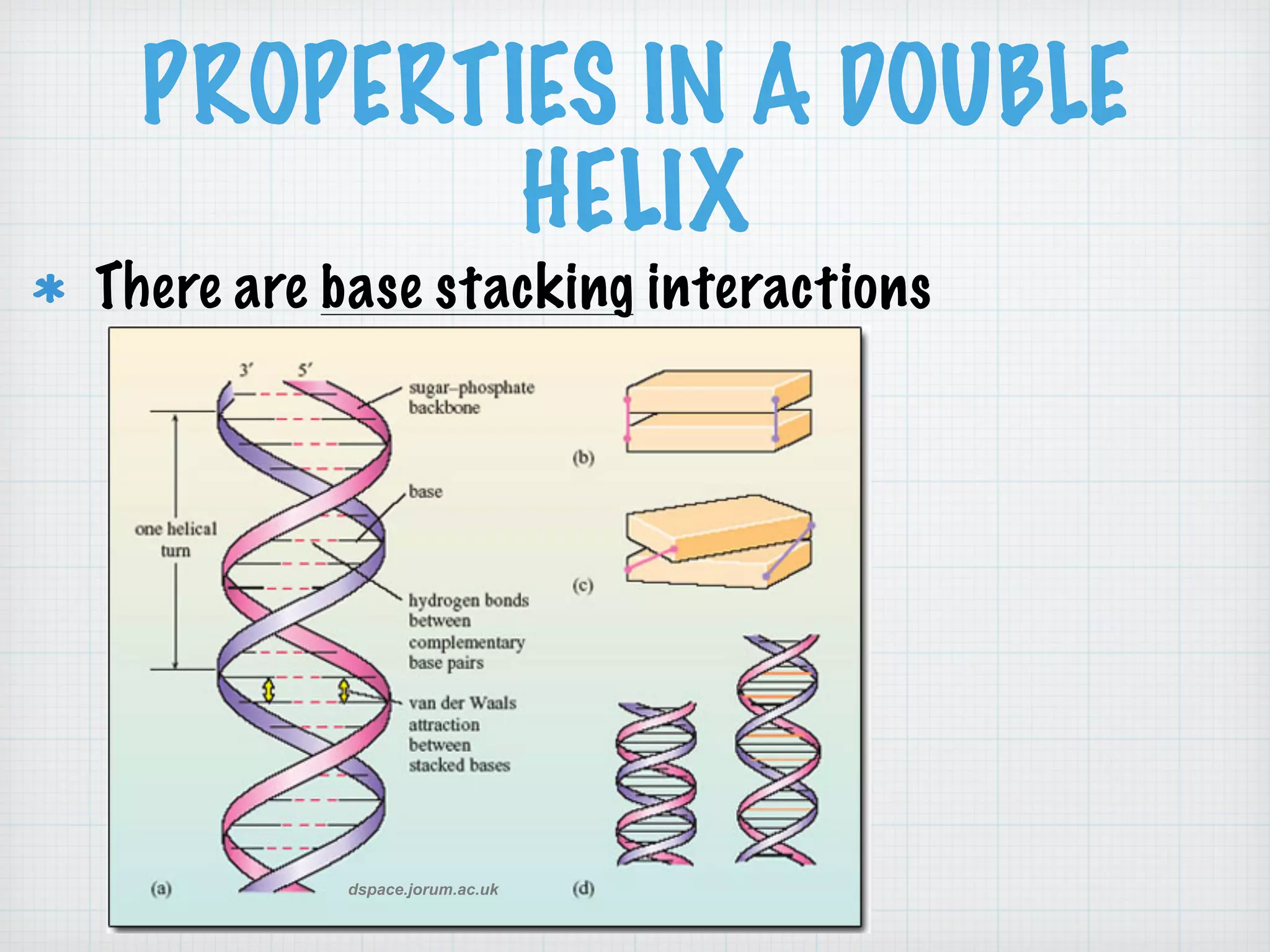
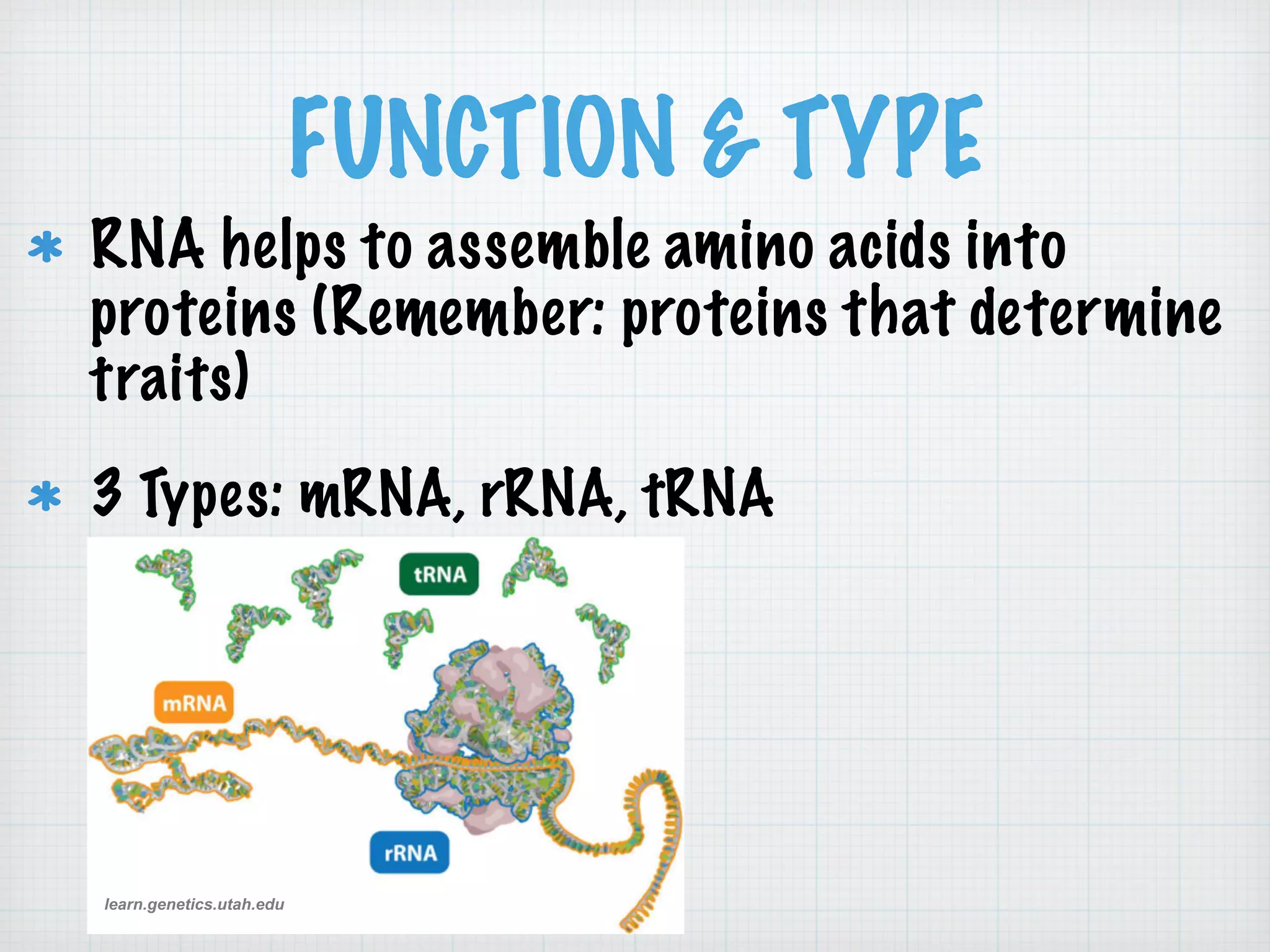
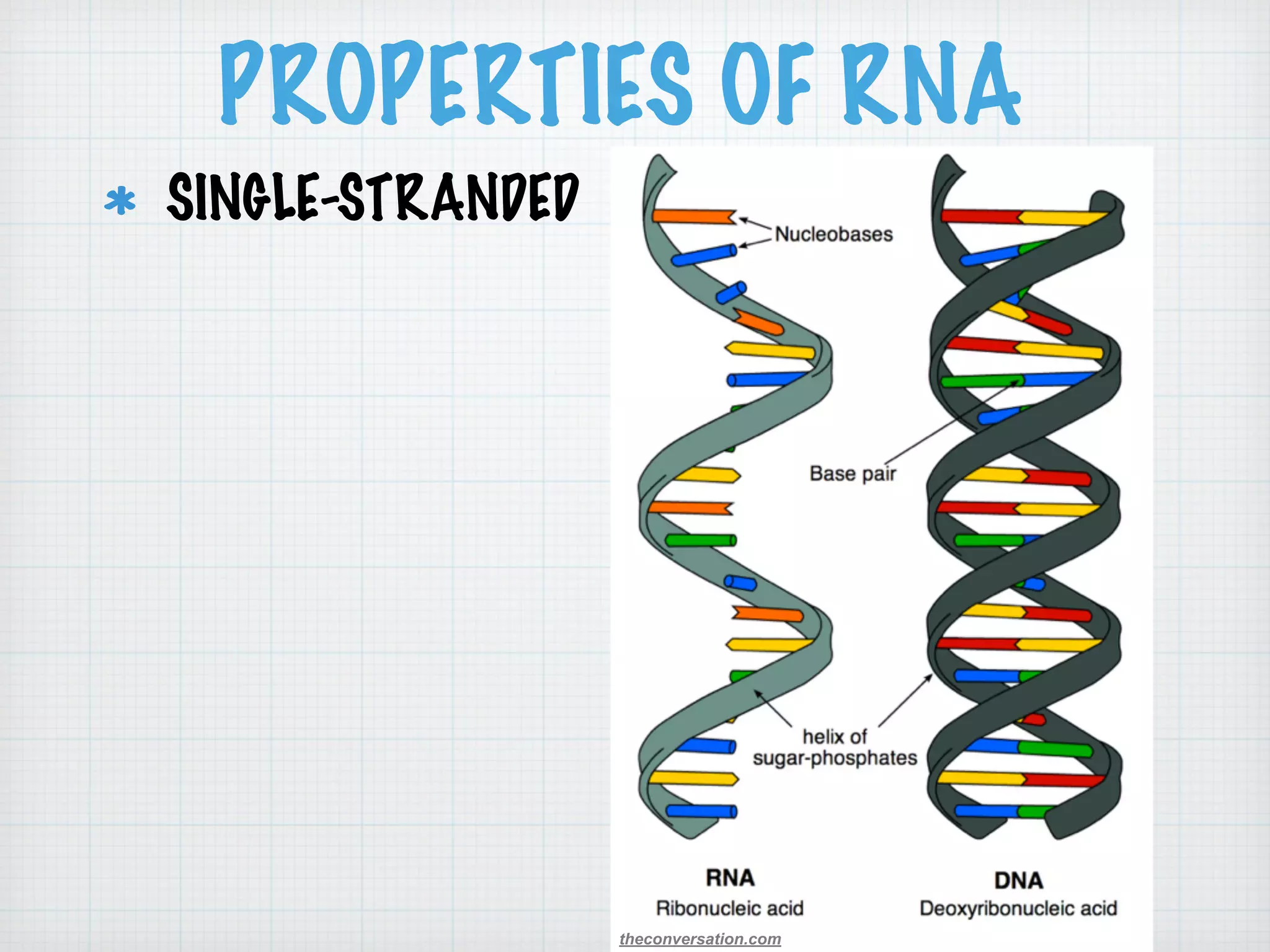
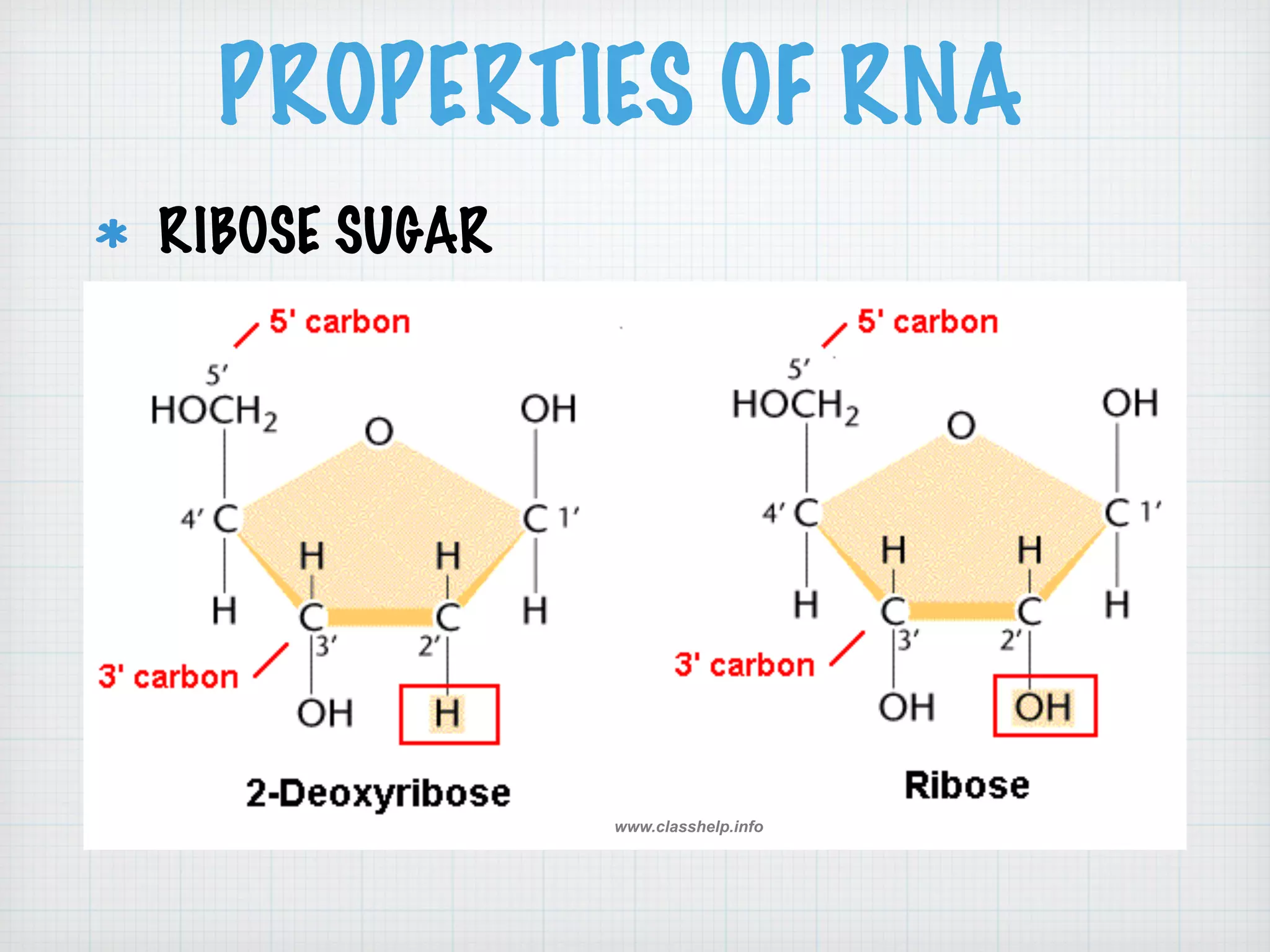
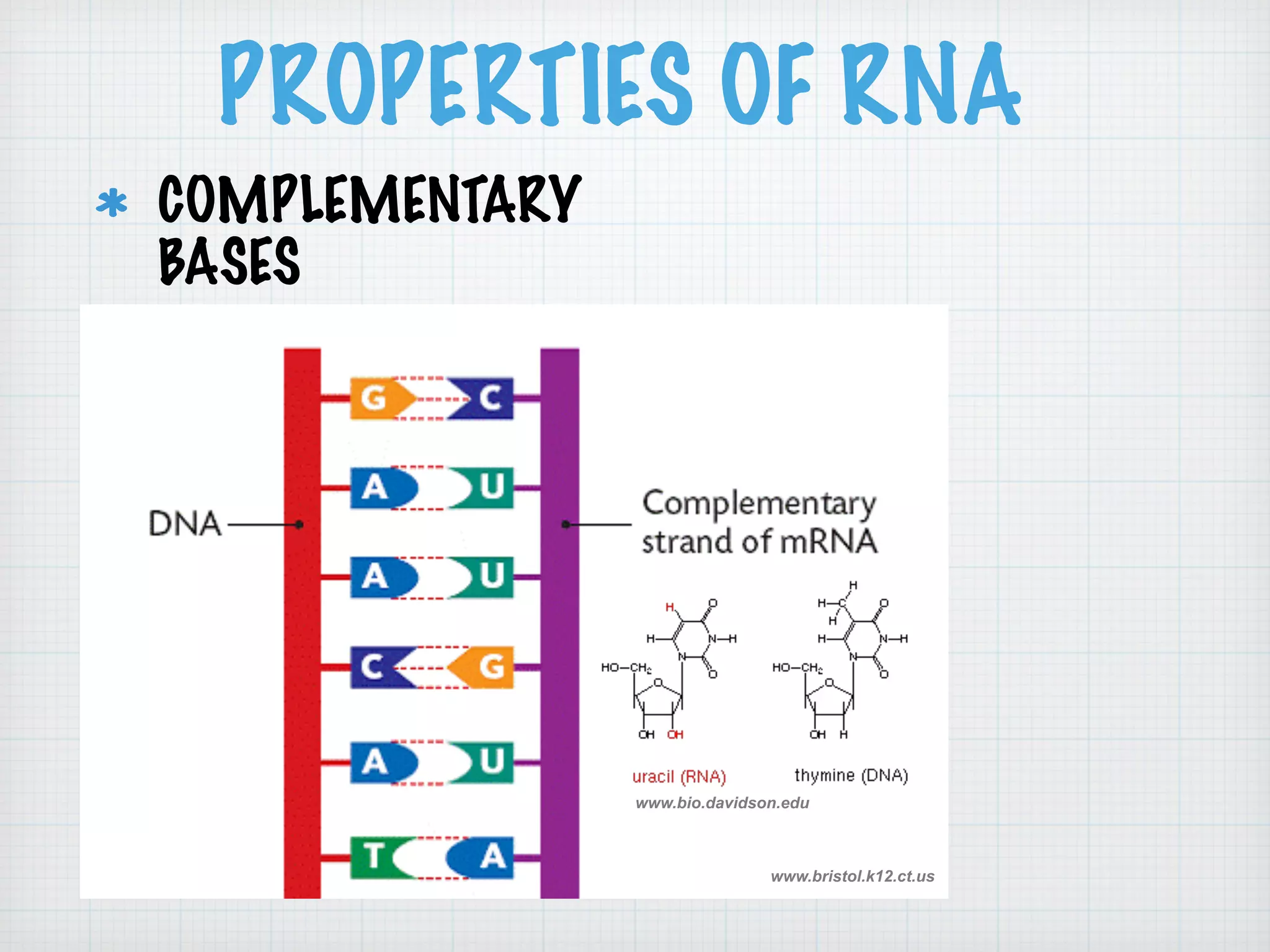
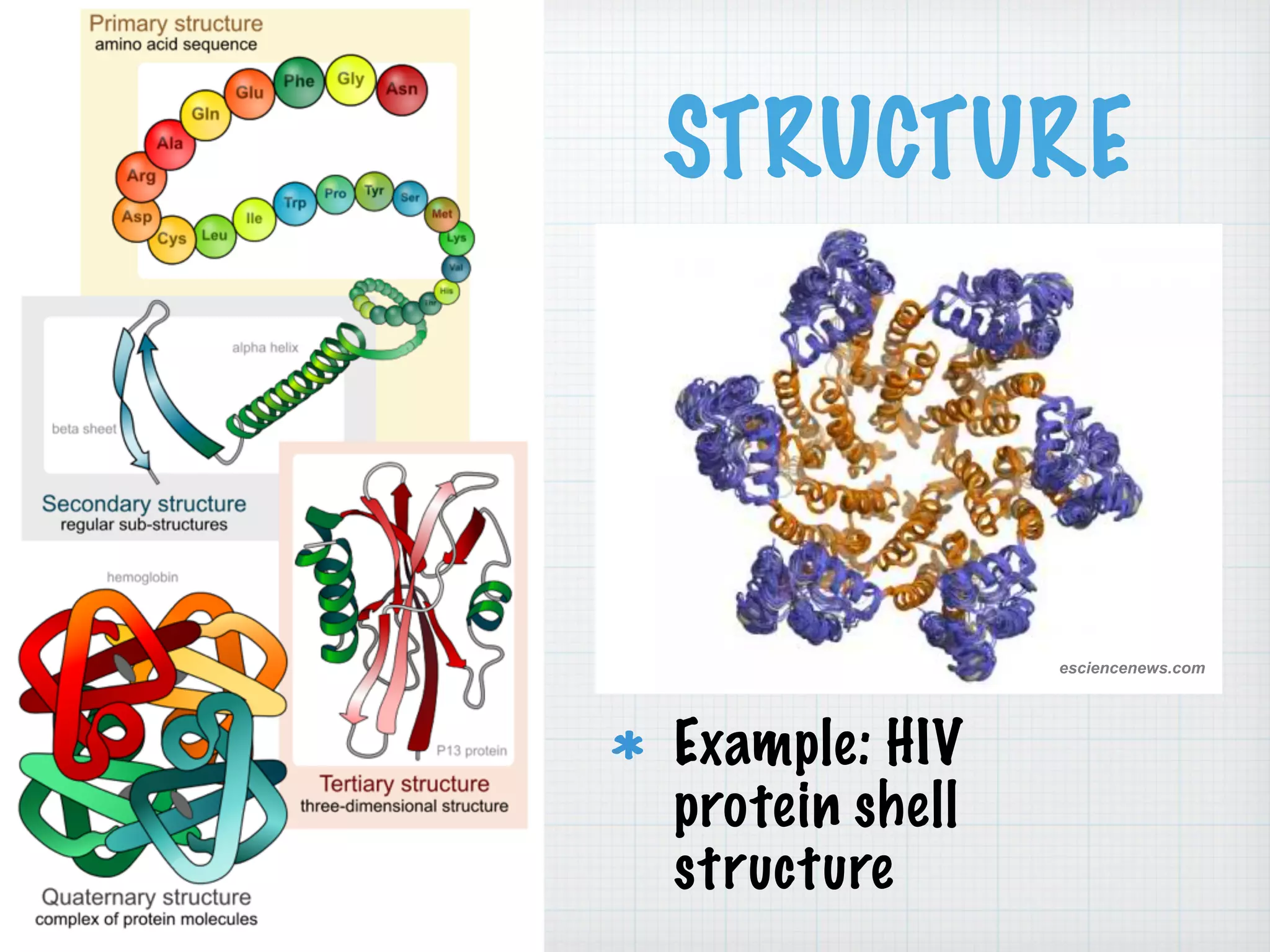
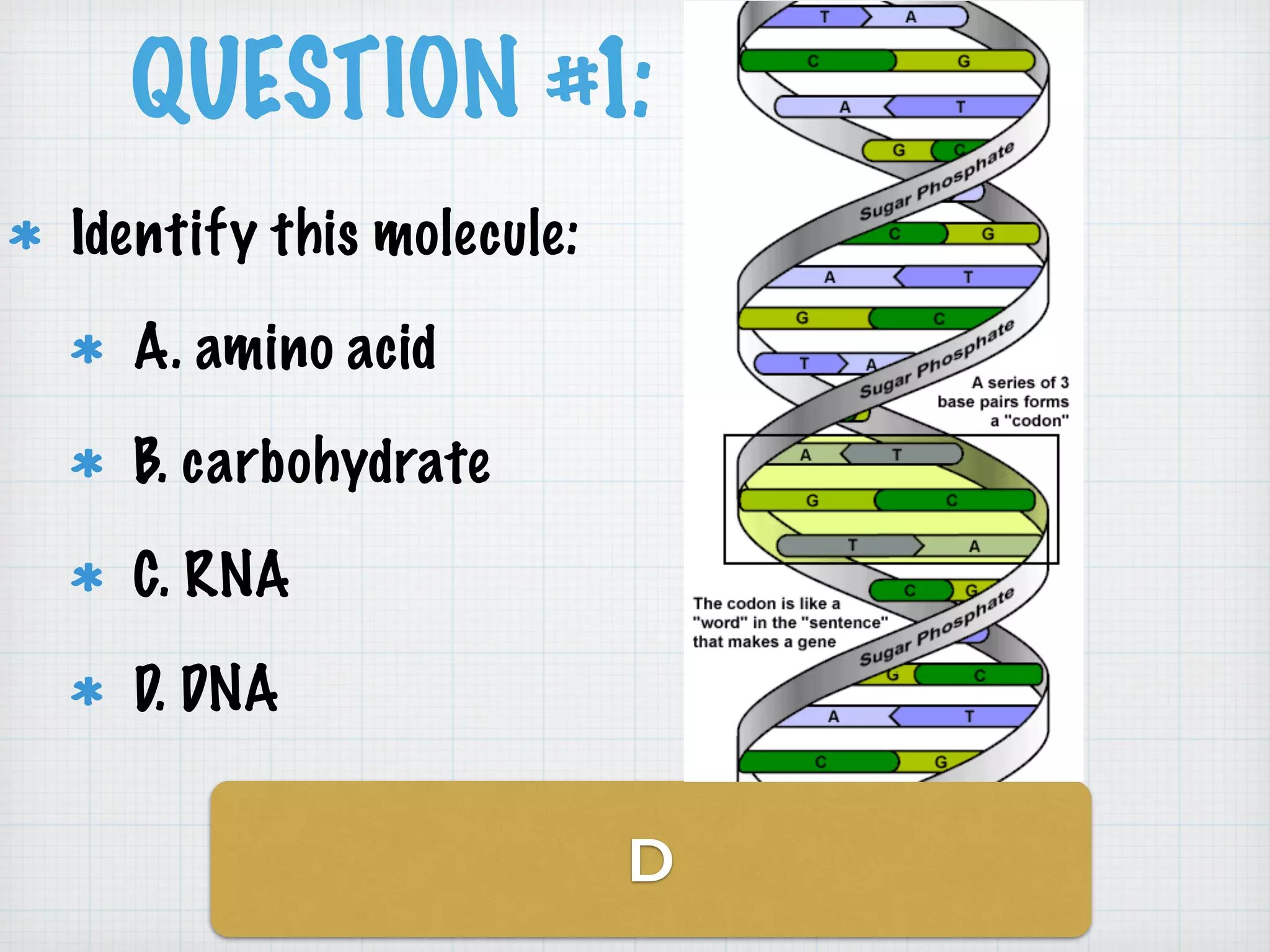
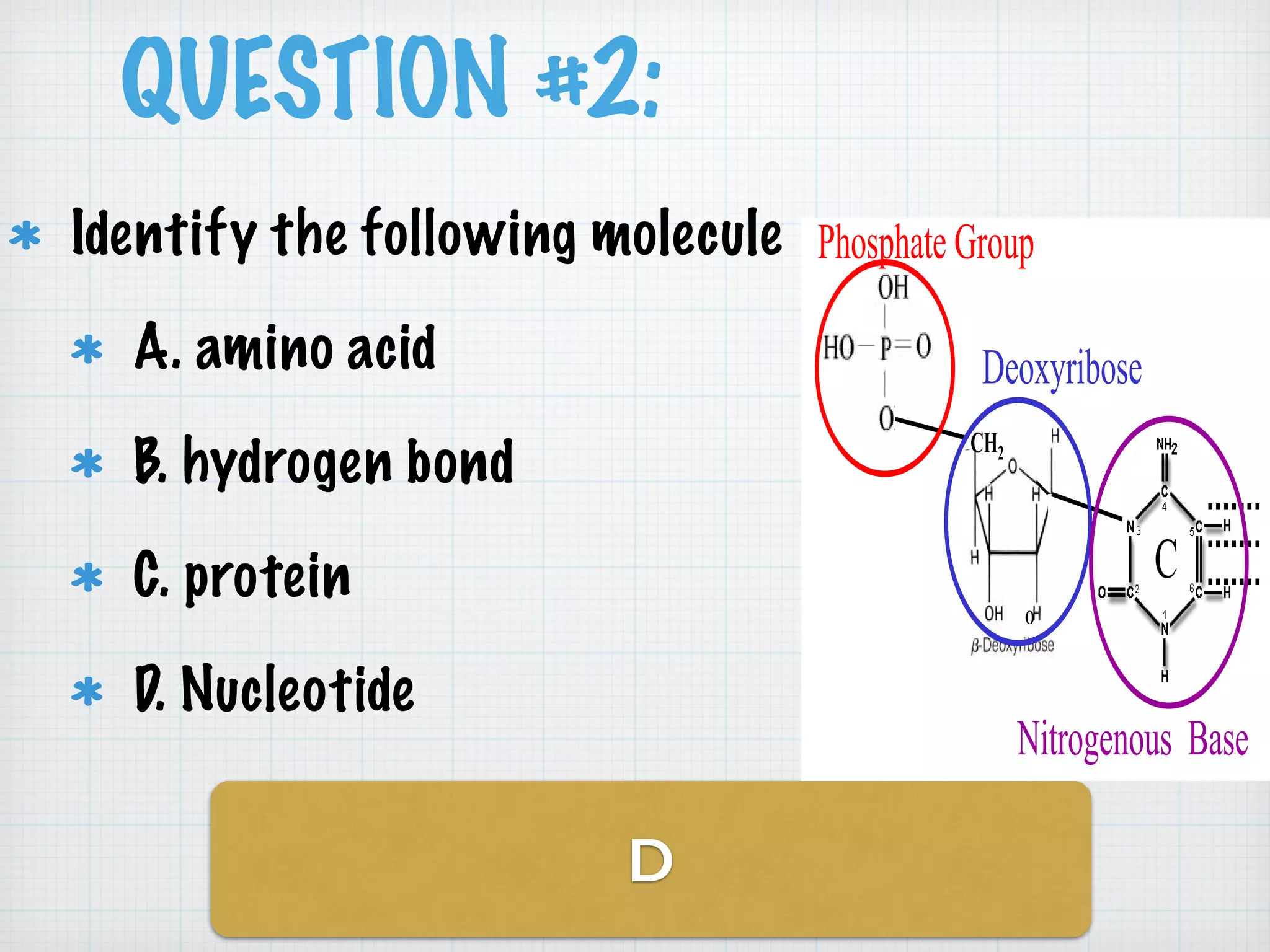
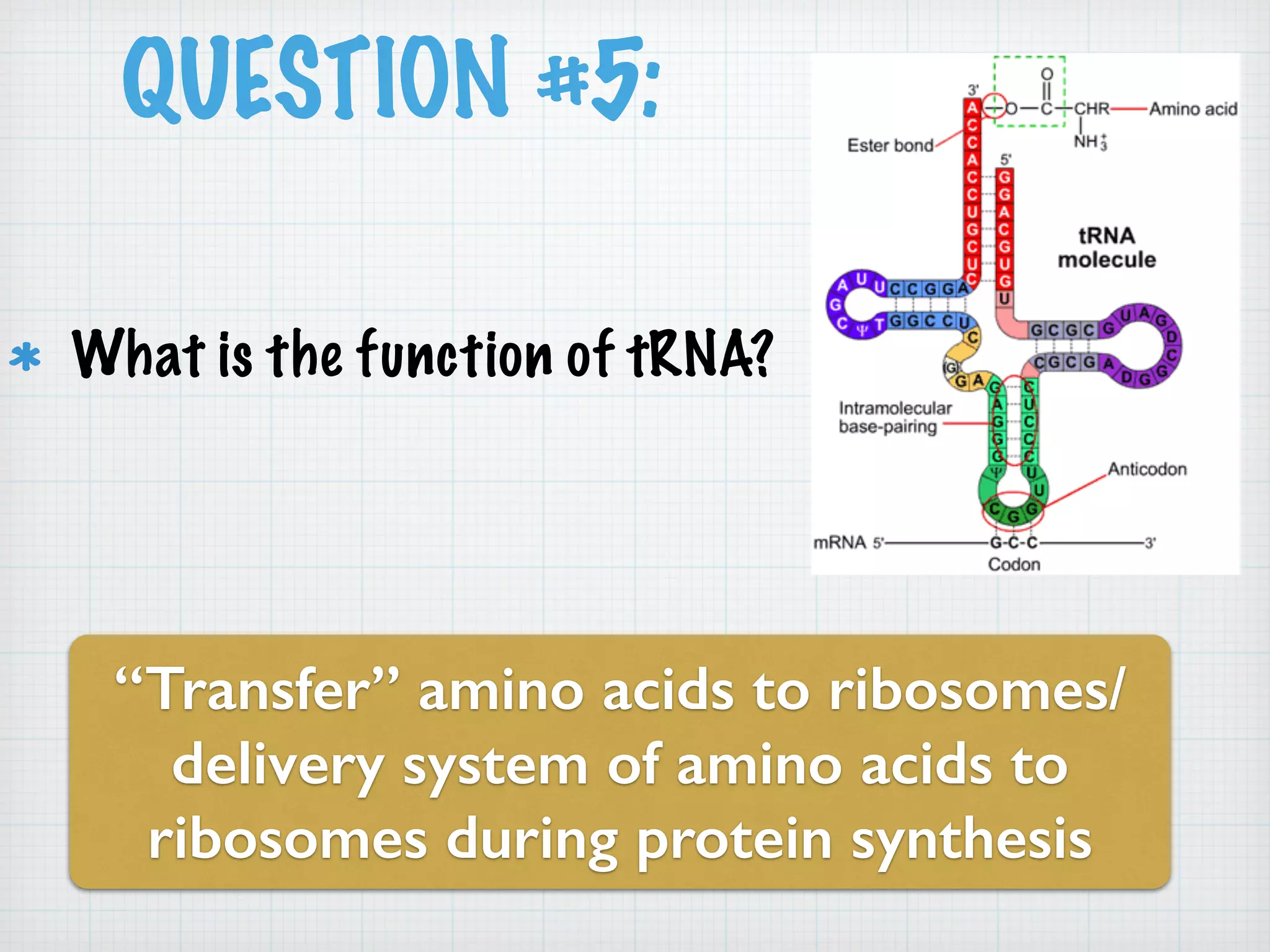
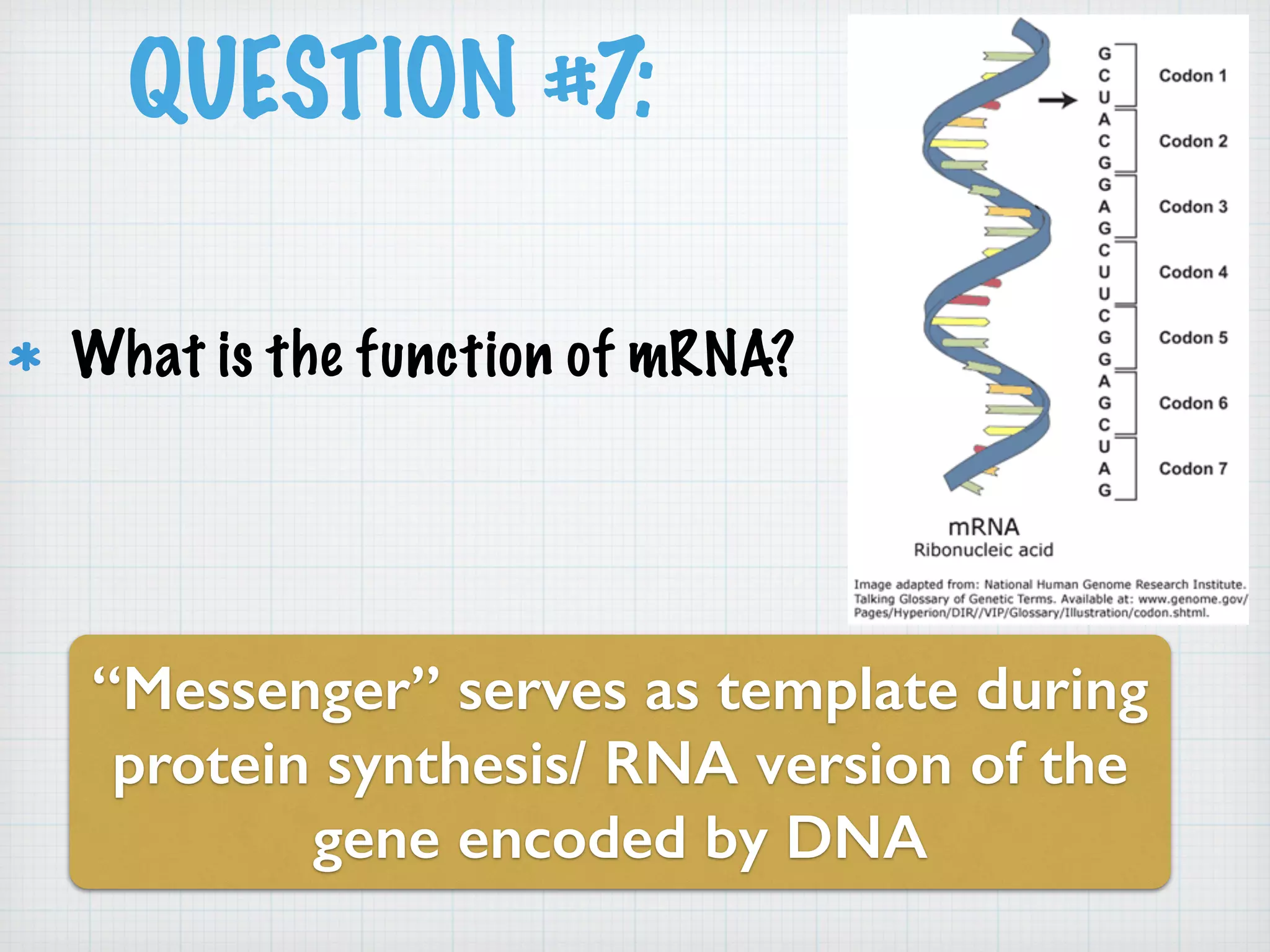
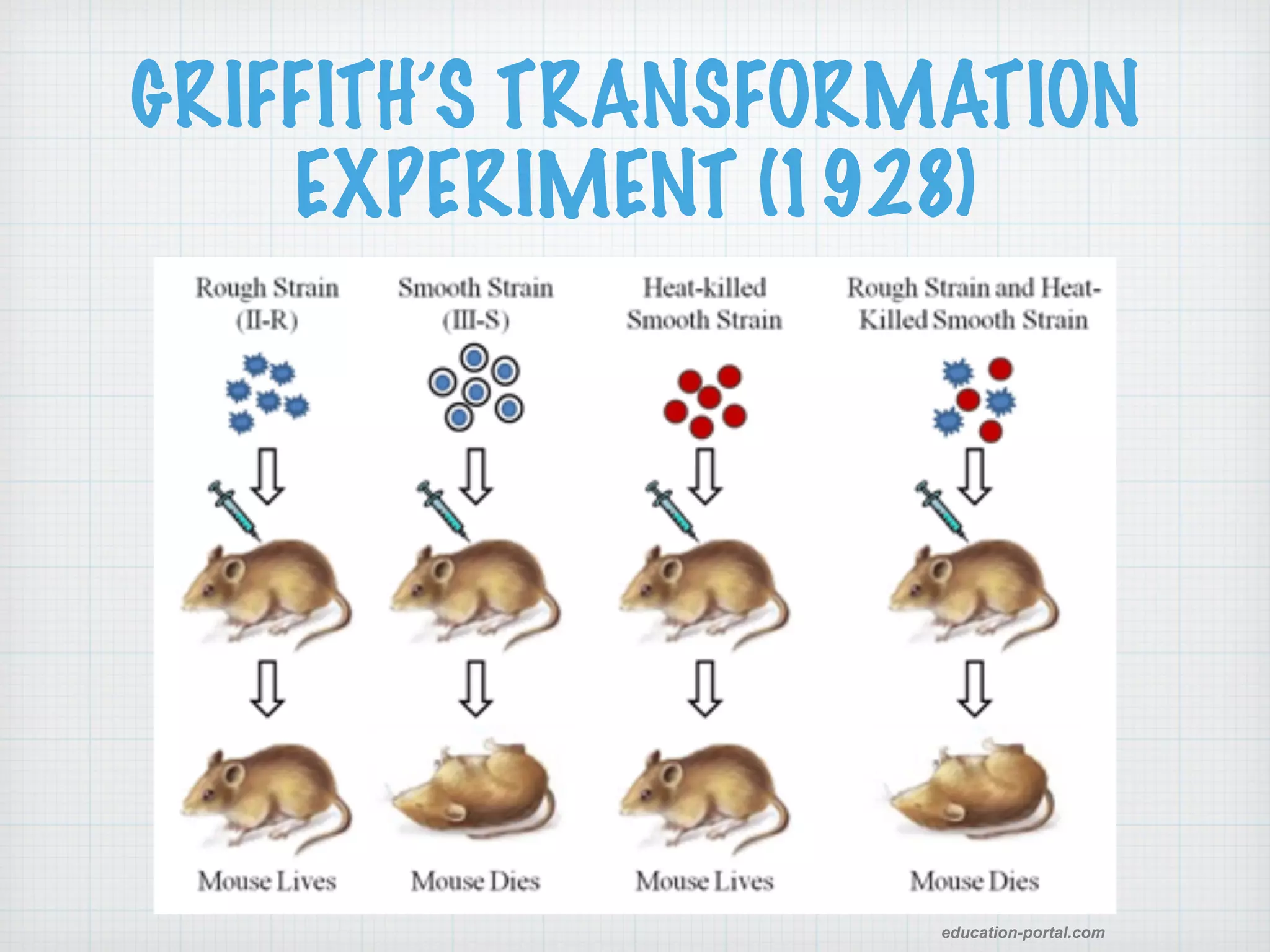
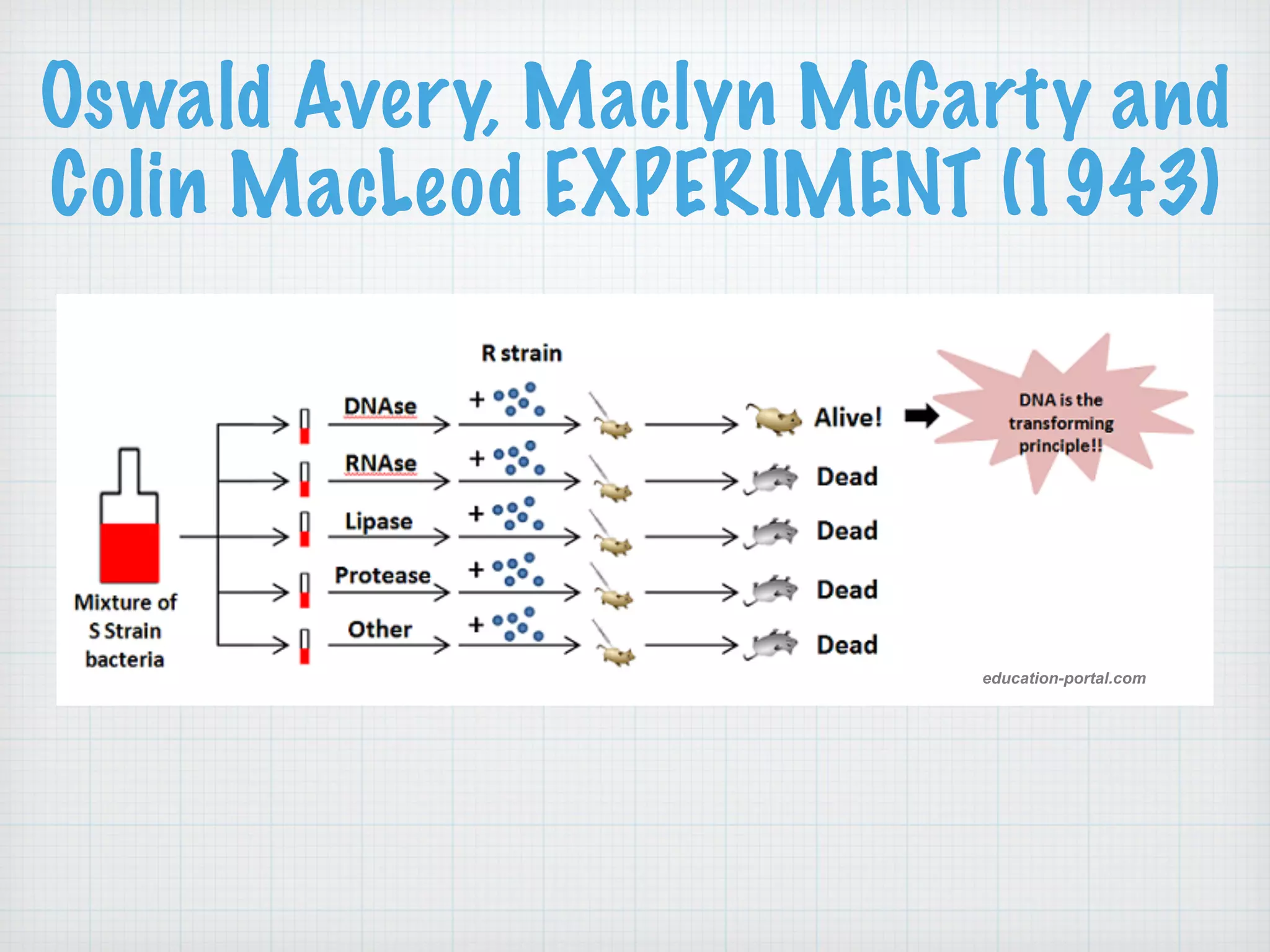
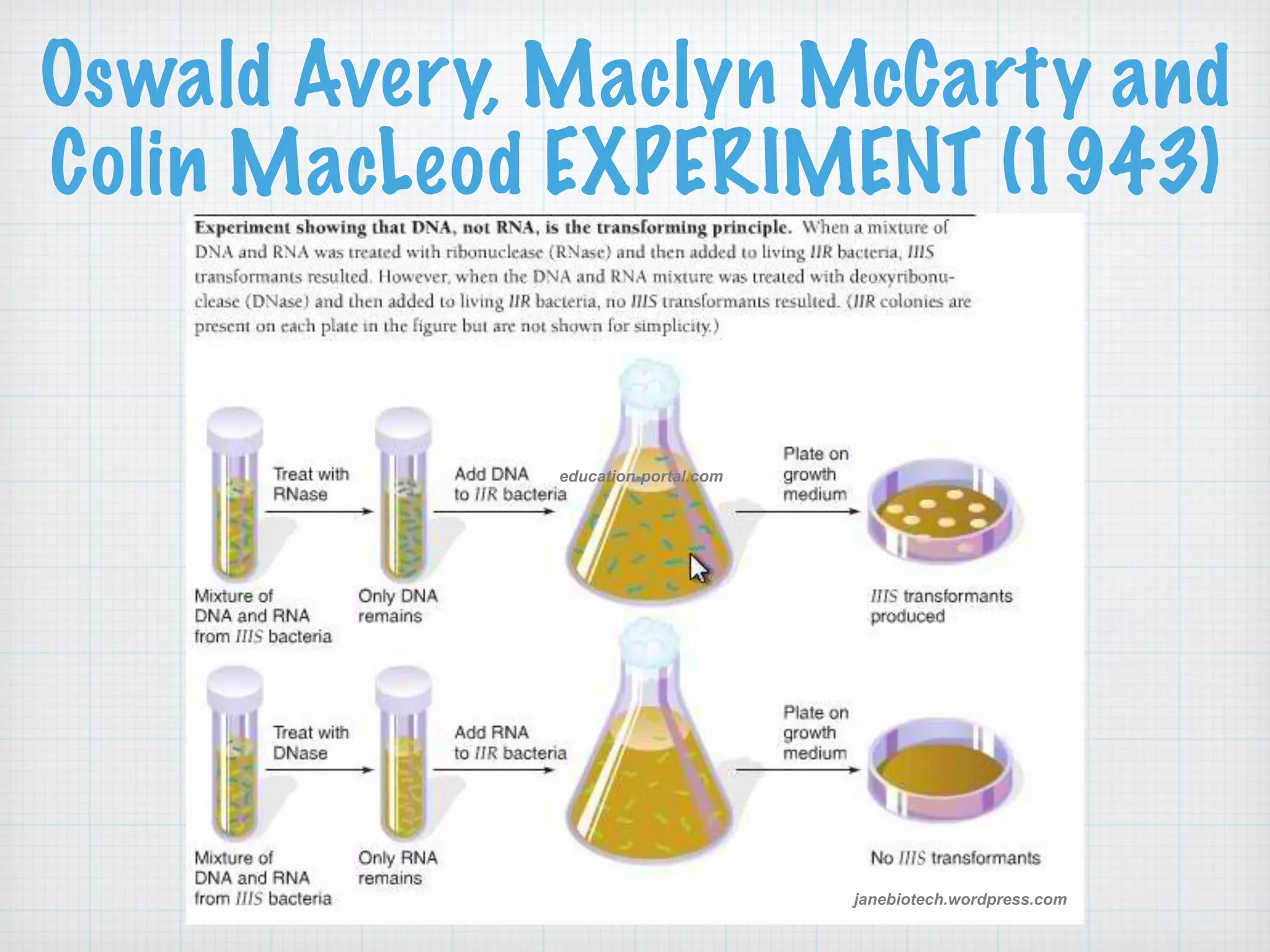
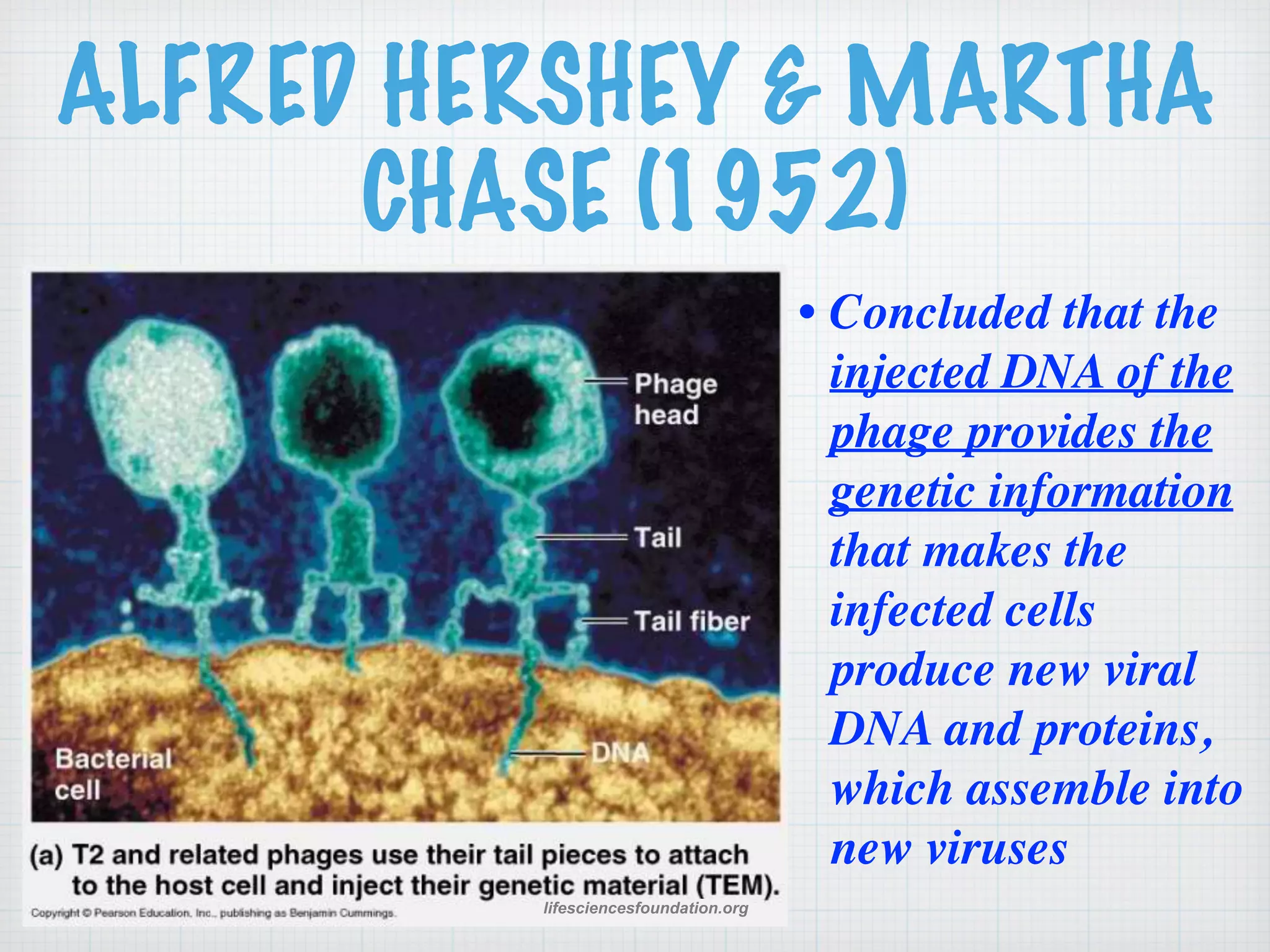
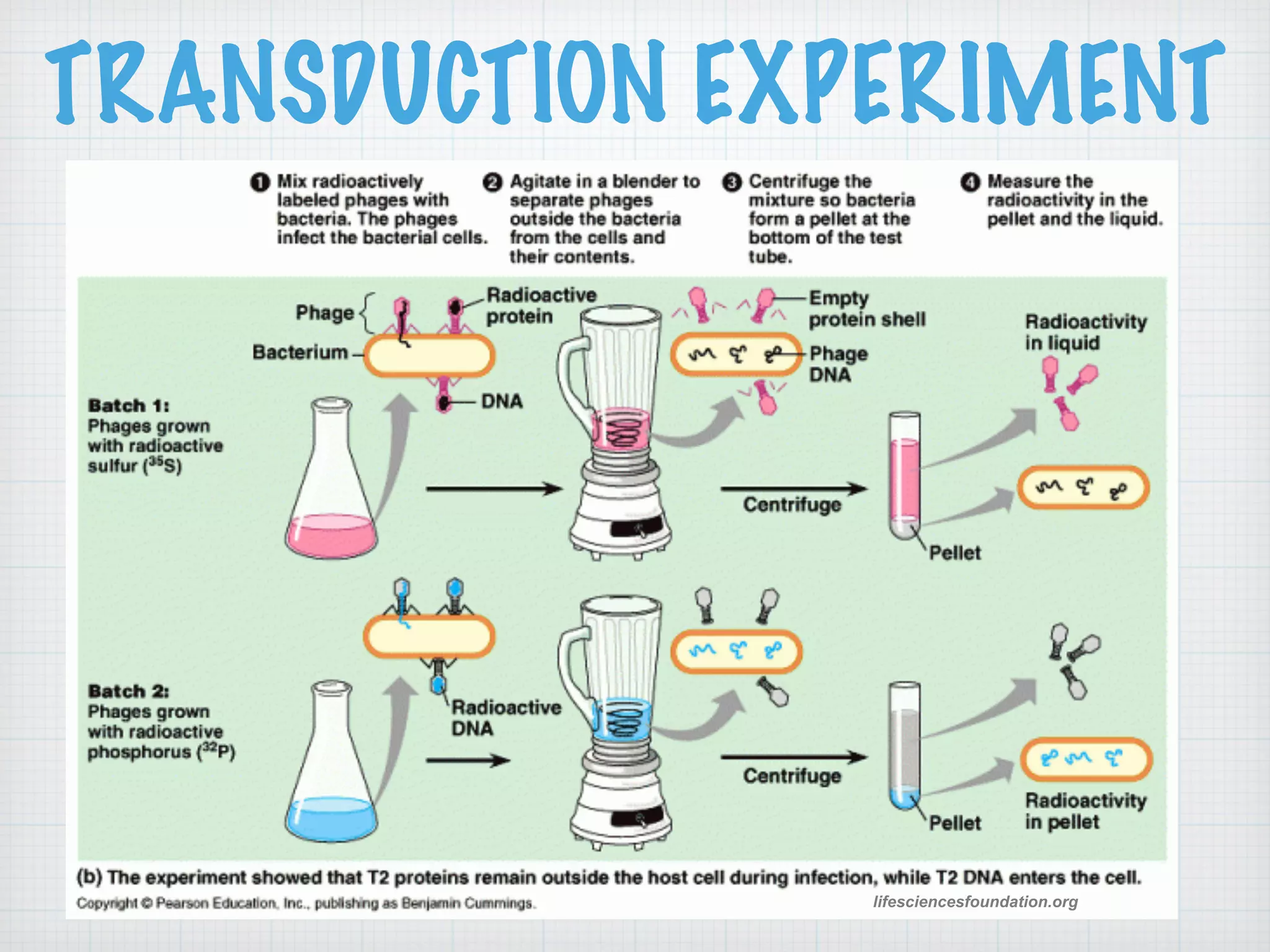
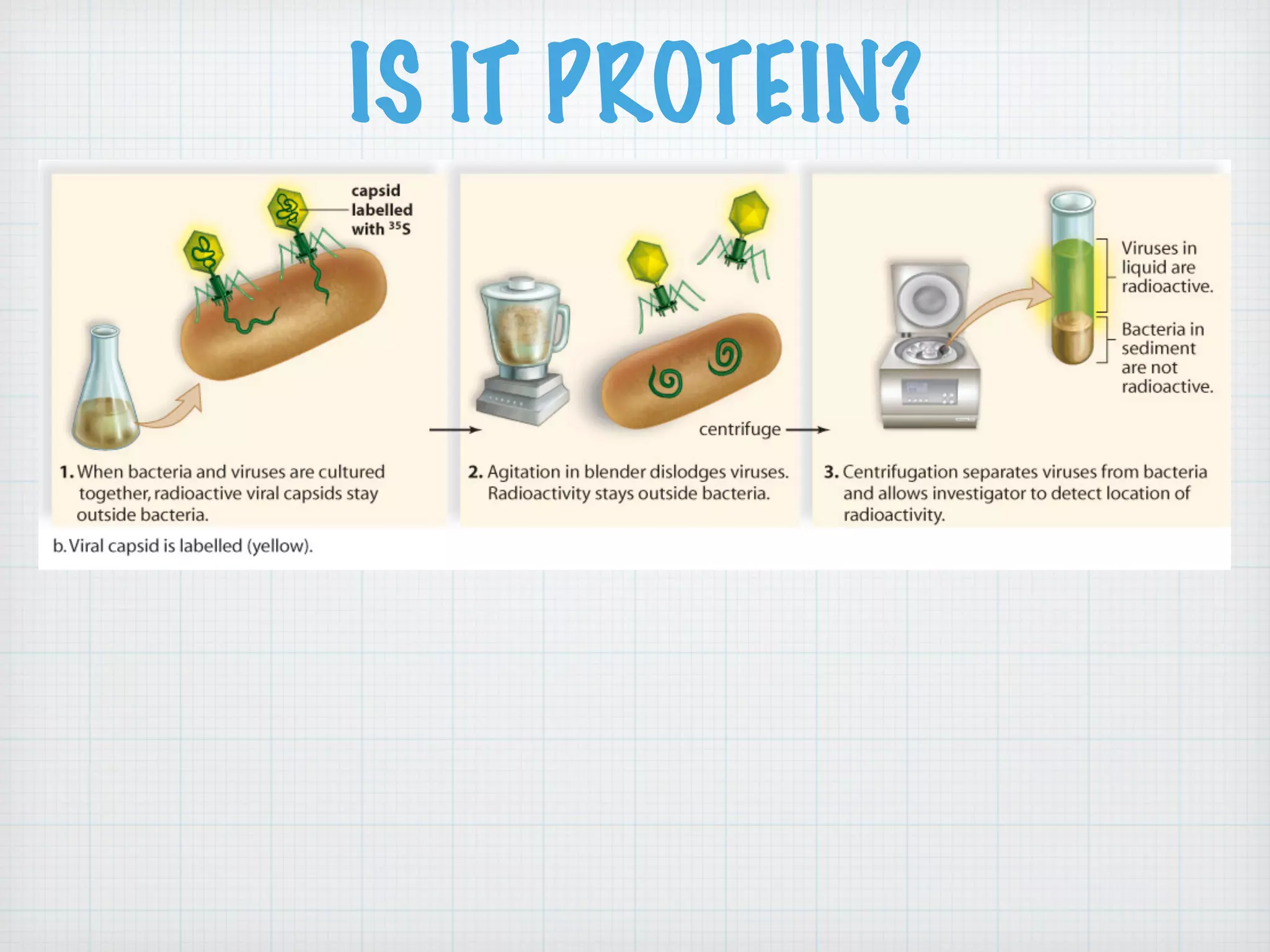
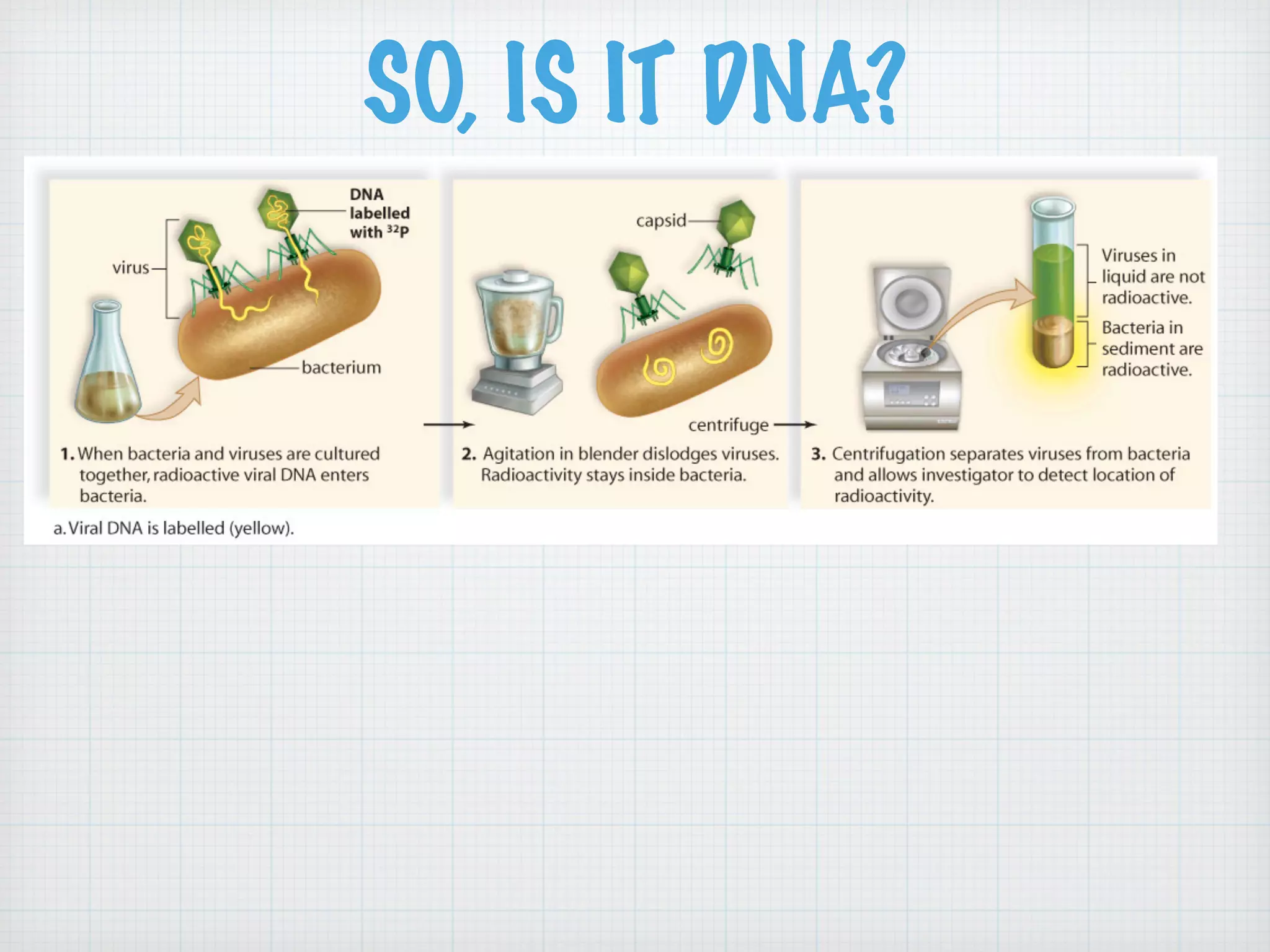
This document discusses nucleic acids and proteins, including their structures and functions. It provides information on DNA and RNA, such as their components, properties, and roles in coding for proteins. Key experiments that helped identify DNA as the genetic material are summarized, including Griffith's transformation experiment, Avery-MacLeod-McCarty experiment, and Hershey-Chase experiment. Questions are also included about nucleic acid and protein structures and these classic experiments.