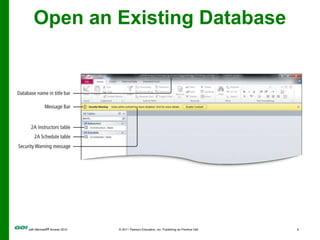
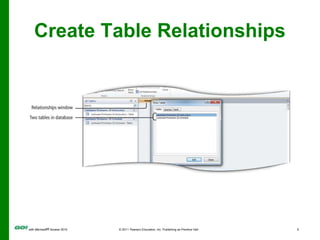
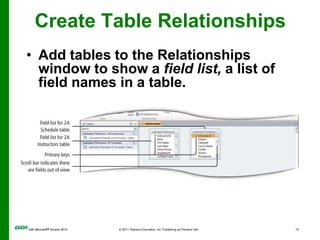
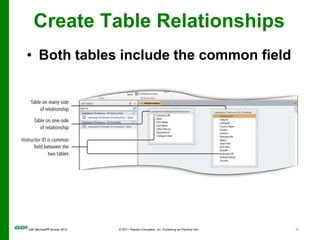
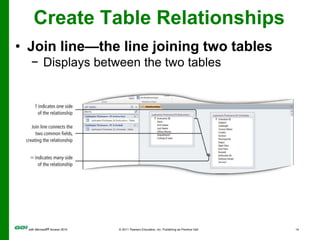
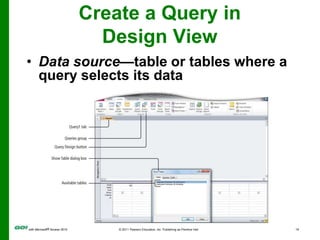
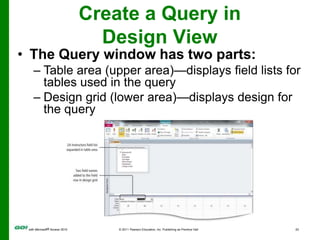
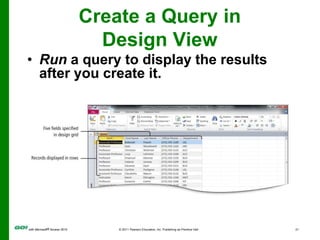
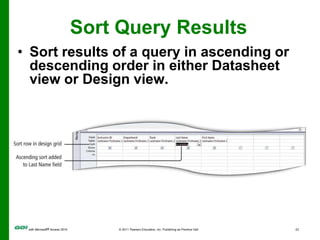
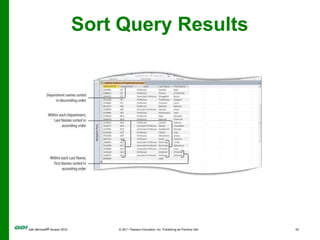
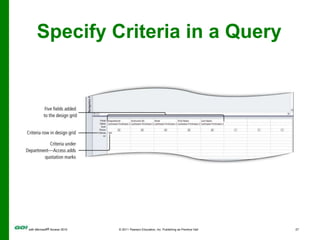
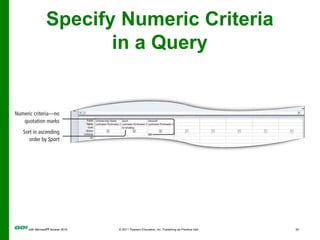
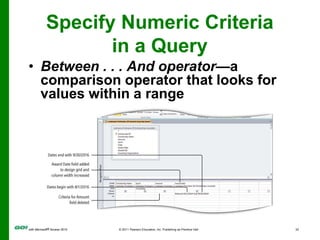
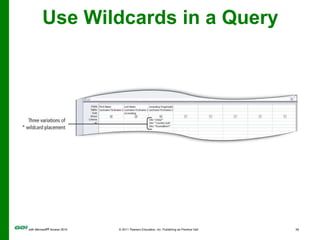
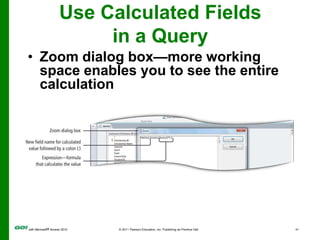
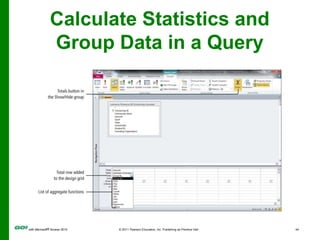
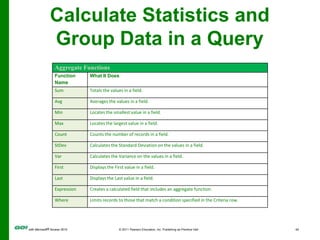
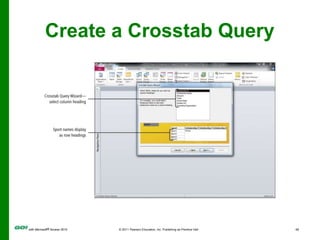
The document covers objectives and instructions for using queries in Microsoft Access 2010 to sort, filter, and analyze data from one or multiple tables. Key points covered include creating relationships between tables, sorting records, designing queries using criteria, calculations, grouping, and statistics to summarize data in a compact crosstab view. The overall goal is to teach how to extract and manipulate specific data through queries to answer questions about the information in a database.