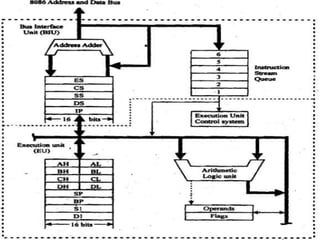
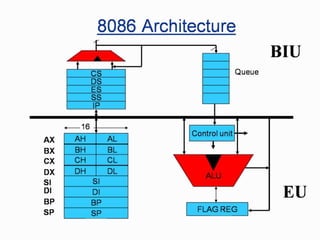
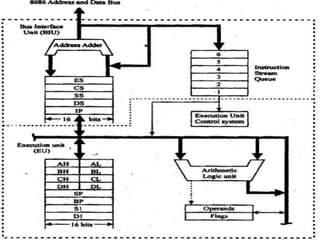
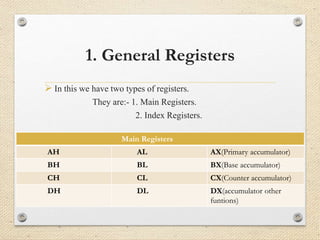
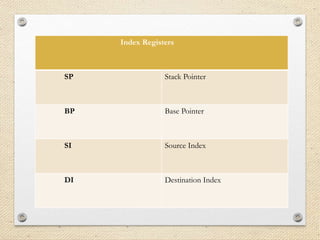
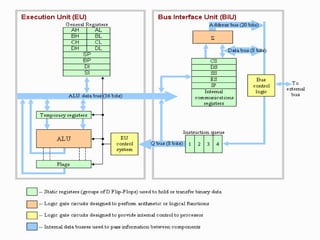
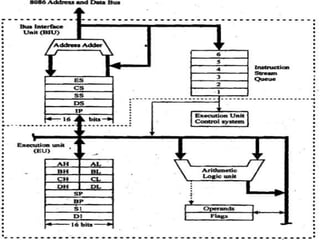
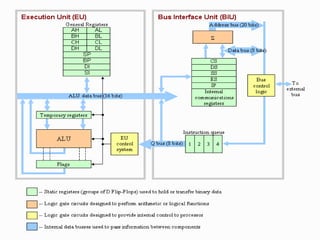
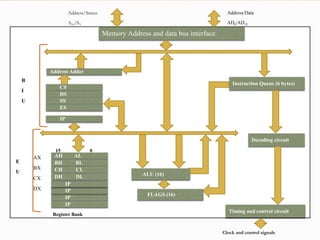
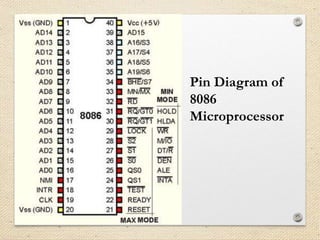
The 8086 microprocessor is a 16-bit processor designed by Intel in the late 1970s. It has a segmented memory architecture that supports a 16-bit ALU, registers, and memory addressing. Its architecture provides improvements over the 8085 including a 16-bit design, segmented memory addressing, and an instruction queue. The main components of the 8086 are the Bus Interface Unit (BIU) which contains the address adder, segment registers, and instruction queue, and the Execution Unit (EU) which contains registers, an ALU, and flag registers for status information.