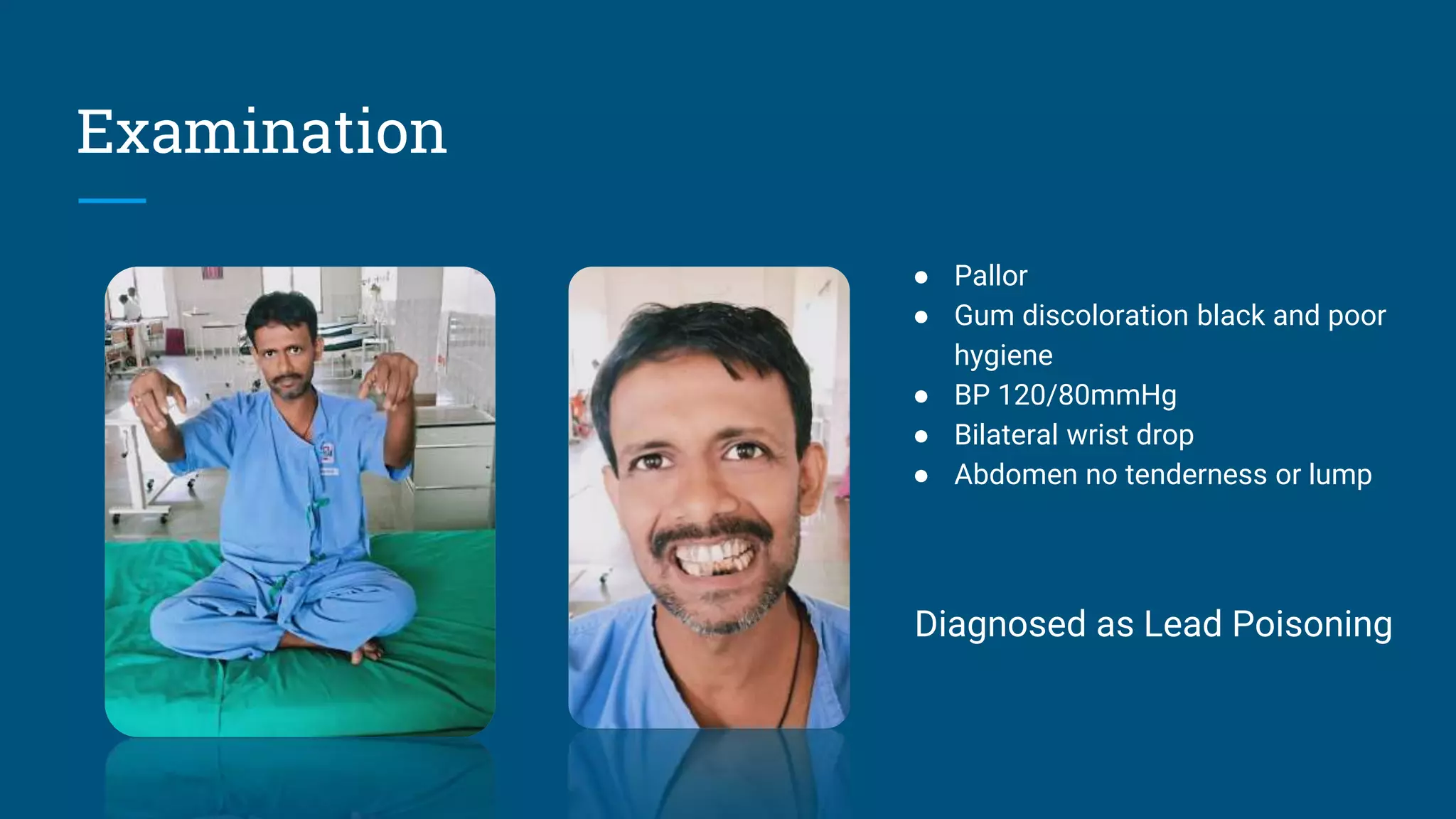
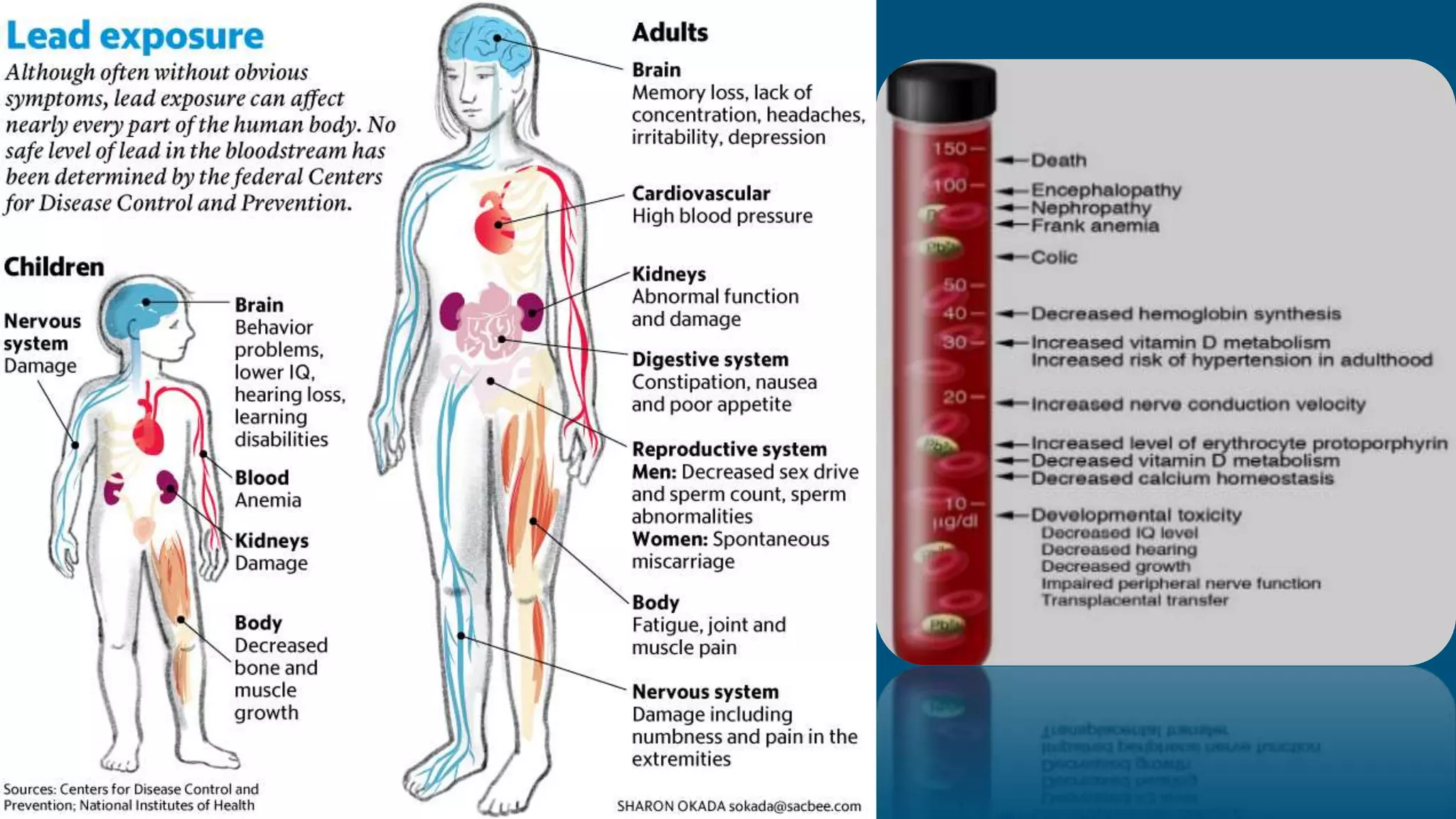
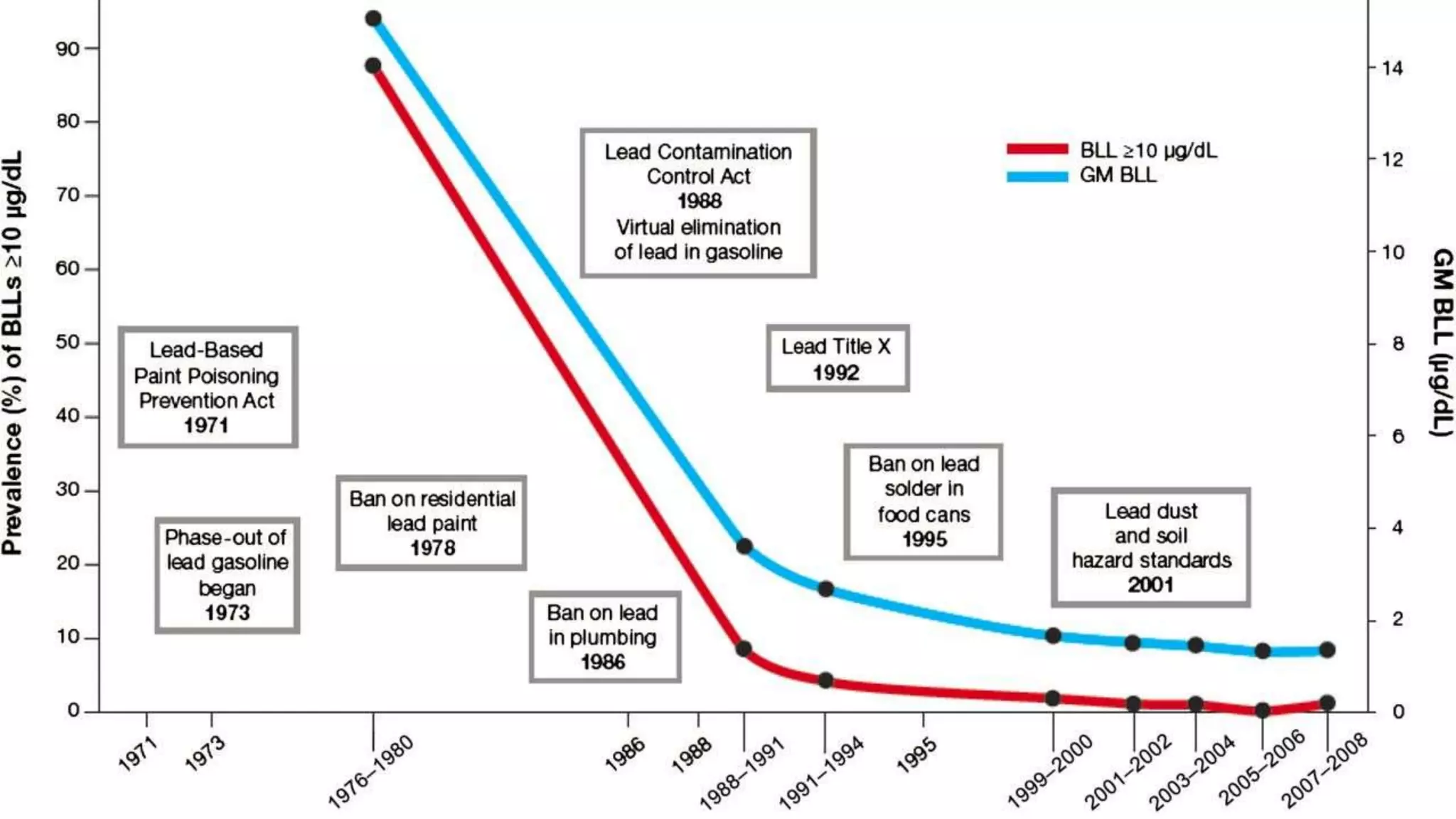
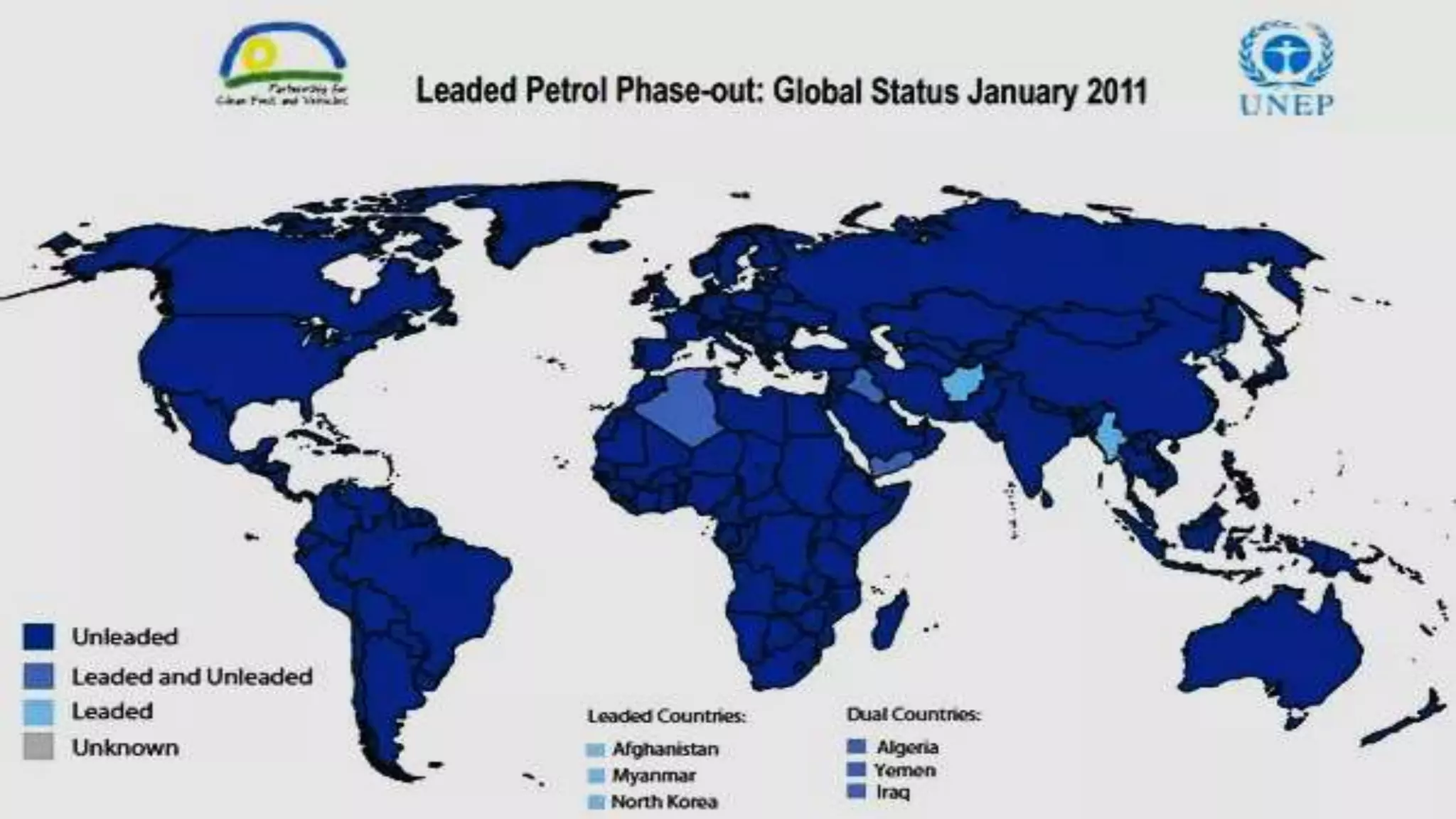
The document discusses lead poisoning in neurology, highlighting a case study of a 45-year-old male battery worker diagnosed with lead poisoning and treated with penicillamine. It emphasizes the global burden of lead-related diseases, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, and presents historical evidence of lead use and toxicity, including its effects on ancient Rome. Additionally, it covers lead exposure prevalence in India, the economic cost of lead poisoning, and efforts to mitigate lead exposure through regulations and research initiatives.