This document discusses athetosis and dystonia. It defines athetosis as irregular, slow writhing movements, often of the extremities and fingers. Dystonia is defined as an abnormal sustained muscle contraction causing twisting movements and abnormal postures. The document describes the clinical presentations and patterns of movement seen in athetosis. It discusses the potential pathophysiology of athetosis involving lesions in the frontal lobes, parietal lobes, and putamen. Causes of athetosis in children and adults are provided. Dystonia is similarly defined and classified. Potential pathology, types, hereditary forms, and secondary causes of dystonia are outlined in detail.















![AETIOLOGY: PRIMARY HEREDITARY
Symbol OMIM Gene Locus Alt Name
DYT1 128100 TOR1A 9q34 Early-onset torsion dystonia
DYT2 224500 unknown unknown Autosomal recessive torsion dystonia
DYT3 314250 TAF1 Xq13 X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism
DYT4 128101 TUBB4[3] 19p13.12-13 Autosomal dominant whispering dysphonia
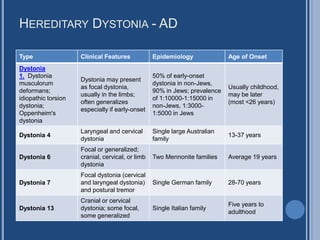
DYT5a 128230 GCH1 14q22.1-q22.2 Autosomal dominant dopamine-responsive
dystonia
DYT5b 191290 TH[disambiguation
needed] 11p15.5 Autosomal recessive dopamine-responsive
dystonia
DYT6 602629 THAP1 8p11.21 Autosomal dominant dystonia with cranio-
cervical predilection
DYT7 602124 unknown 18p (questionable) Autosomal dominant primary focal cervical
dystonia
DYT8 118800 MR1 2q35 Paroxysmal nonkinesigenic dyskinesia
DYT9 601042 SLC2A1 1p35-p31.3 Episodic choreoathetosis/spasticity (now
known to be synonymous with DYT18)
DYT10 128200 PRRT2 16p11.2-q12.1 Paroxysmal kinesigenic dyskinesia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/athetosisanddystonia-130819225732-phpapp02/85/Athetosis-and-dystonia-16-320.jpg)
![AETIOLOGY: PRIMARY HEREDITARY
DYT11 159900 SGCE 7q21 Myoclonic dystonia
DYT12 128235 ATP1A3 19q12-q13.2
Rapid onset dystonia parkinsonism
and alternating hemiplegia of
childhood
DYT15 607488 unknown 18p11[5] Myoclonic dystonia not linked to
SGCE mutations
DYT16 612067 PRKRA 2q31.3 Autosomal recessive young onset
dystonia parkinsonism
DYT17 612406 unknown, near D20S107[6] 20p11.2-q13.12 Autosomal recessive dystonia in one
family
DYT18 612126 SLC2A1 1p35-p31.3 Paroxysmal exercise-induced
dyskinesia
DYT19 611031 probably PRRT2 16q13-q22.1 Episodic kinesigenic dyskinesia 2,
probably synonymous with DYT10
DYT20 611147 unknown 2q31 Paroxysmal nonkinesigenic
dyskinesia 2
DYT21 614588 unknown 2q14.3-q21.3 Late-onset torsion dystonia
DYT23 610110 ANO3[7] 11p14.2 Autosomal dominant cranio-cervical
dystonia with prominent tremor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/athetosisanddystonia-130819225732-phpapp02/85/Athetosis-and-dystonia-17-320.jpg)