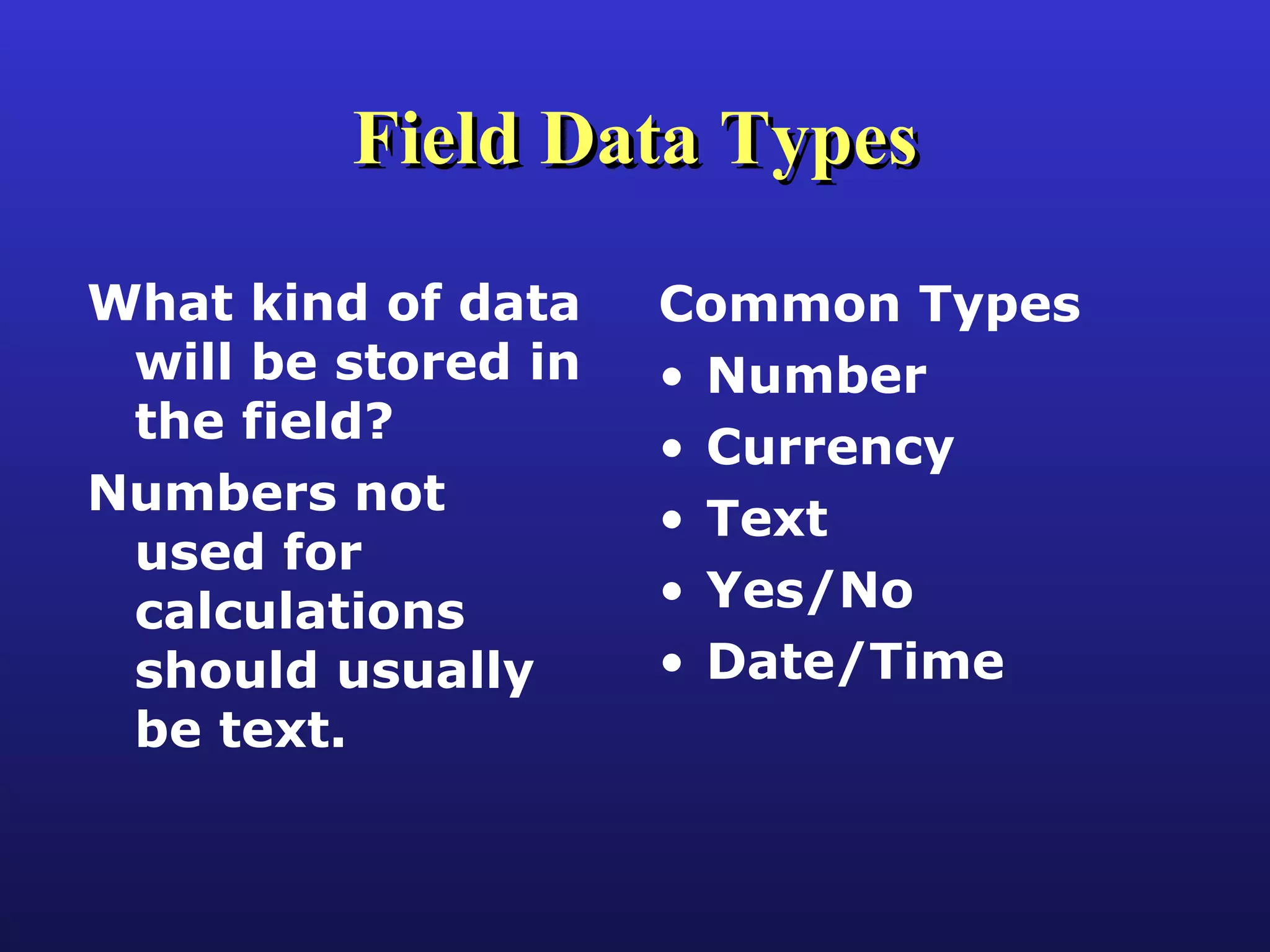
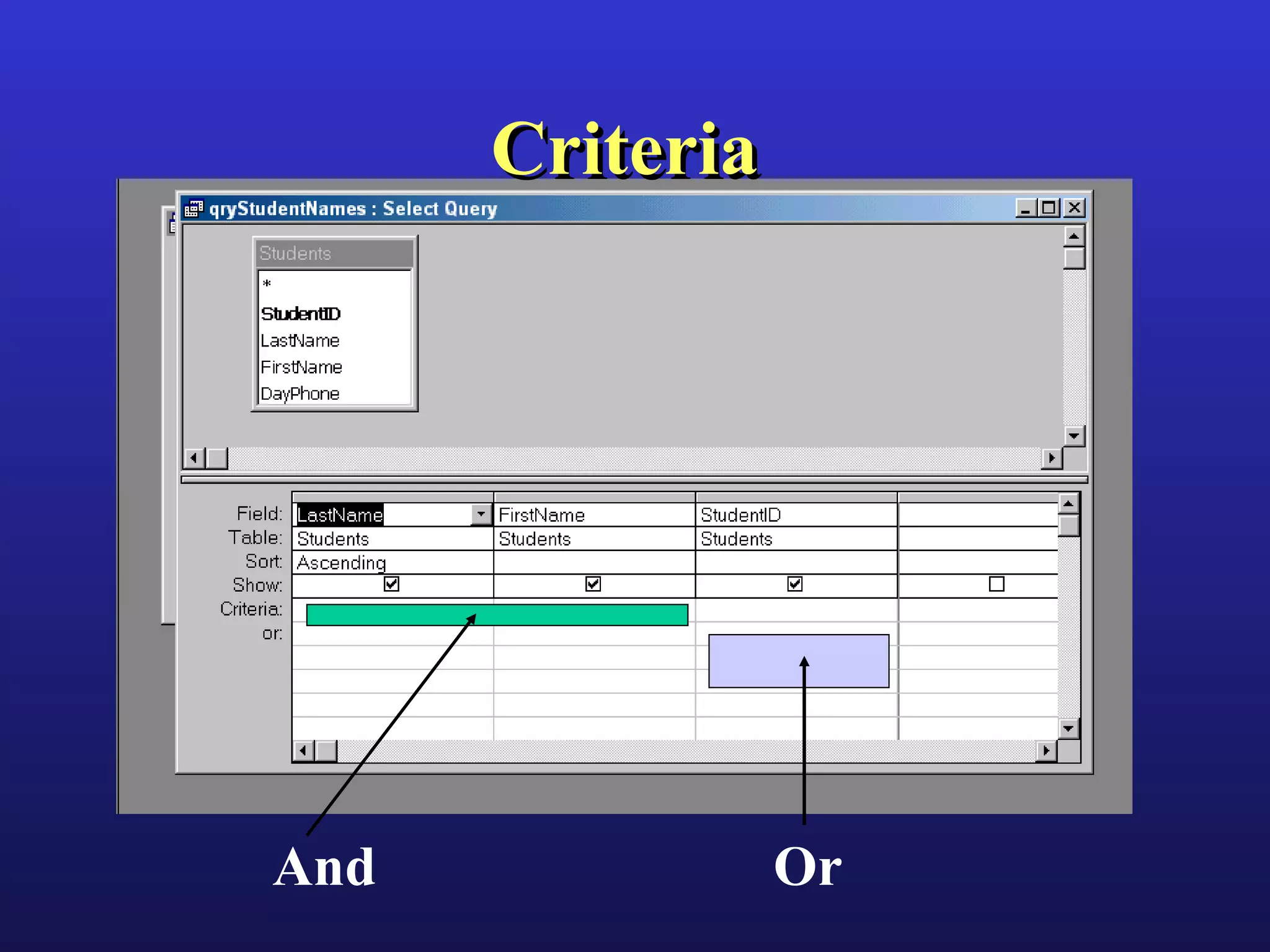
This document provides an overview of key concepts for working with databases in Microsoft Access, including tables, queries, forms, reports, and relationships. It discusses table design, field data types, properties, validation rules, and referential integrity. It also covers topics like one-to-many and many-to-many relationships, joins, parameters, and action queries. Forms and reports are discussed, including their use of sections, controls, sorting, grouping, and subforms/subreports.