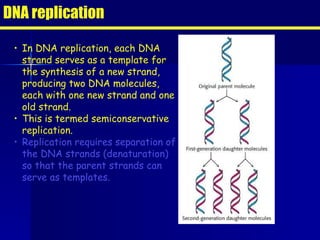
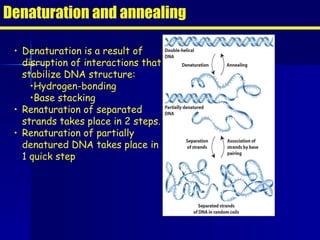
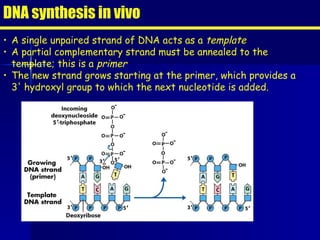
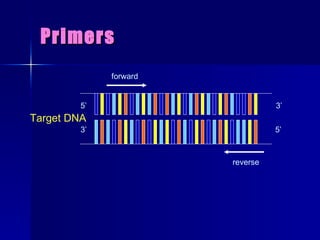
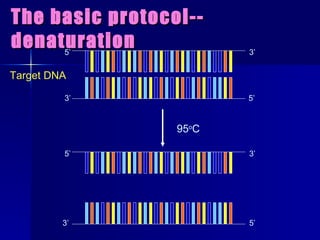
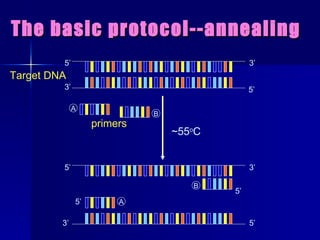
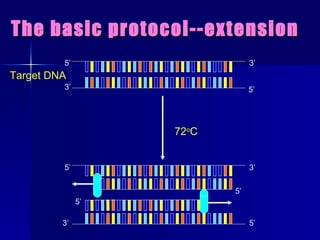
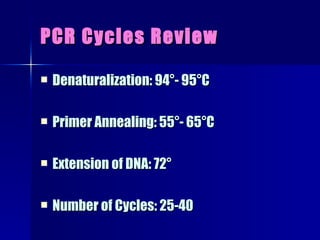
PCR is a technique that amplifies specific DNA sequences. It involves denaturing DNA strands, annealing primers to the strands, and extending the primers using DNA polymerase. This cycling process exponentially amplifies the target DNA sequence. Key components are thermostable DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus, primers, nucleotides, buffer, and repeated heating and cooling. PCR is used in applications like disease diagnosis, forensics, and sequencing.