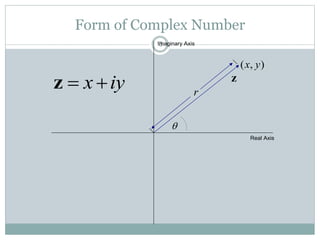
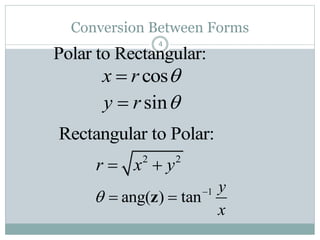
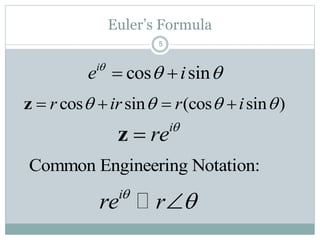
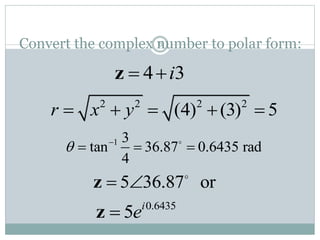
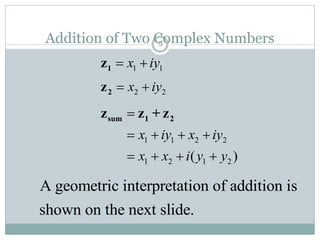
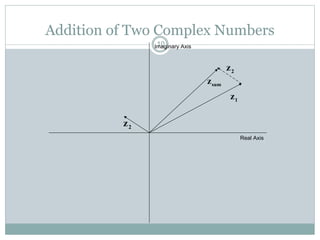
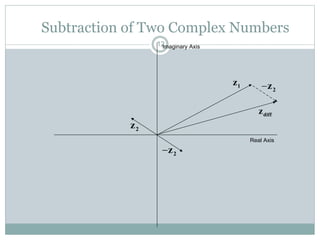
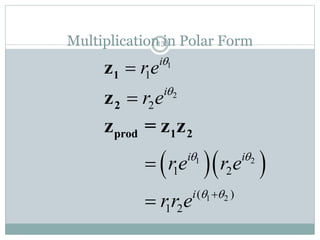
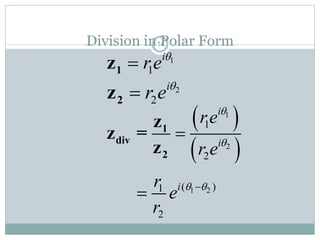
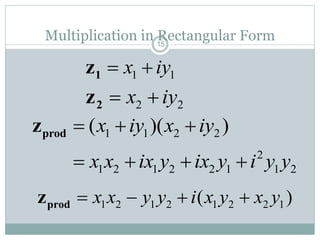
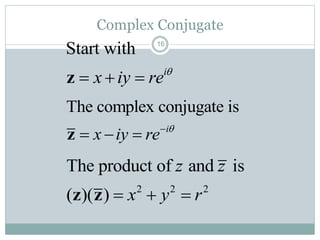
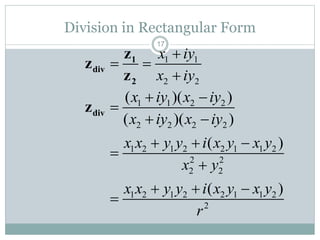
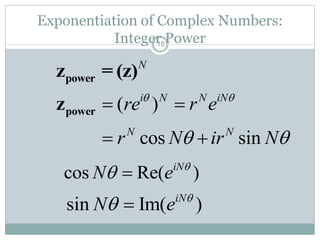
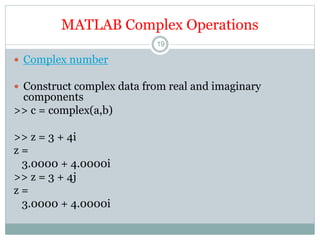
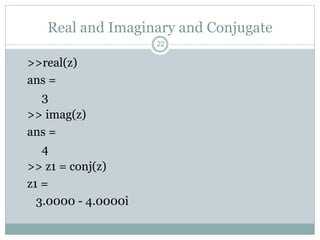
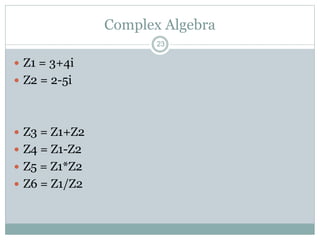
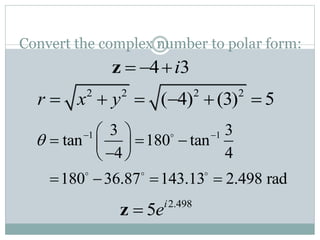This document discusses complex numbers in MATLAB. It begins by introducing the complex plane and representing complex numbers in rectangular and polar forms. It then covers converting between the forms, Euler's formula, and basic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and exponentiation of complex numbers. The document ends by demonstrating how to work with complex numbers in MATLAB, including entering them in polar/rectangular forms, plotting complex numbers, and performing operations like finding the real/imaginary parts and conjugate.