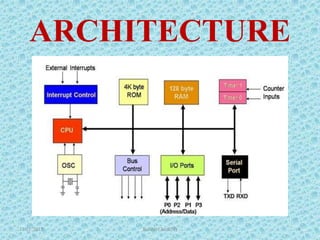
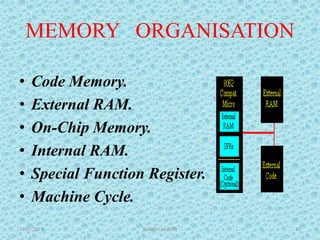
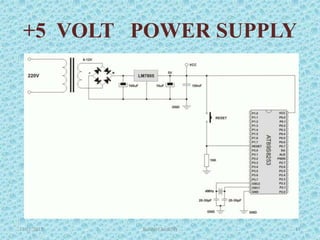
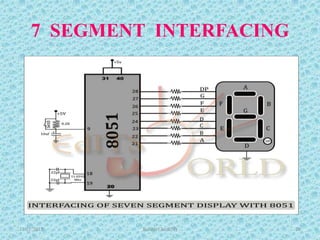
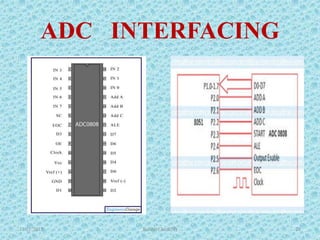
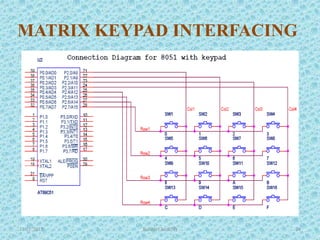
The document discusses the 8051 microcontroller, including its architecture, pin configuration, memory organization, timers, interrupts, and interfacing capabilities. It describes the 8051's features like on-chip RAM, ROM, timers and low power consumption which make it suitable for control applications. The document outlines the differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers, and covers various interfacing examples like switches, LEDs, 7-segment displays, LCDs, ADCs and relay interfacing. It concludes with common applications of the 8051 such as in automobiles, industrial processing, robotics and consumer electronics.