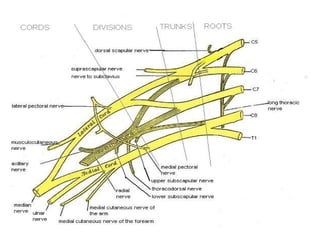
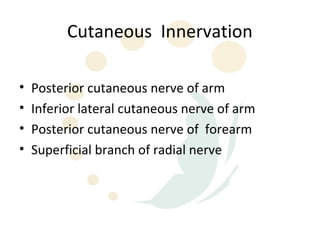
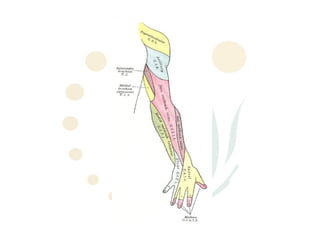
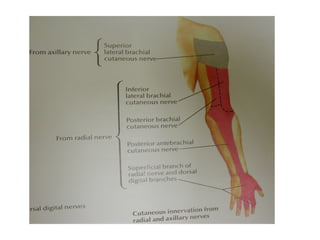
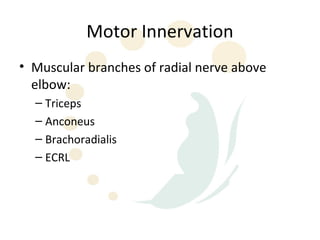
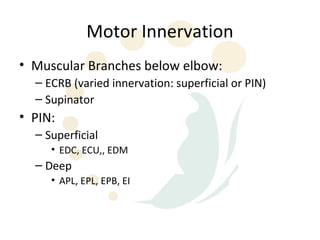
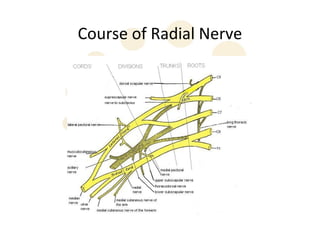
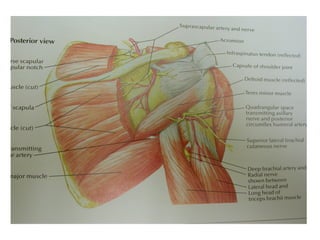
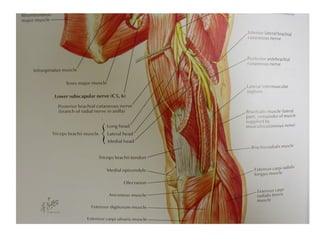
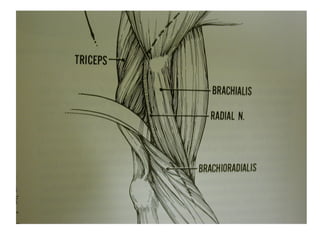
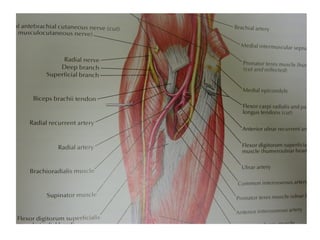
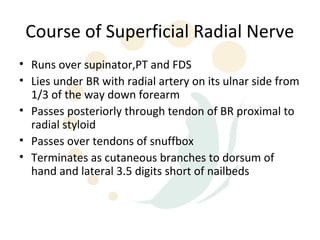
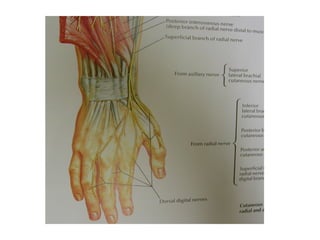
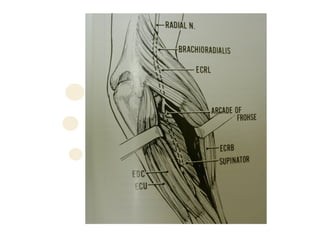
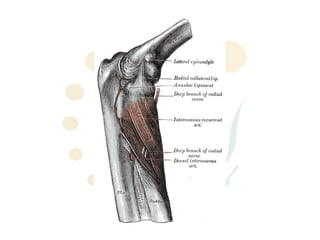
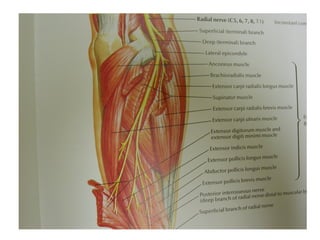
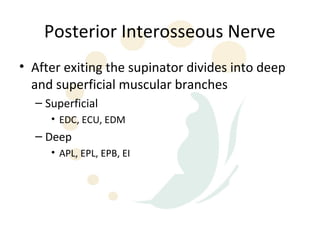
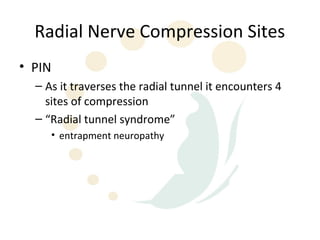
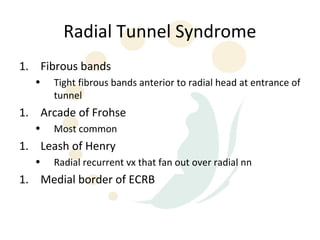
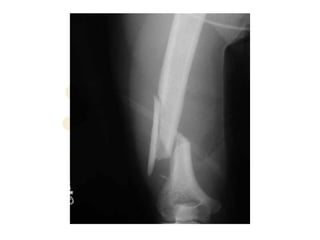
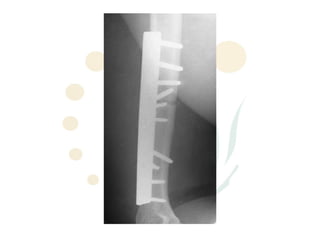
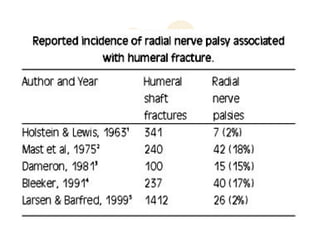
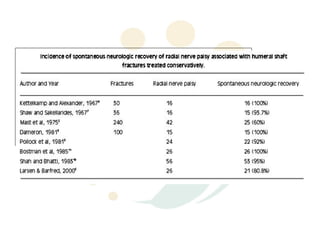
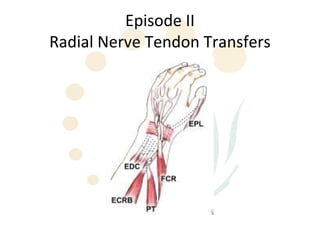
The radial nerve originates from cervical and thoracic nerve roots and is the largest branch of the brachial plexus. It provides cutaneous innervation to the posterior arm and forearm and motor innervation to triceps, brachioradialis, and extensor muscles of the forearm and hand. The radial nerve is vulnerable to compression at the radial tunnel as it travels through the forearm. Compression can cause radial tunnel syndrome. The superficial branch of the radial nerve can be affected by Wartenberg syndrome. Radial nerve palsy can result from fractures, injuries, tumors, or iatrogenic causes.