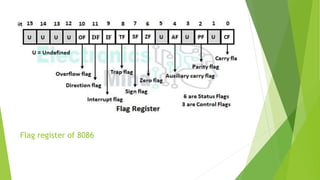
The flag register in the 8086 microprocessor is a 16-bit register that contains status and control flags. It has 9 flags that indicate the status of arithmetic or logical operations performed by the ALU. The 6 status flags are: the carry flag (CF), parity flag (PF), auxiliary carry flag (AF), zero flag (ZF), sign flag (SF), and overflow flag (OF). These flags provide information about the results of operations, such as whether there was a carry out, if the result was even or odd parity, or if the operation resulted in a zero value.