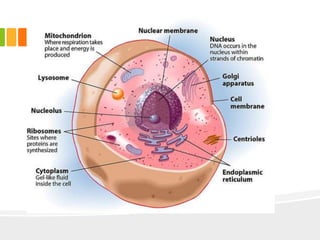
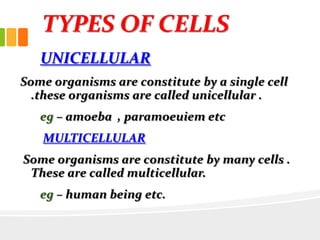
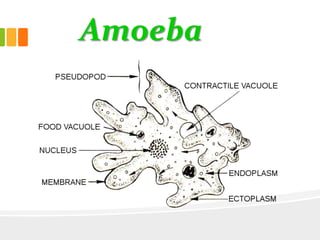
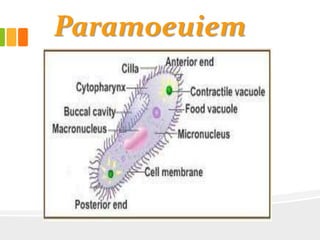
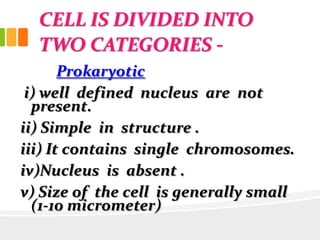
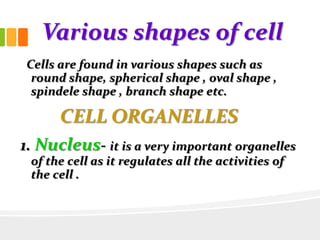
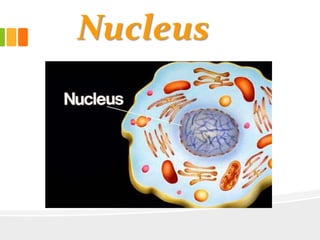
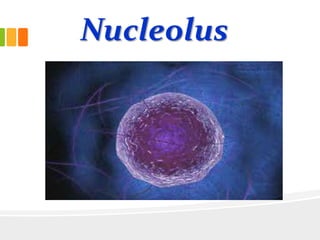
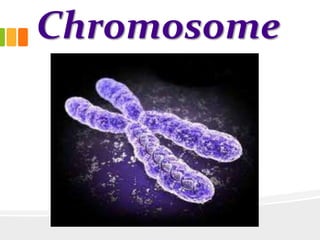
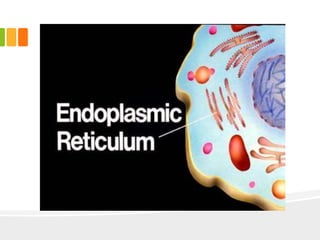
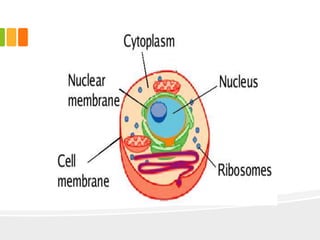
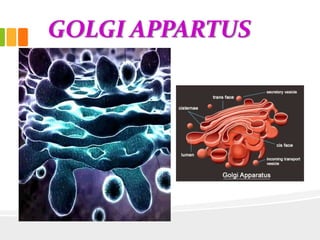
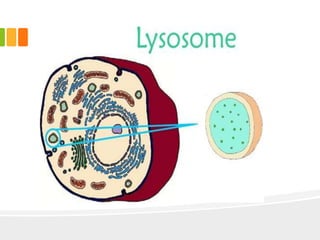
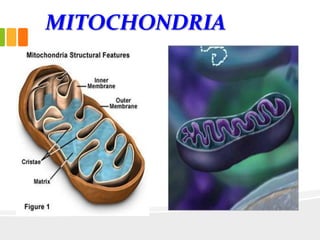
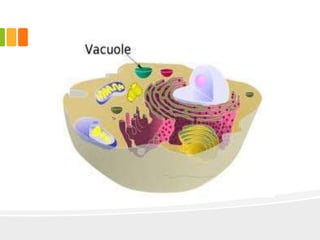
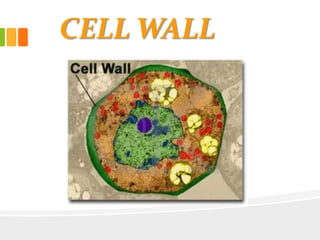
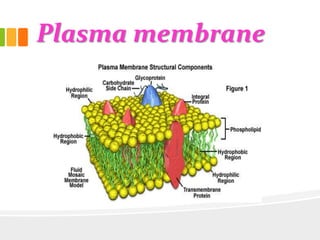
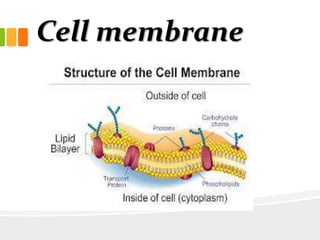
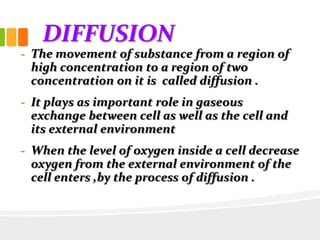
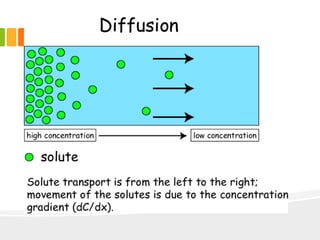
The document discusses the key characteristics and components of cells. It states that the cell is the fundamental unit of life and is the structural and functional basic unit that makes up the whole body. Cells come in both unicellular and multicellular forms. The cell consists of various organelles that allow it to carry out its functions, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. Cells can also be categorized as prokaryotic or eukaryotic based on their structure. The document further describes the roles and characteristics of various cell organelles and components like the nucleus, cell membrane, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and cell wall. It also explains





















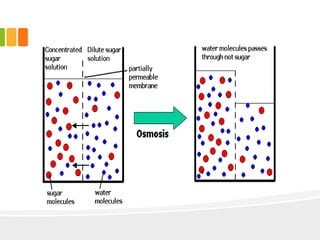
![• If a cell is placed in a medium
which has higher water
concentration and lower solute
concentration , that is the outside
solution is dilute , cell will again
water by osmosis and swell up .
such a solution is called hypotonic
solution .
• If a cell is placed in a medium which
has lower water concentration then
cell sap [hytonic] , then the cell will
again water. This is called osmosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-130623012554-phpapp01/85/THE-FUNDAMENTAL-UNIT-OF-LIFE-47-320.jpg)
![• When cell are kept in a solution more
concentrated than cell sap
[hypertonic] they start shrinking , as
water comes out this is called
exosmosis .
• The absorption of water from soil by
plant root takes place by osmosis .
• If the water concentration outside the
cell is similar to inside the cell , it is
called as isotonic solution No net
movement of water takes place in such
conditions .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation3-130623012554-phpapp01/85/THE-FUNDAMENTAL-UNIT-OF-LIFE-48-320.jpg)