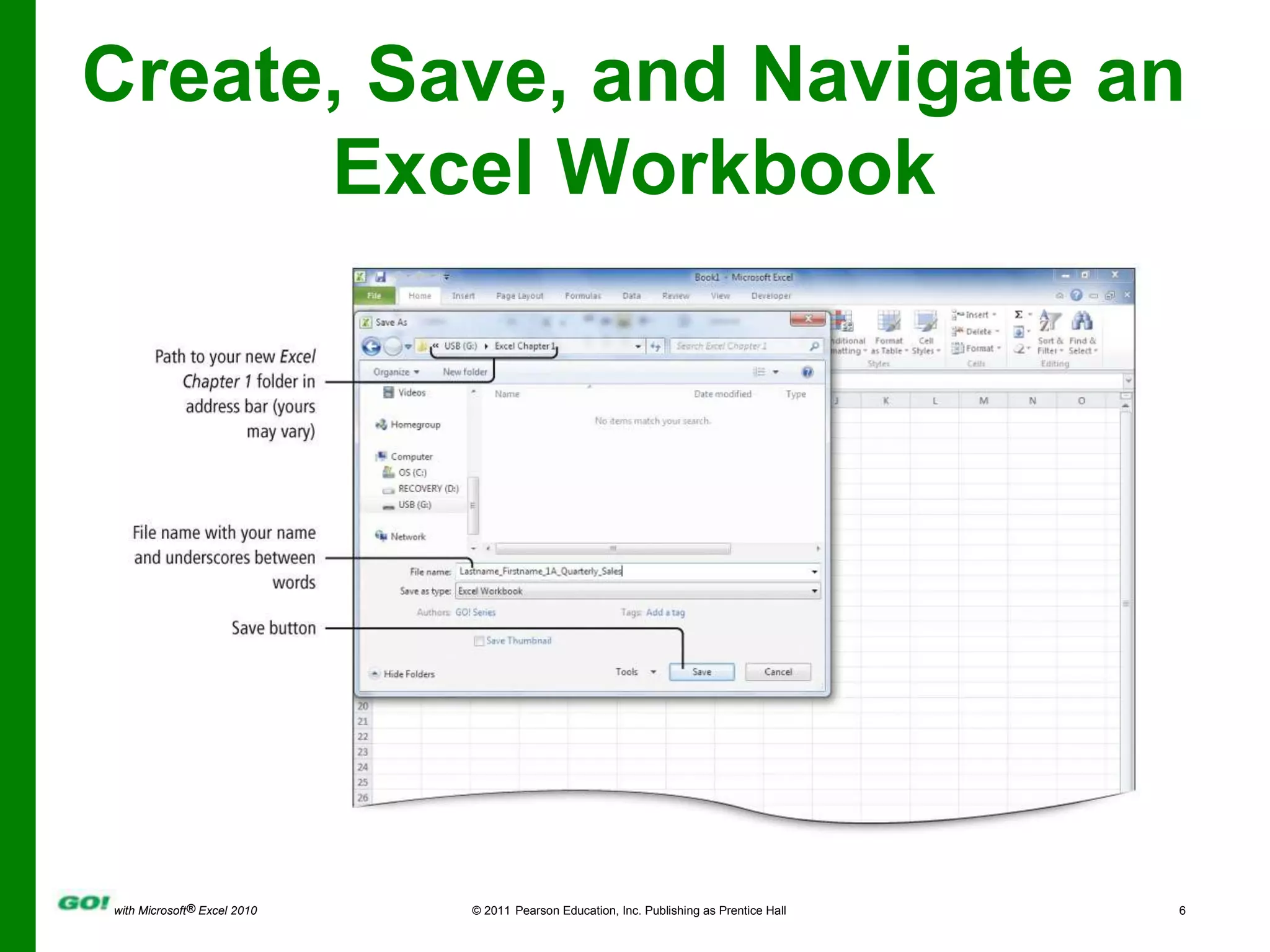
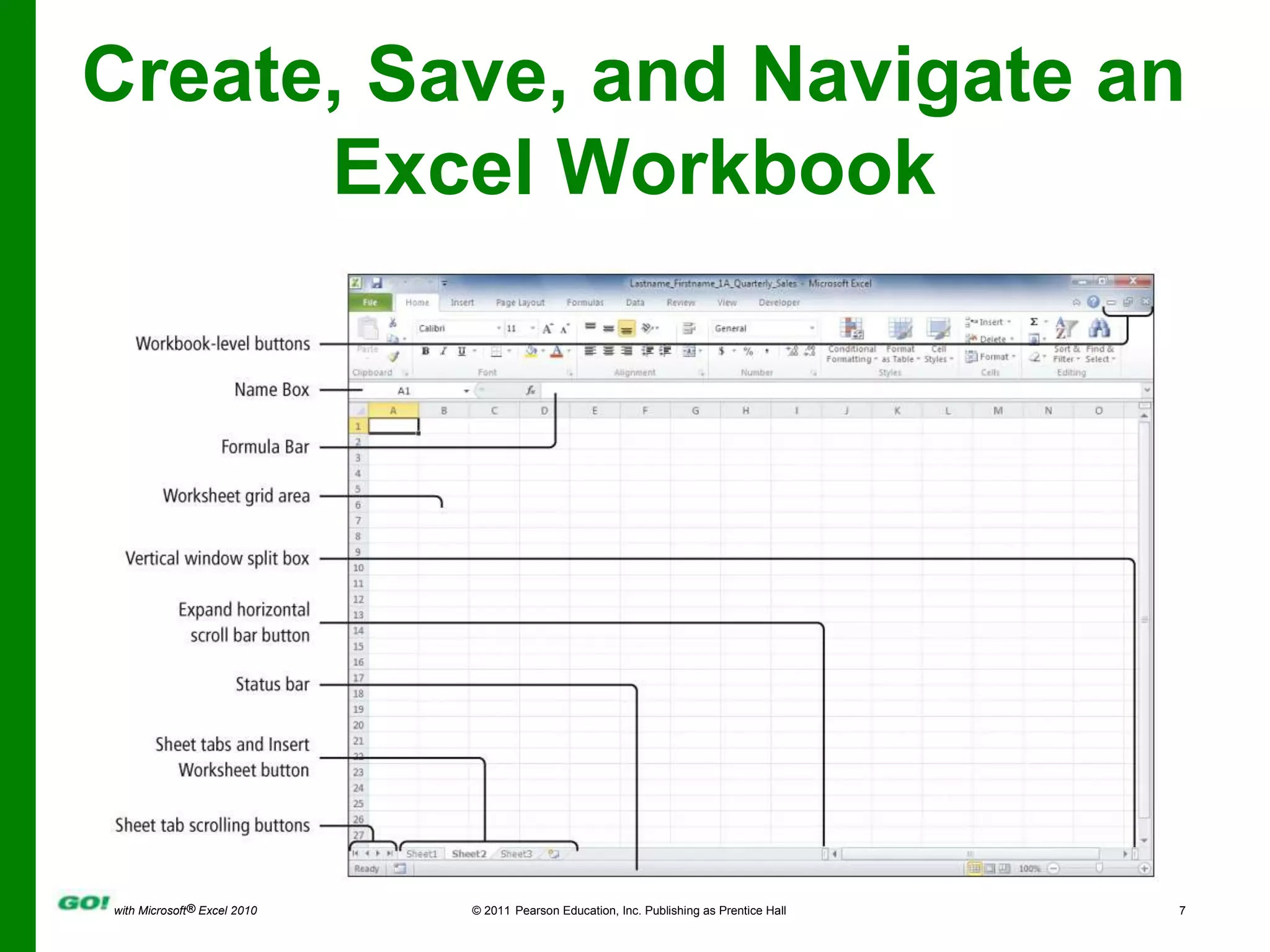
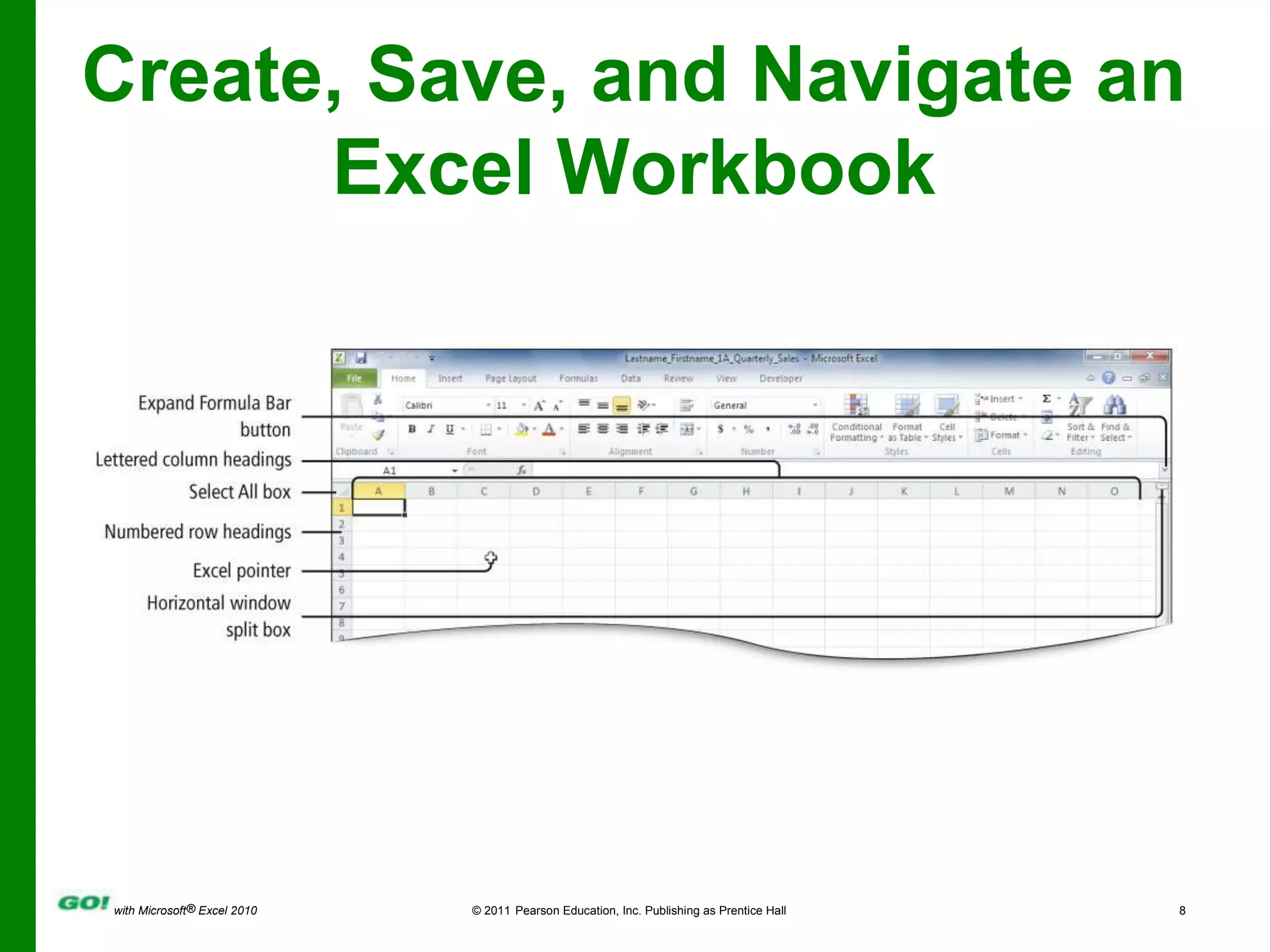
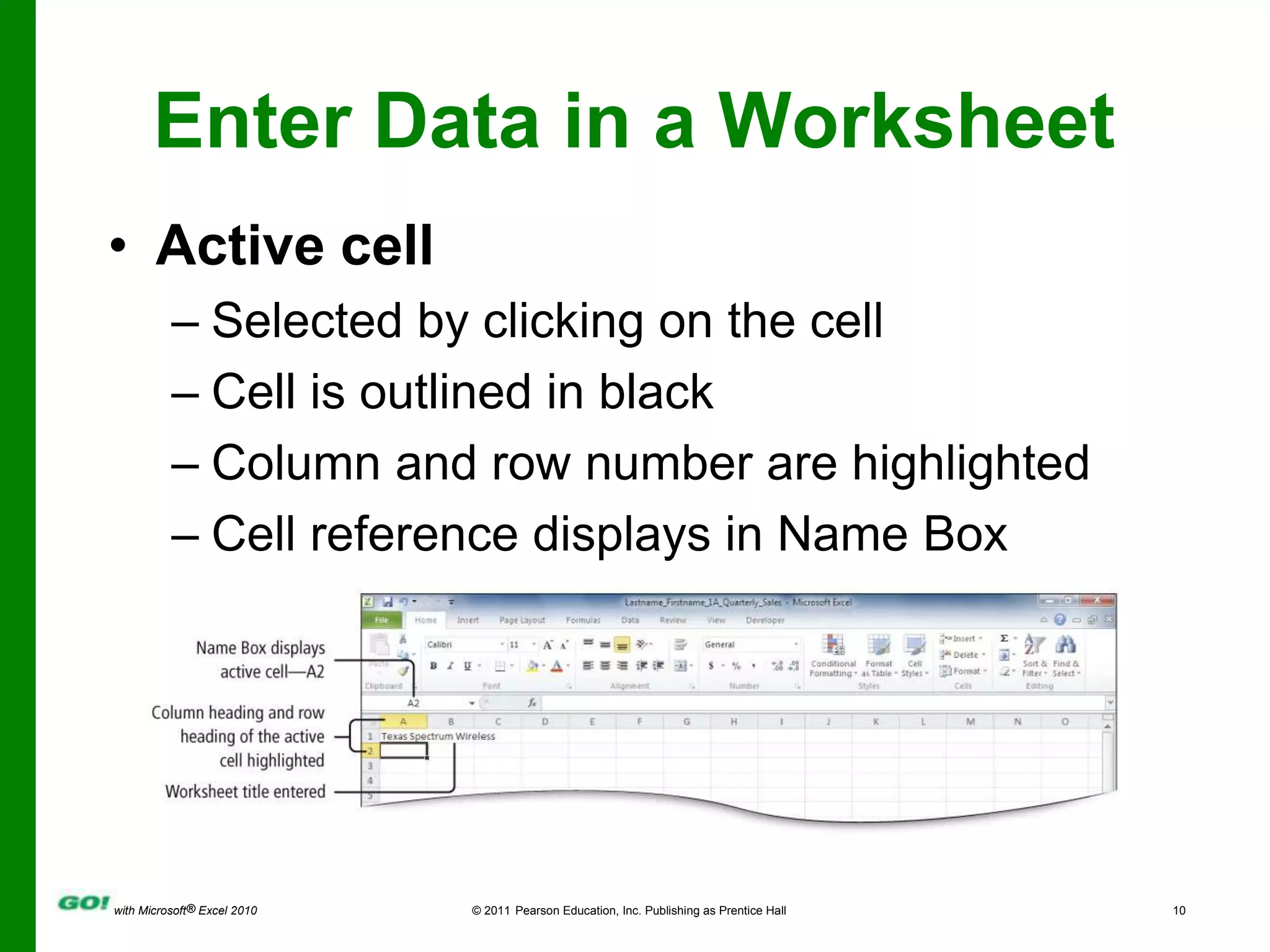
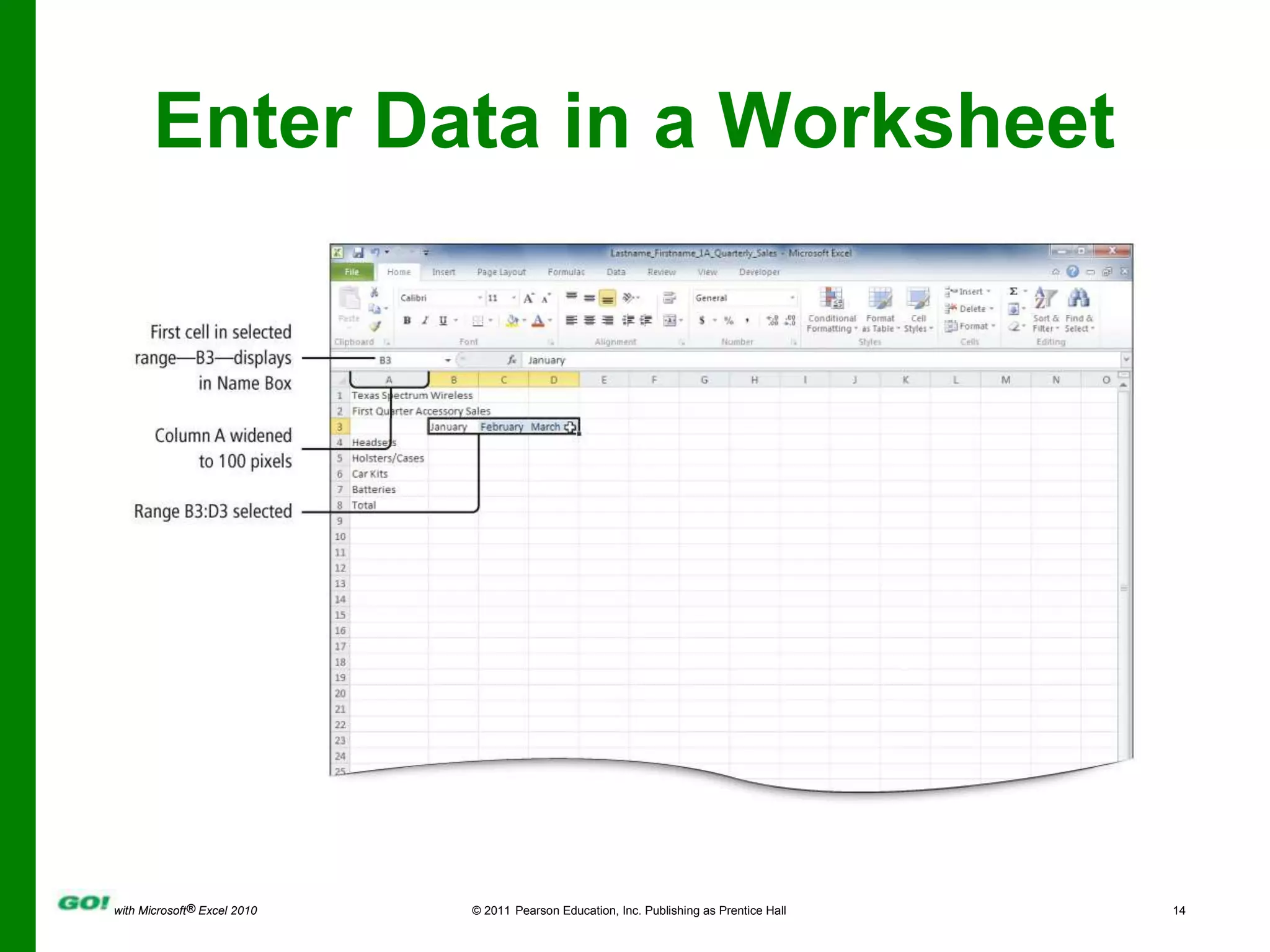
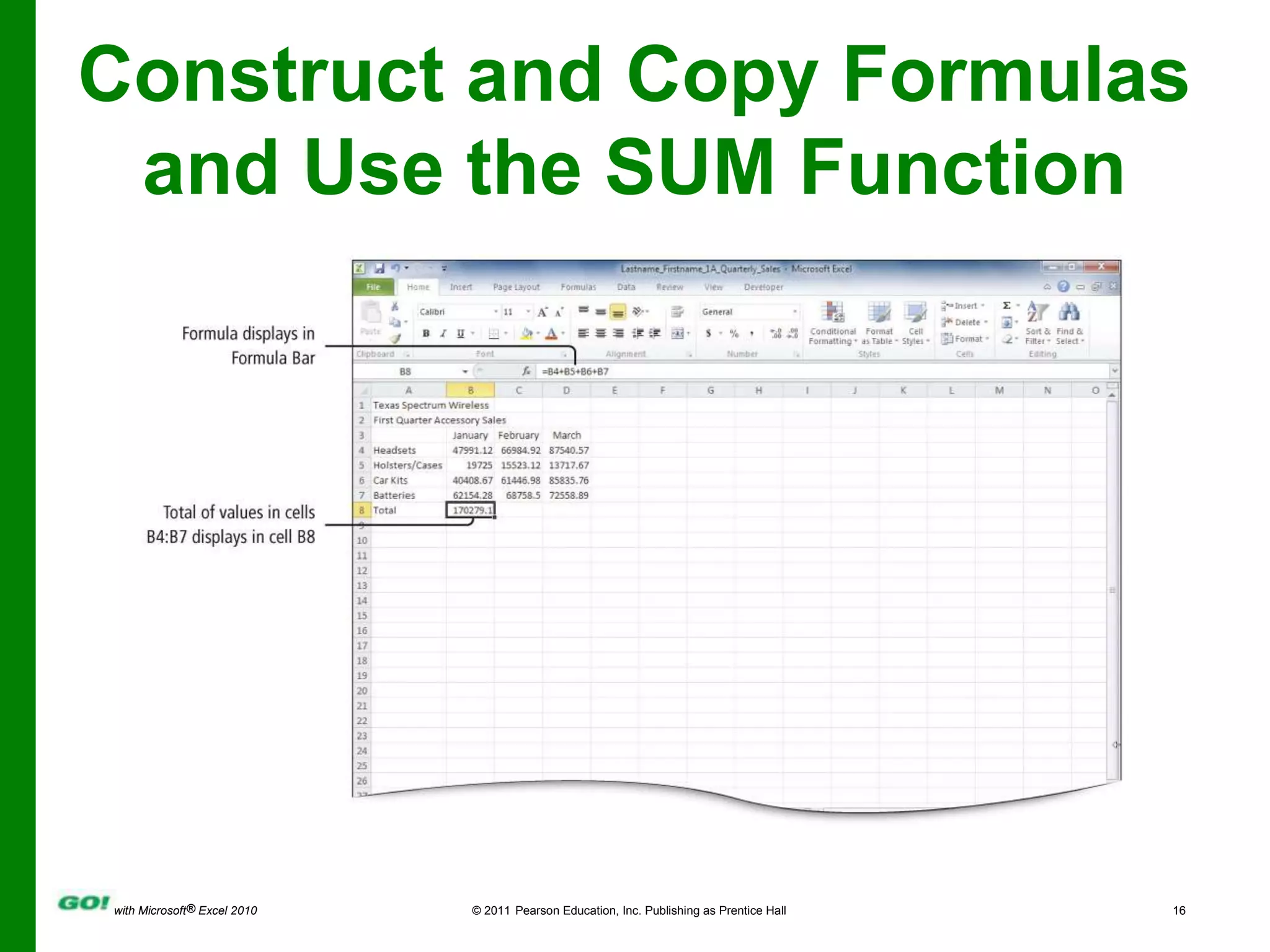
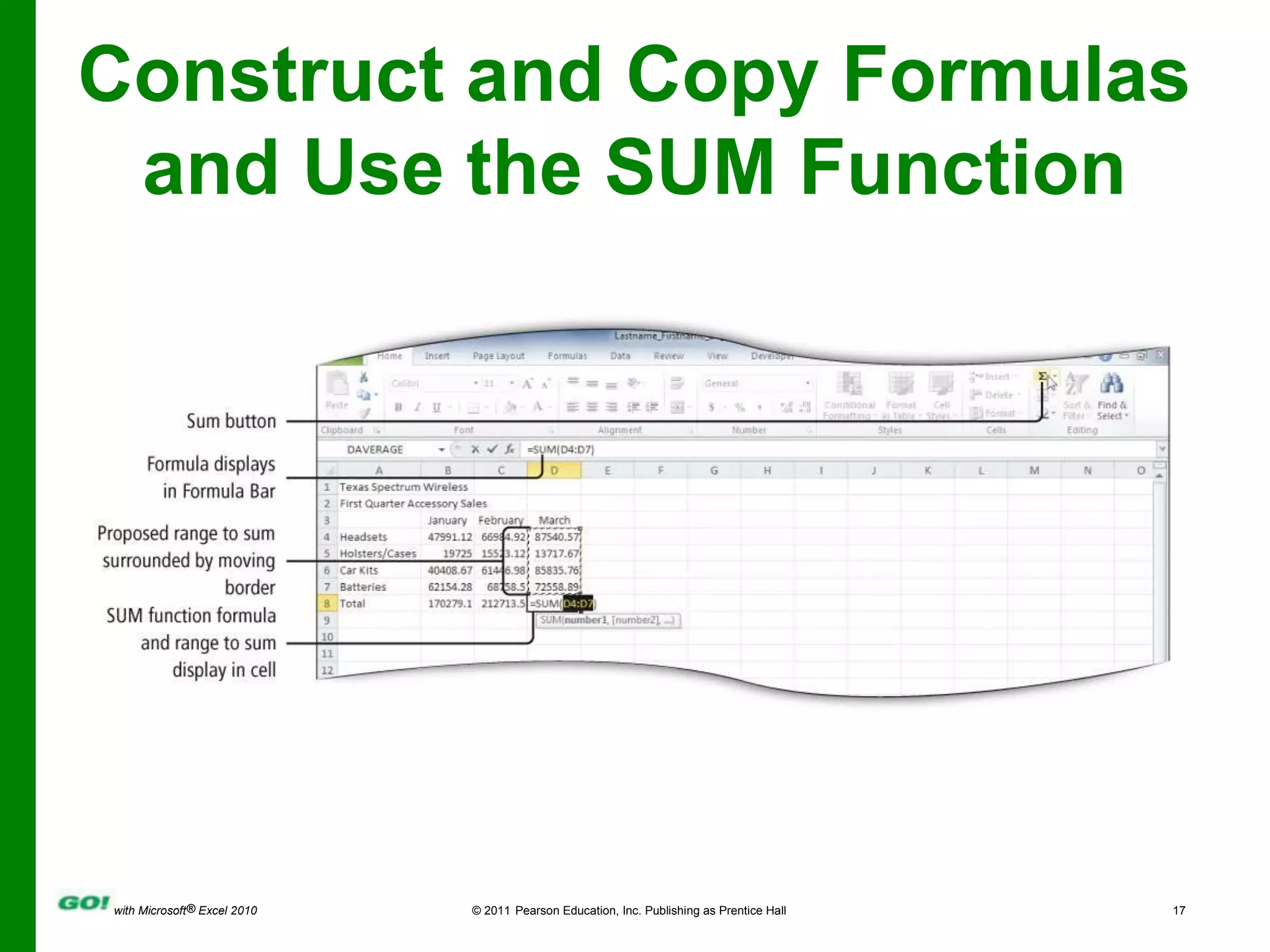
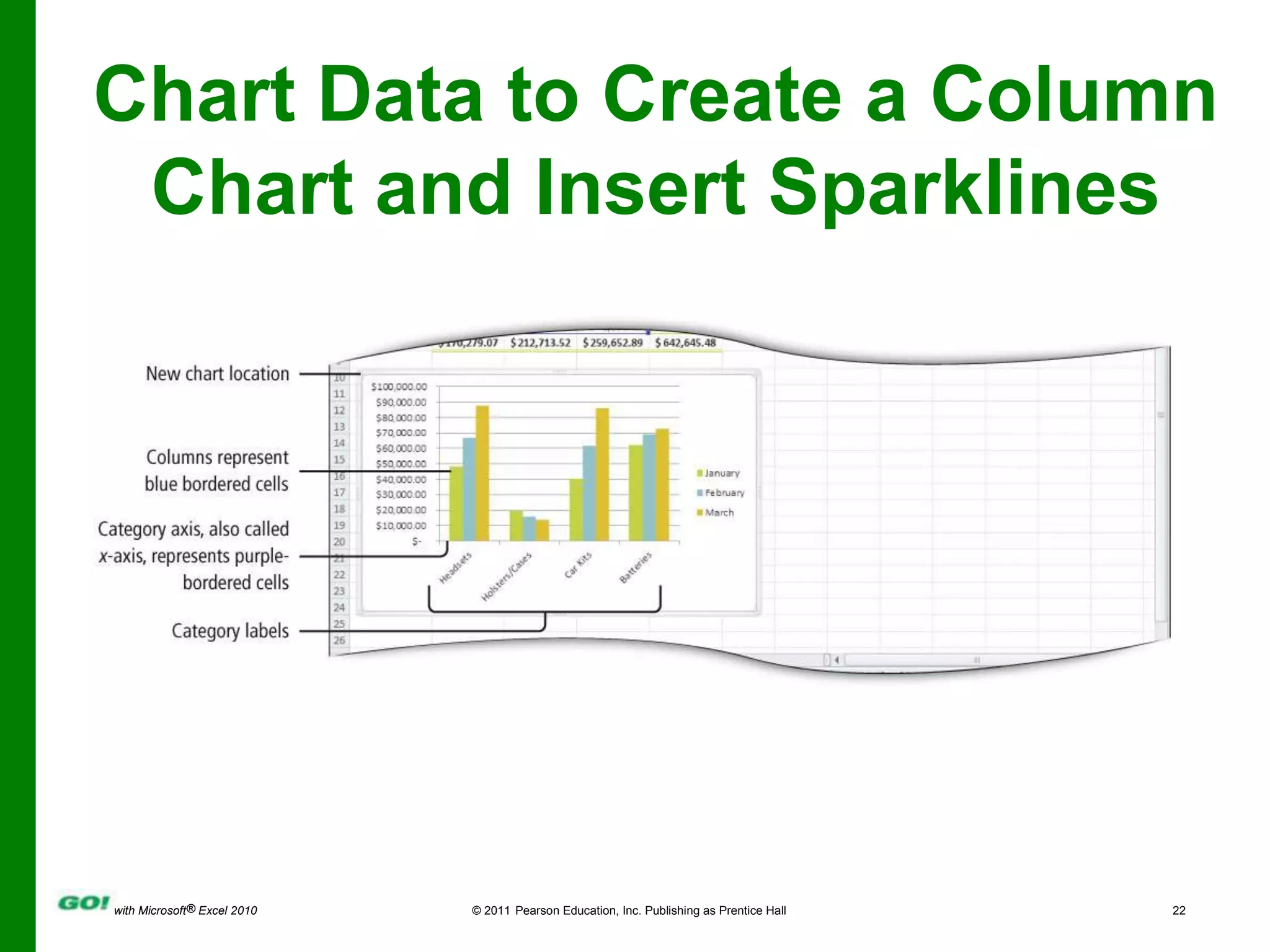
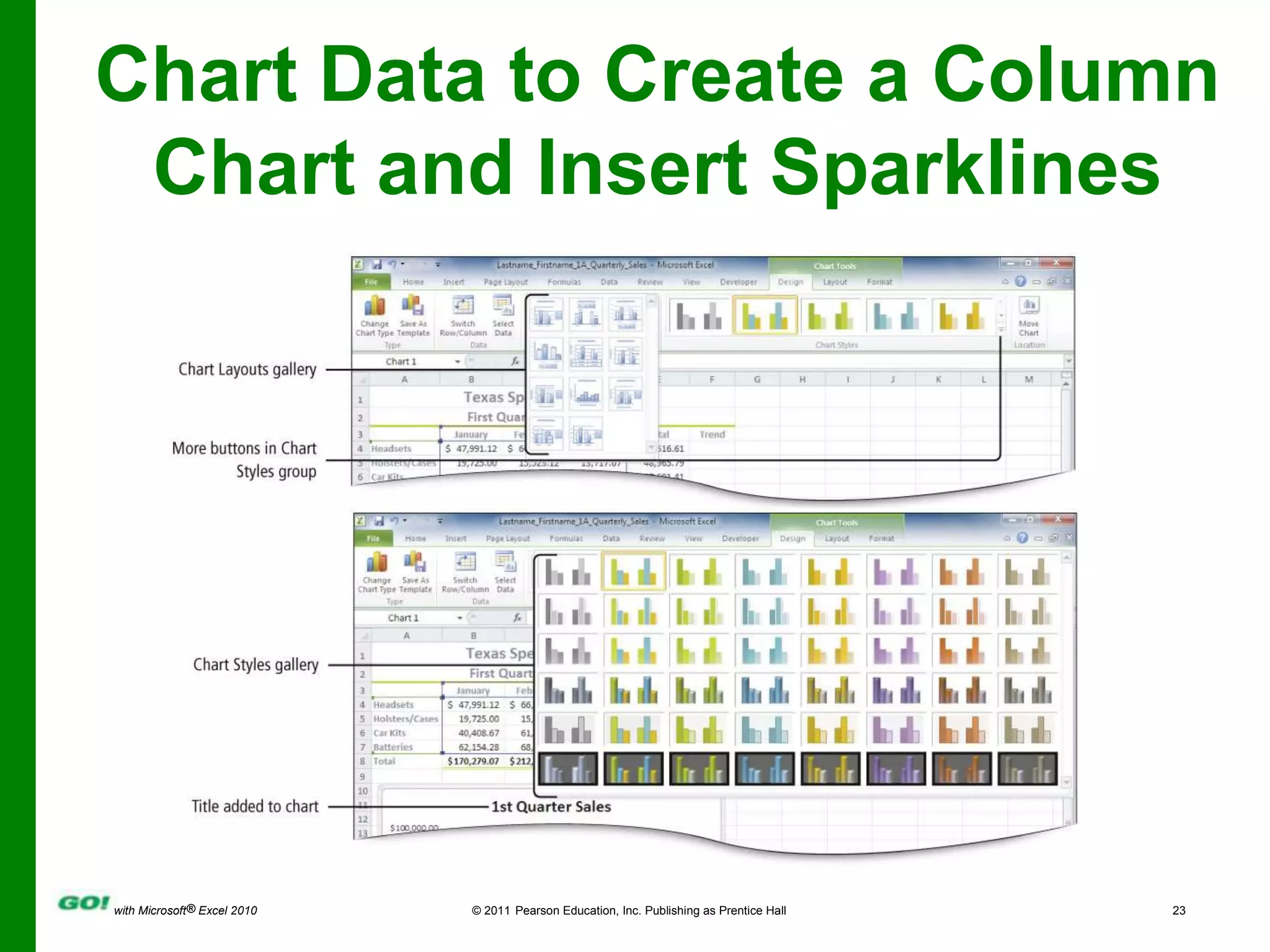
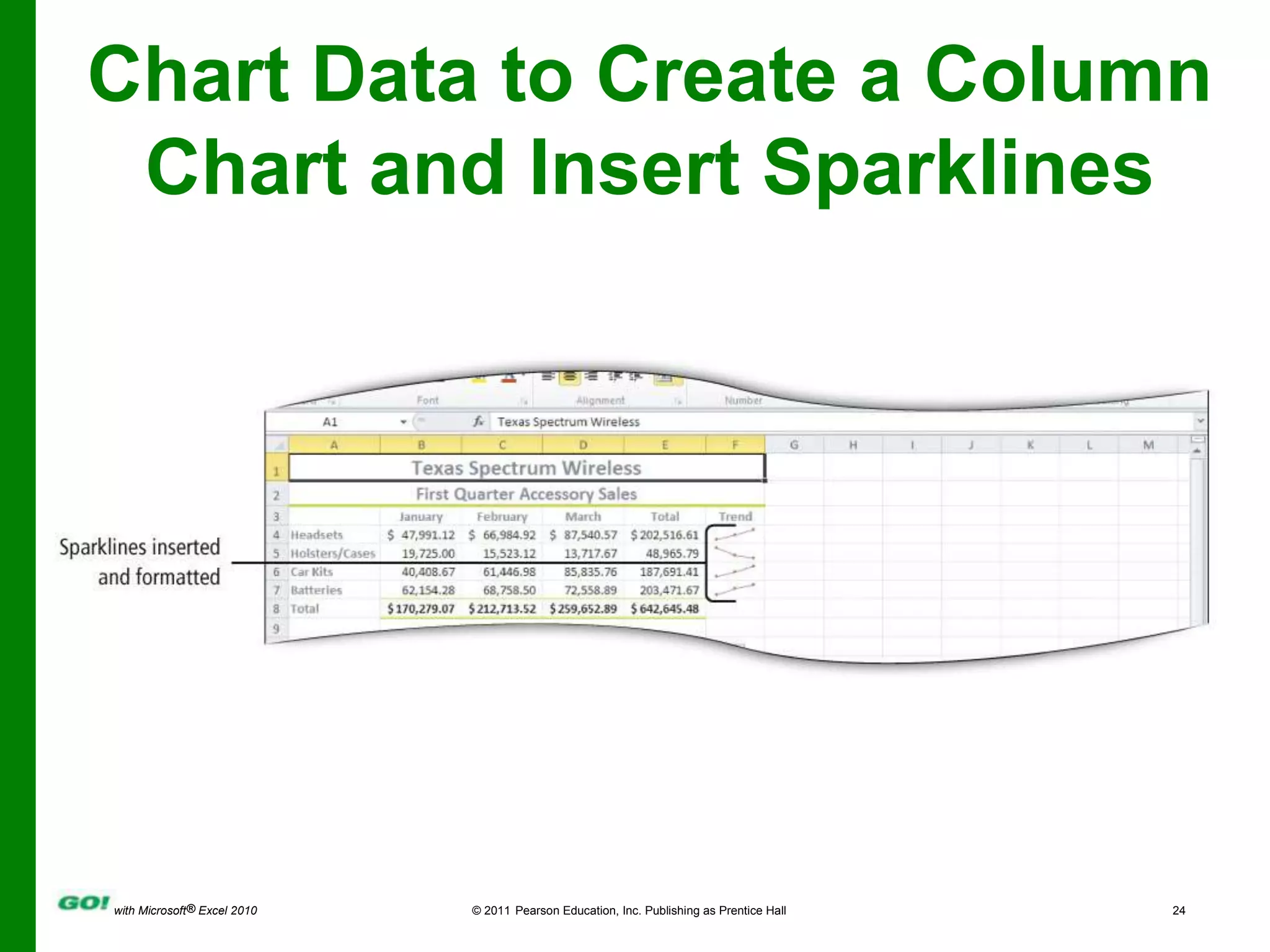
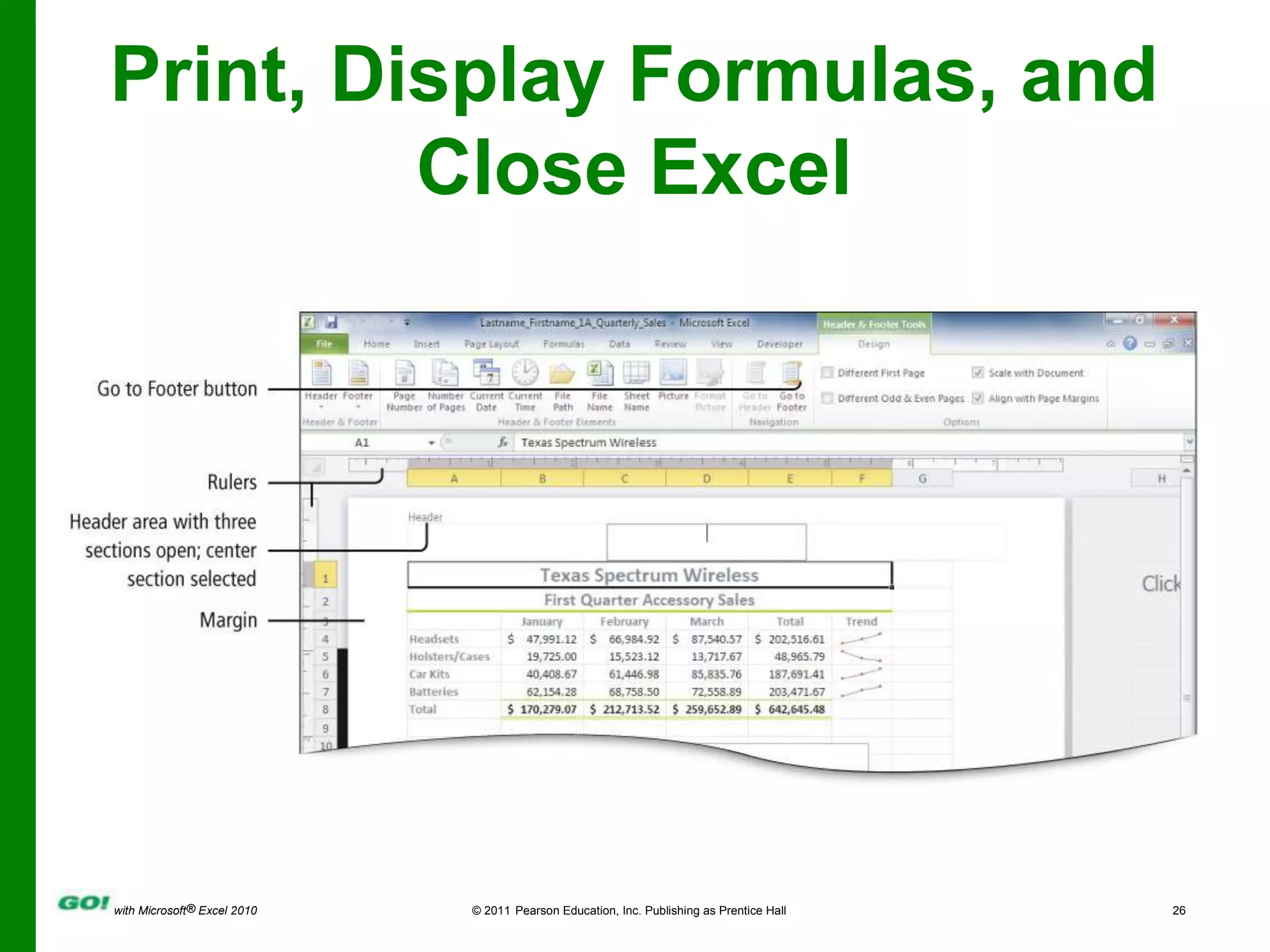
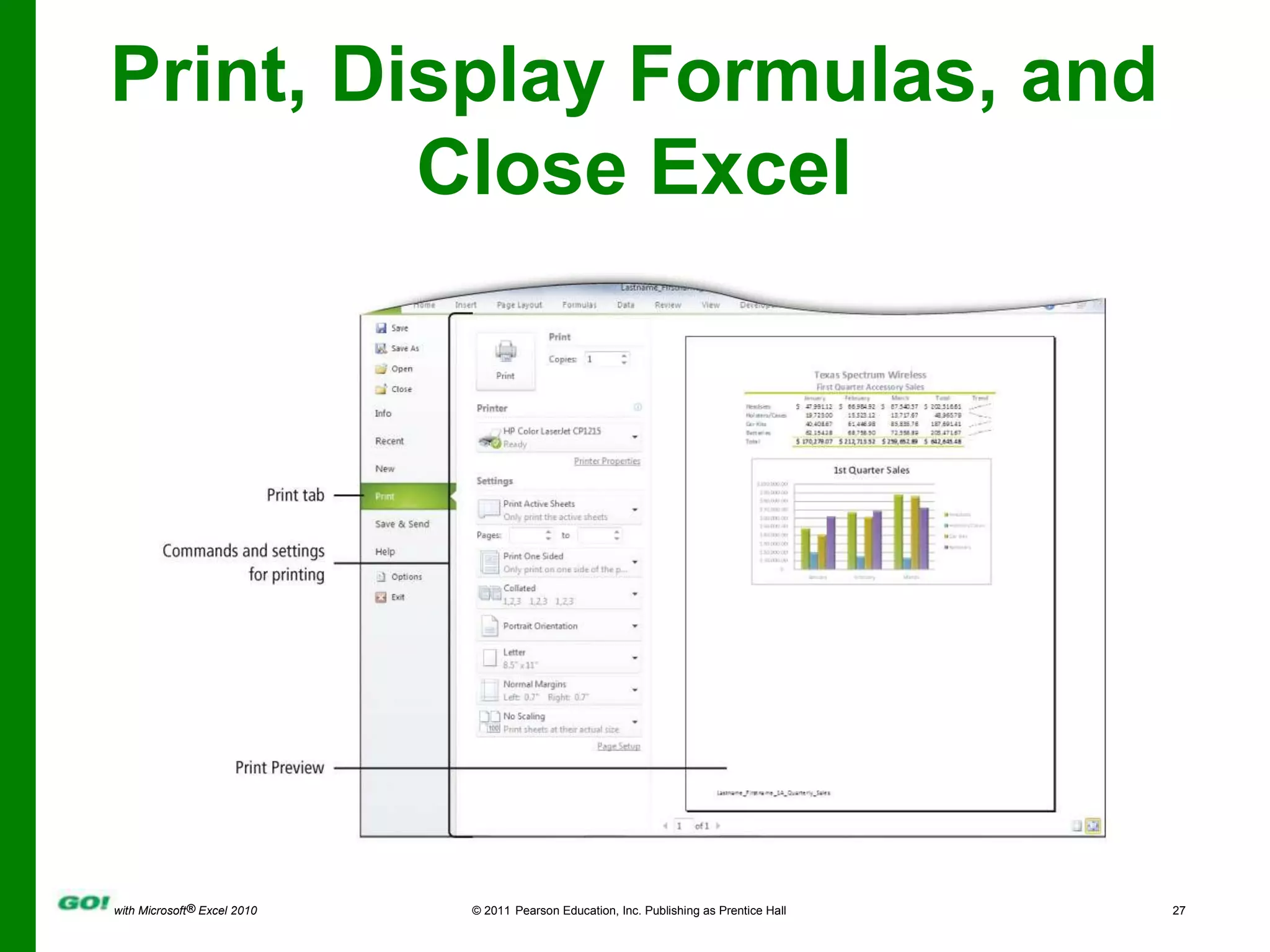
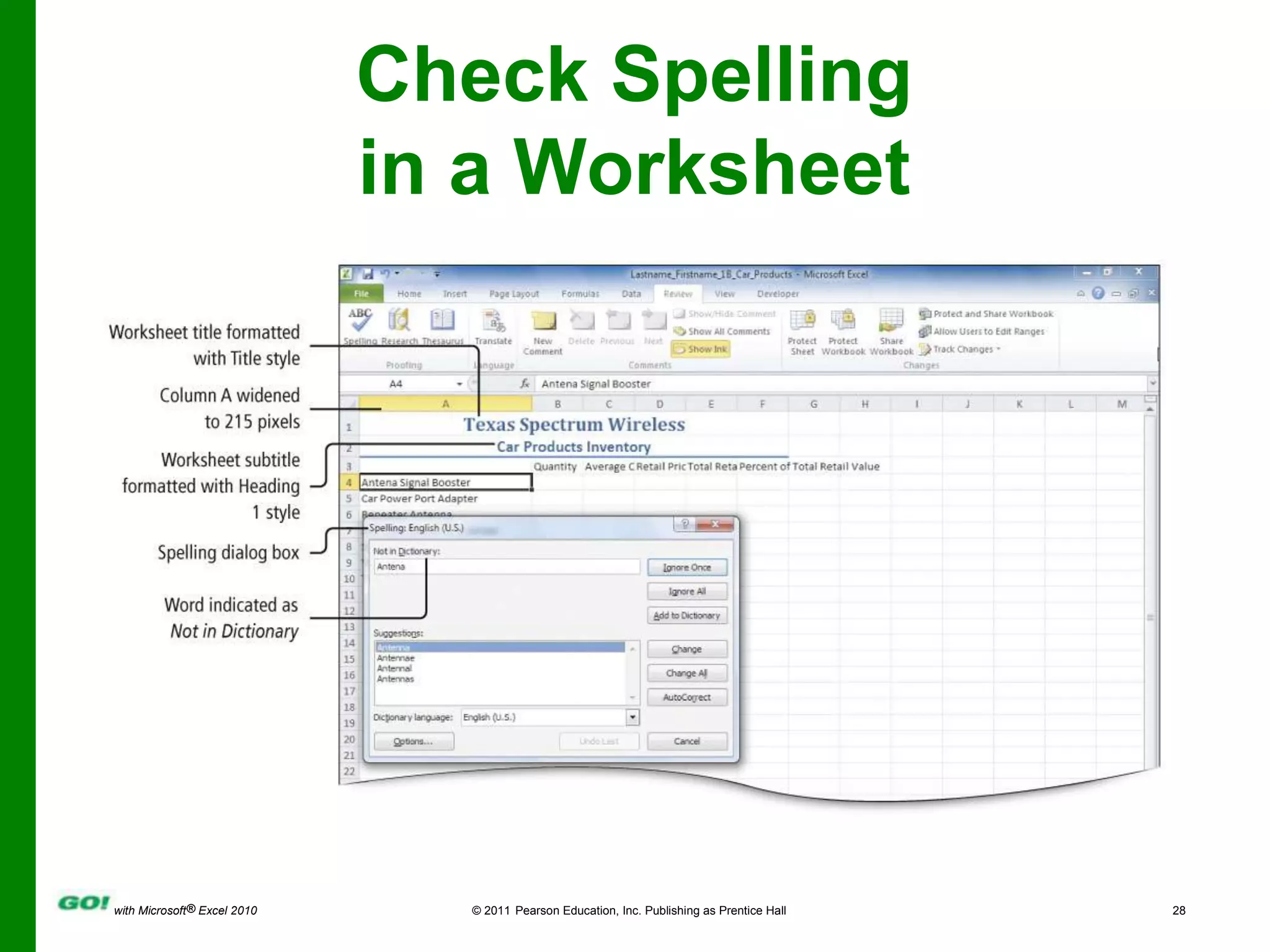
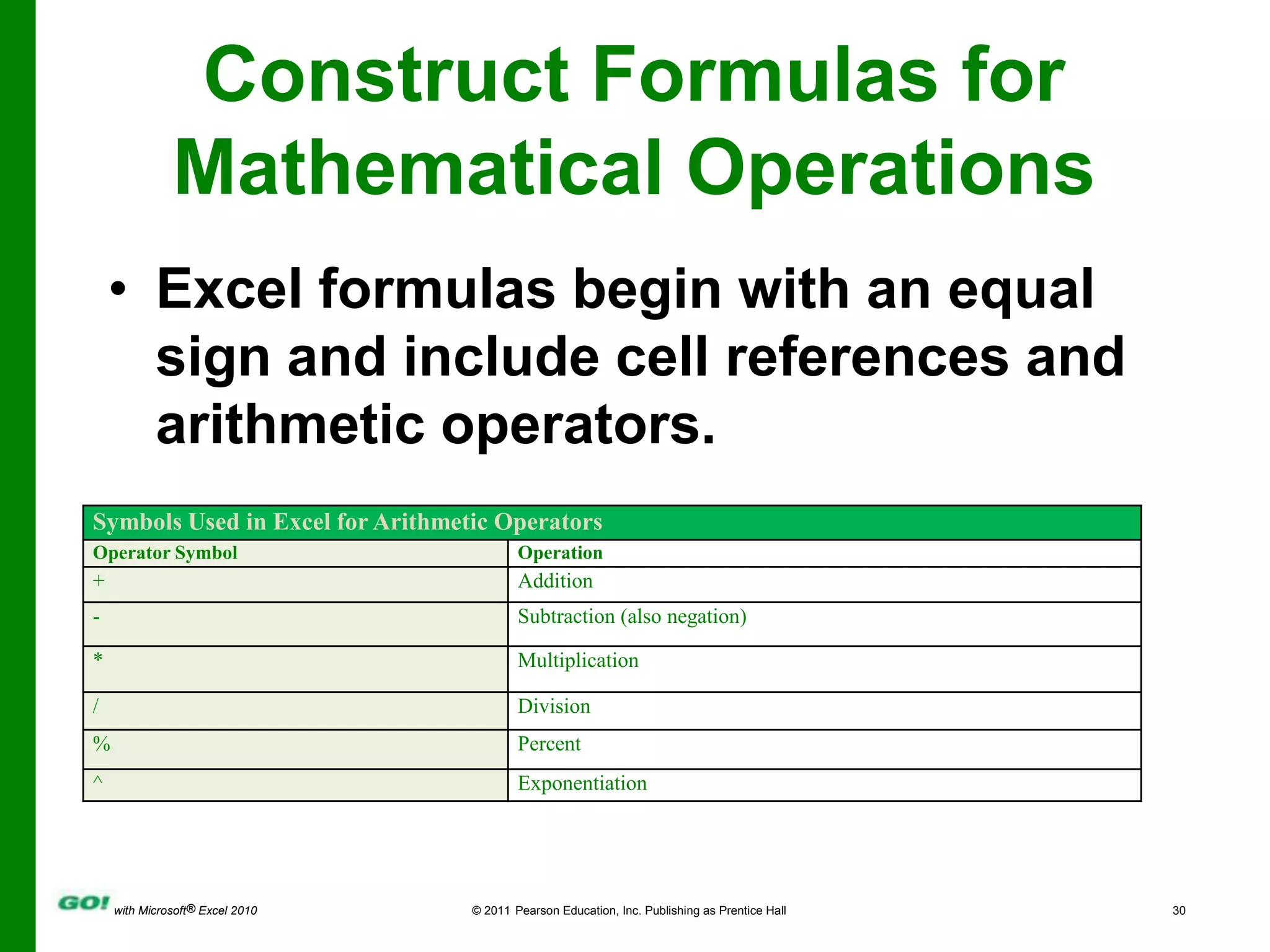
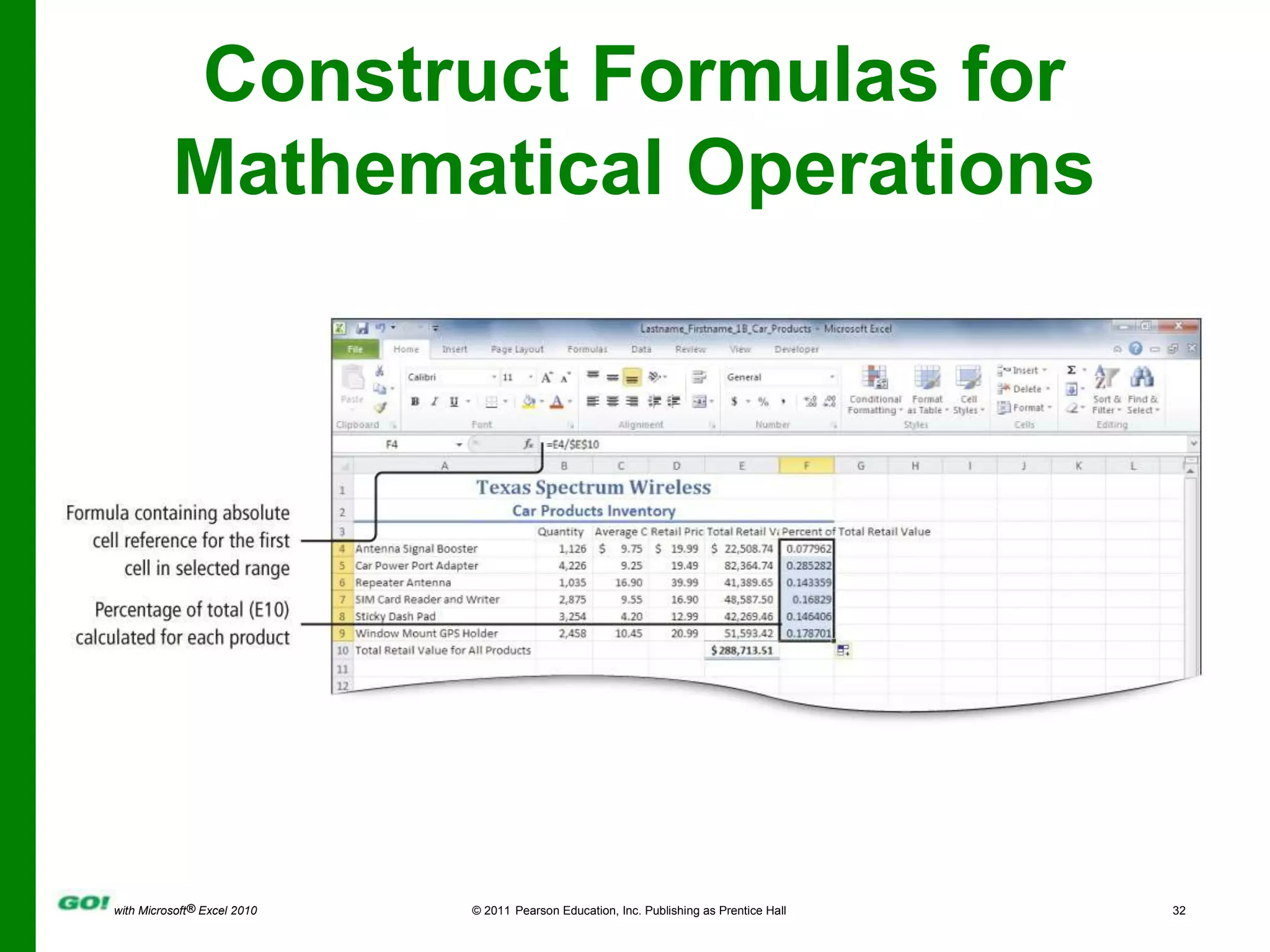
This PowerPoint presentation covers the objectives of Chapter 1 in the book "GO! with Microsoft Excel 2010". It includes how to create and navigate an Excel workbook, enter data and formulas, format cells, create column charts and sparklines, print worksheets, check spelling, enter data by range, construct mathematical formulas, edit values, and format worksheets. The objectives are to learn the basic functions of Excel through hands-on practice with worksheets and charts.