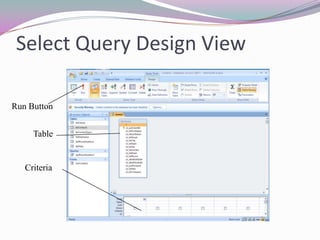
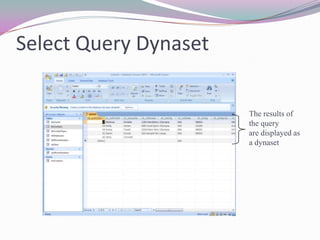
This document discusses queries in Microsoft Access. It explains that queries are used to find, organize, and summarize data from tables to create information. Queries can include calculations and join data from multiple tables. The document outlines the design view for creating queries, including specifying criteria to filter rows and fields to return. It also covers concepts like joins, criteria, wildcards, logical operators, grouping, and sorting that are important for building effective queries.