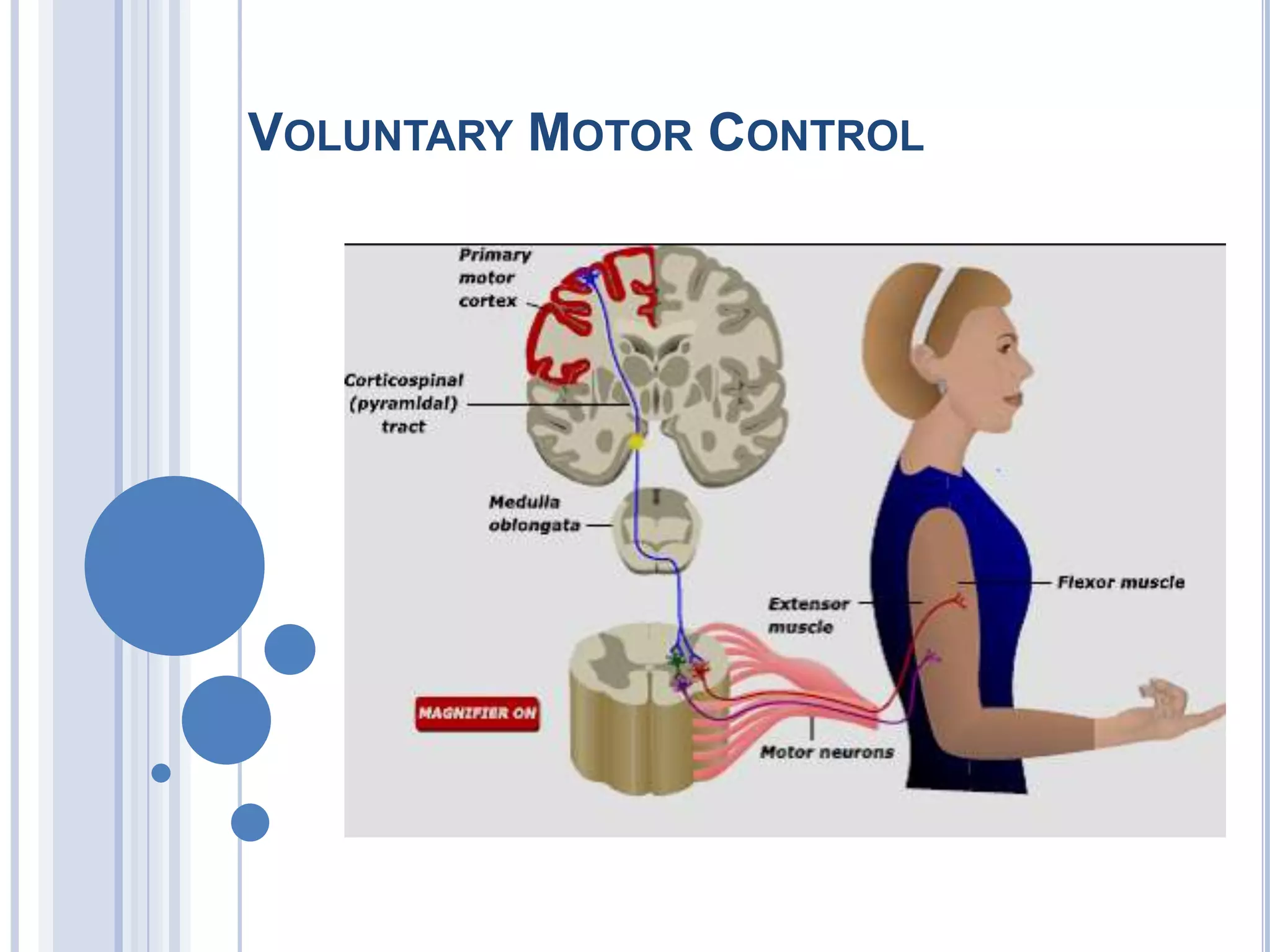
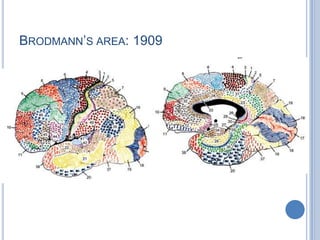
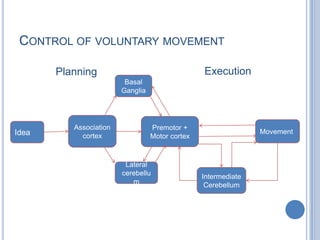
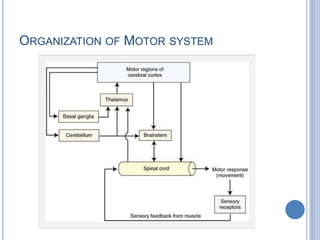
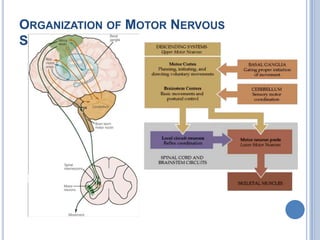
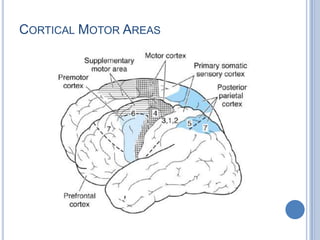
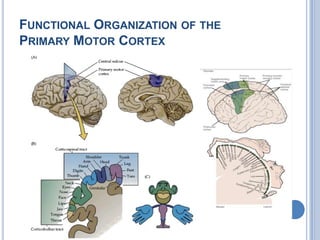
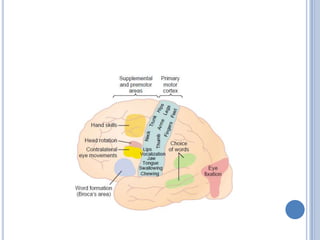
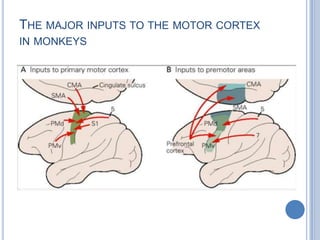
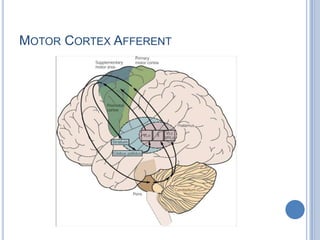
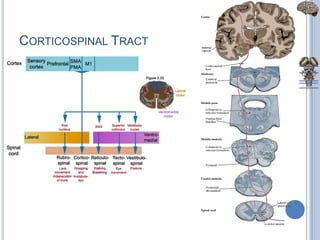
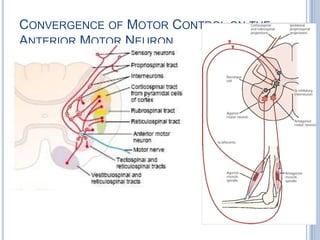
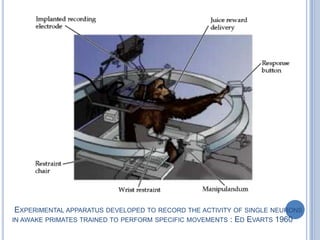
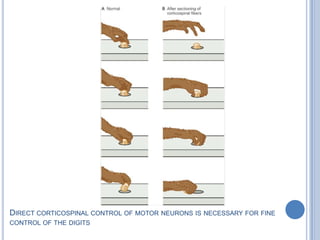
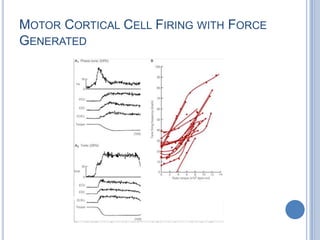
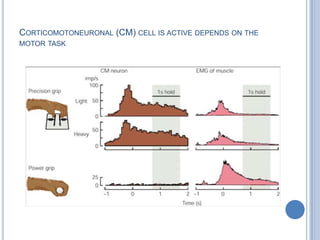
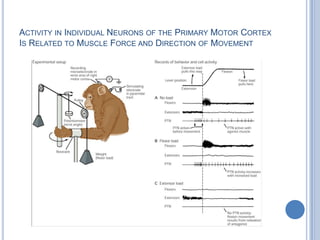
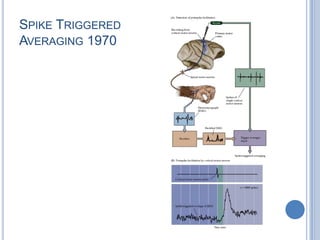
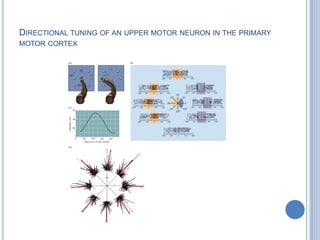
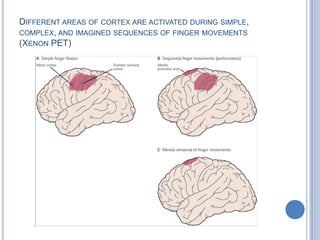
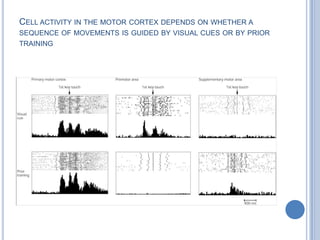
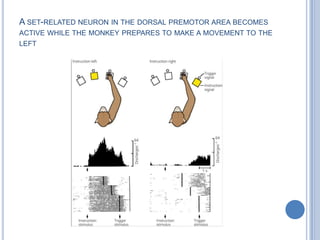
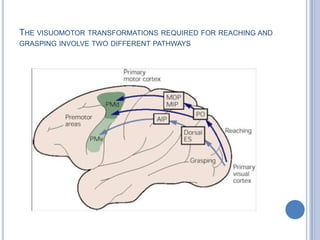
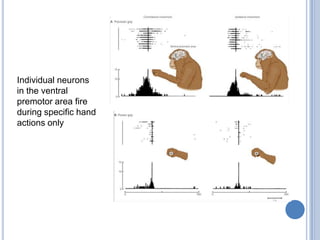
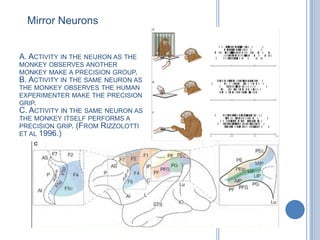
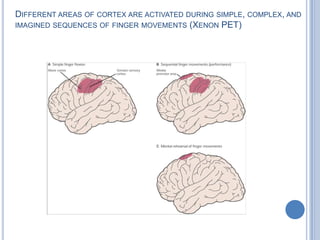
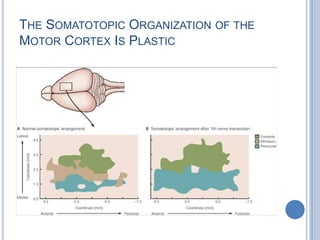
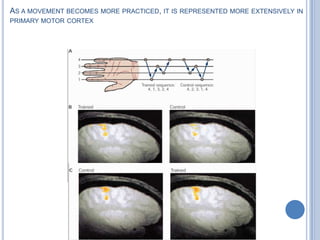
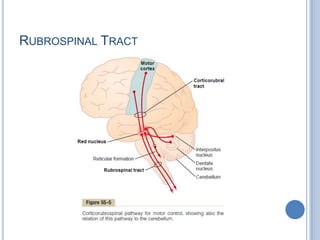
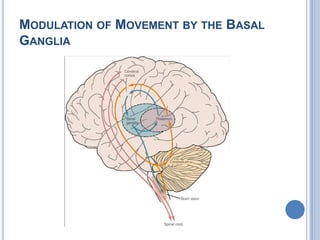
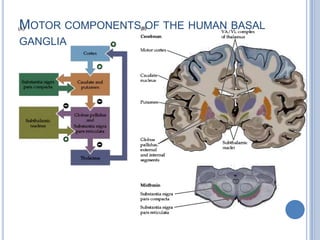
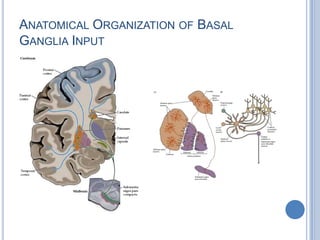
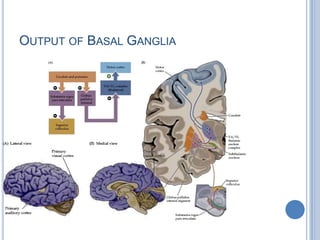
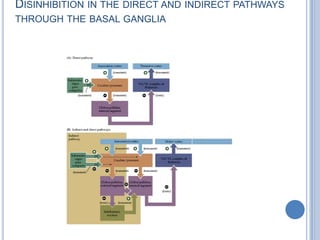
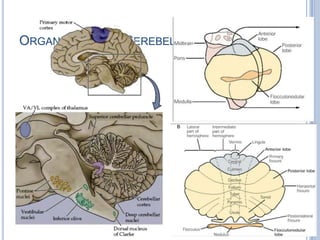
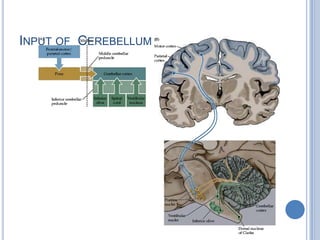
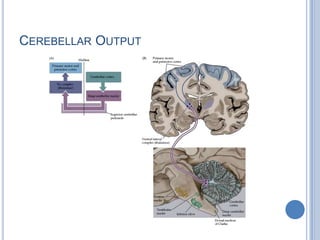
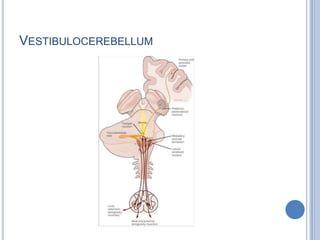
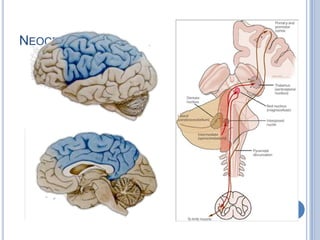
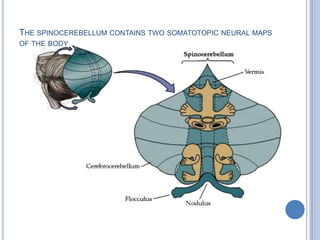
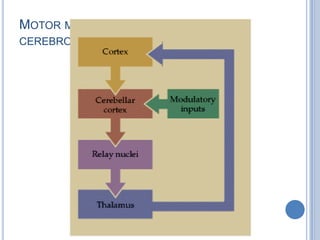
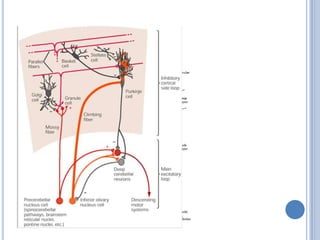
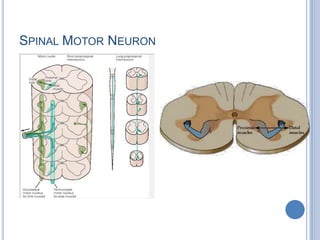
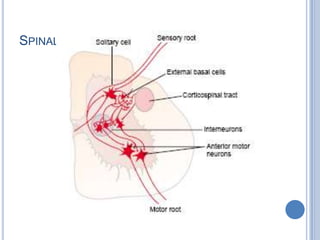
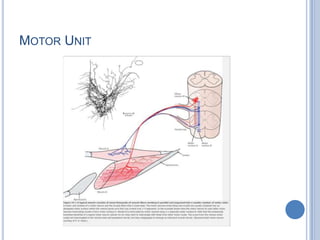
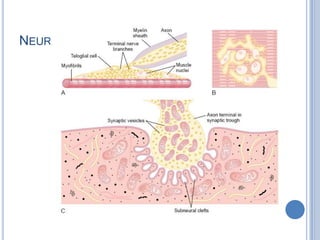
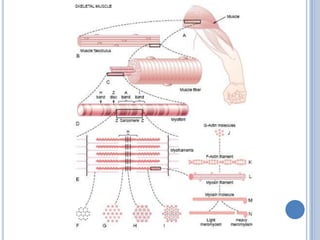
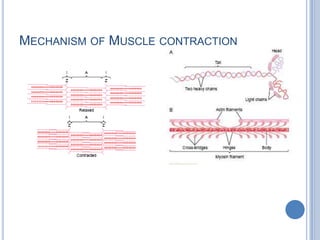
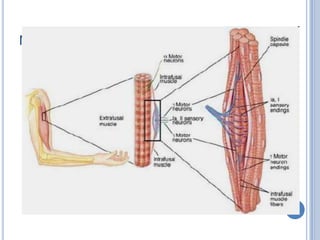
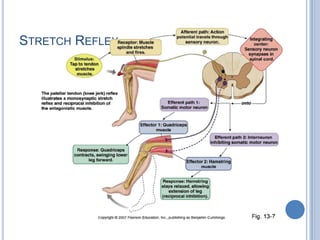
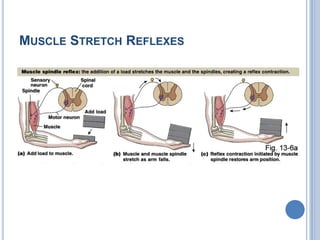
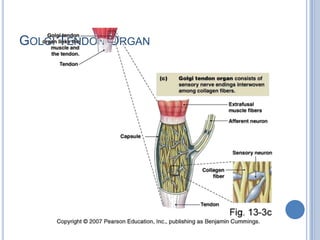
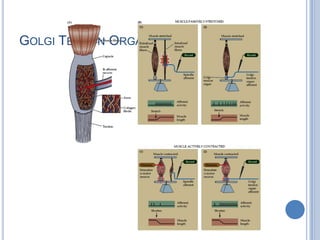
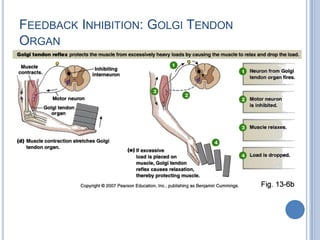
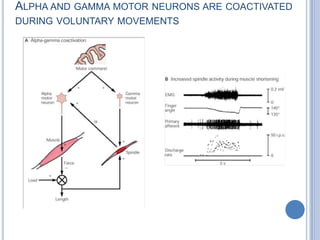
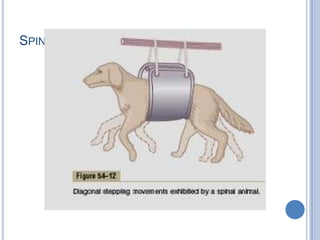
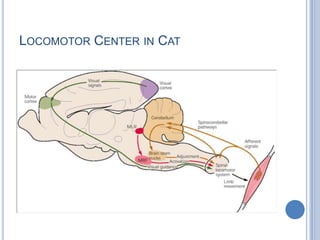
Voluntary motor control involves multiple brain areas that work together. The primary motor cortex directly controls spinal motor neurons and codes for movement force and direction. Other areas like the dorsal premotor cortex encode sensorimotor transformations for visual and sensory cues. The basal ganglia and cerebellum help modulate and coordinate movement through disinhibition of pathways. Feedback from muscles and joints via sensory neurons also helps regulate movement.