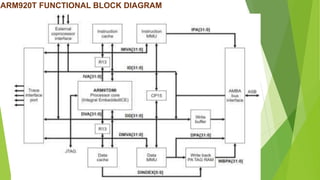
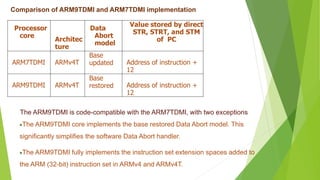
The document discusses the features and architecture of the ARM9 processor. It describes the ARM9 as having a 5-stage pipeline, 32 registers, and support for both ARM and Thumb instruction sets. It supports DSP enhancements like single-cycle 32x16 multiplication and saturating arithmetic. The ARM9 powers applications in devices like smartphones, networking equipment, automotive systems, and embedded devices. The document then focuses on the specific ARM920T processor, which adds a 16KB cache and memory management unit to the ARM9 core.