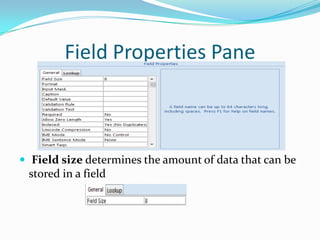
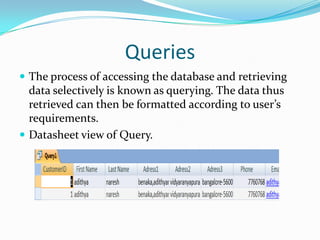
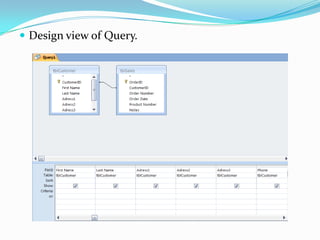
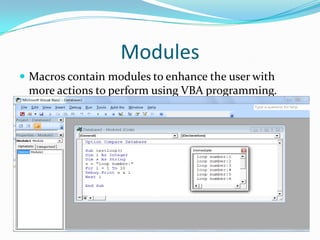
Microsoft Access is a desktop database system intended for home or small business use. It allows users to create and manage related tables of information through features like forms, queries, reports, macros and modules. The basics of Access involve creating tables with fields to store record data. Relationships can then be formed between tables, and forms allow customized layouts for viewing, editing and entering information. Queries retrieve selective data based on criteria, and reports format data from tables for printing. Macros automate tasks, while modules add programming logic using Visual Basic for Applications.