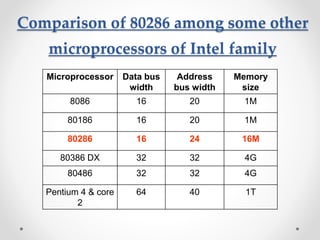
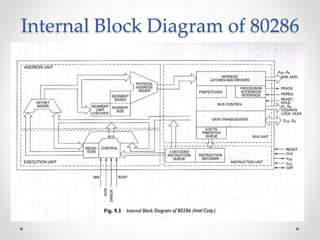
The document discusses the Intel 80286 microprocessor. It was introduced in 1982 as the 5th generation of Intel's x86 family. It had several improvements over the 8086 including a faster clock speed of 12.5MHz, more transistors at 125K, and an advanced memory management system. The 80286 could address up to 16MB of memory and had two operating modes: real address mode for compatibility and protected virtual address mode for multitasking. It also introduced the ability to use virtual memory in protected mode.