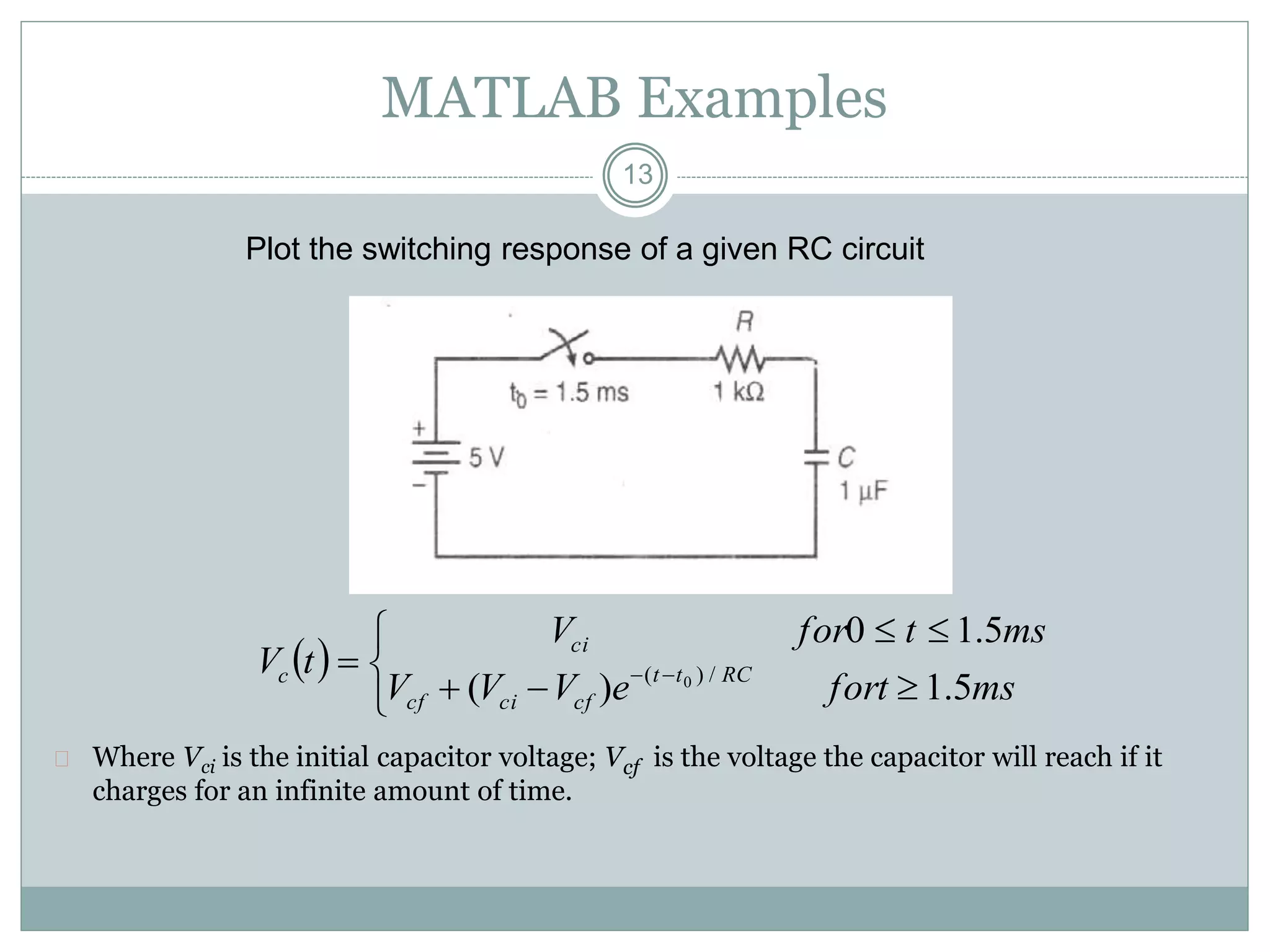
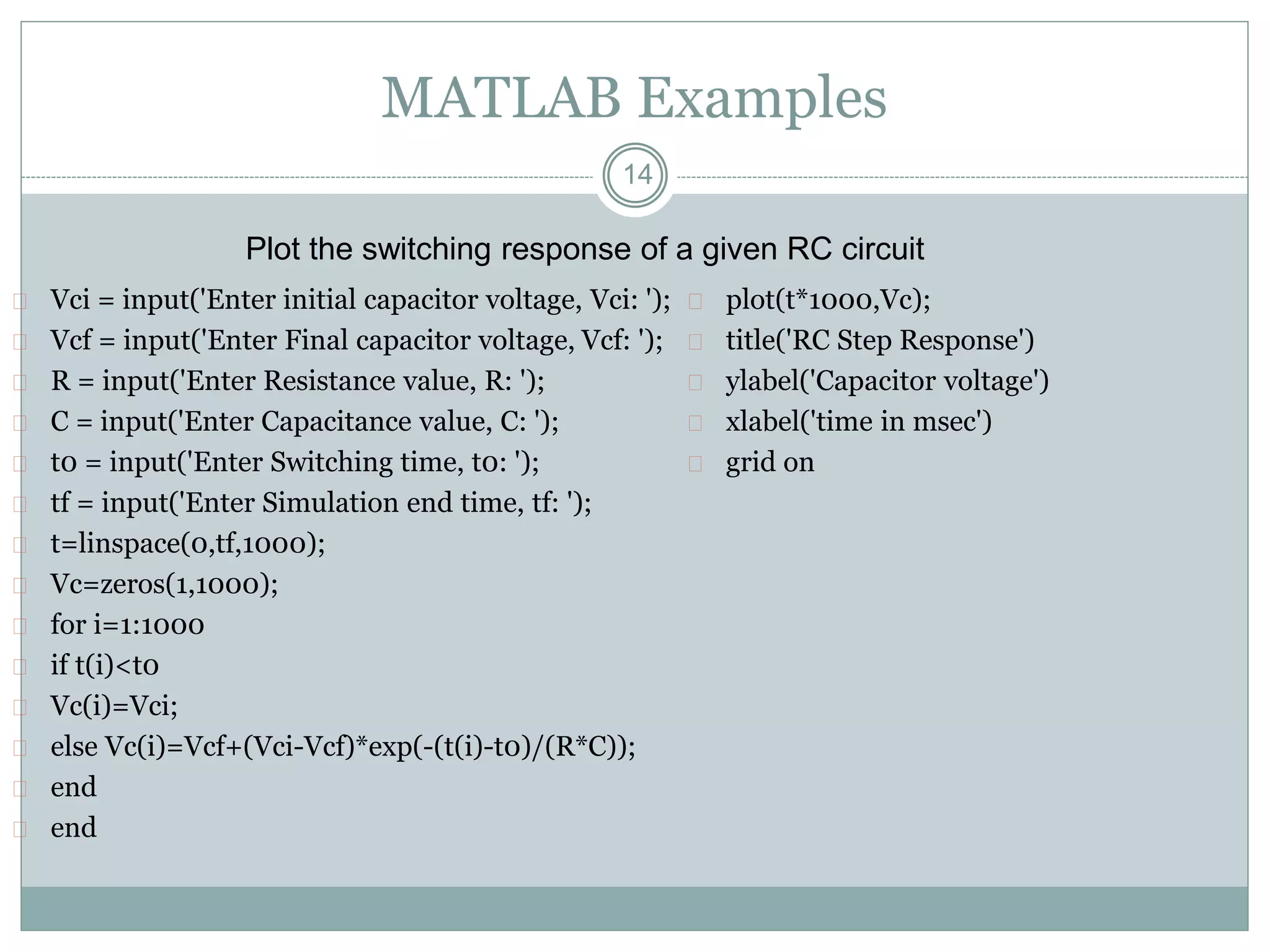
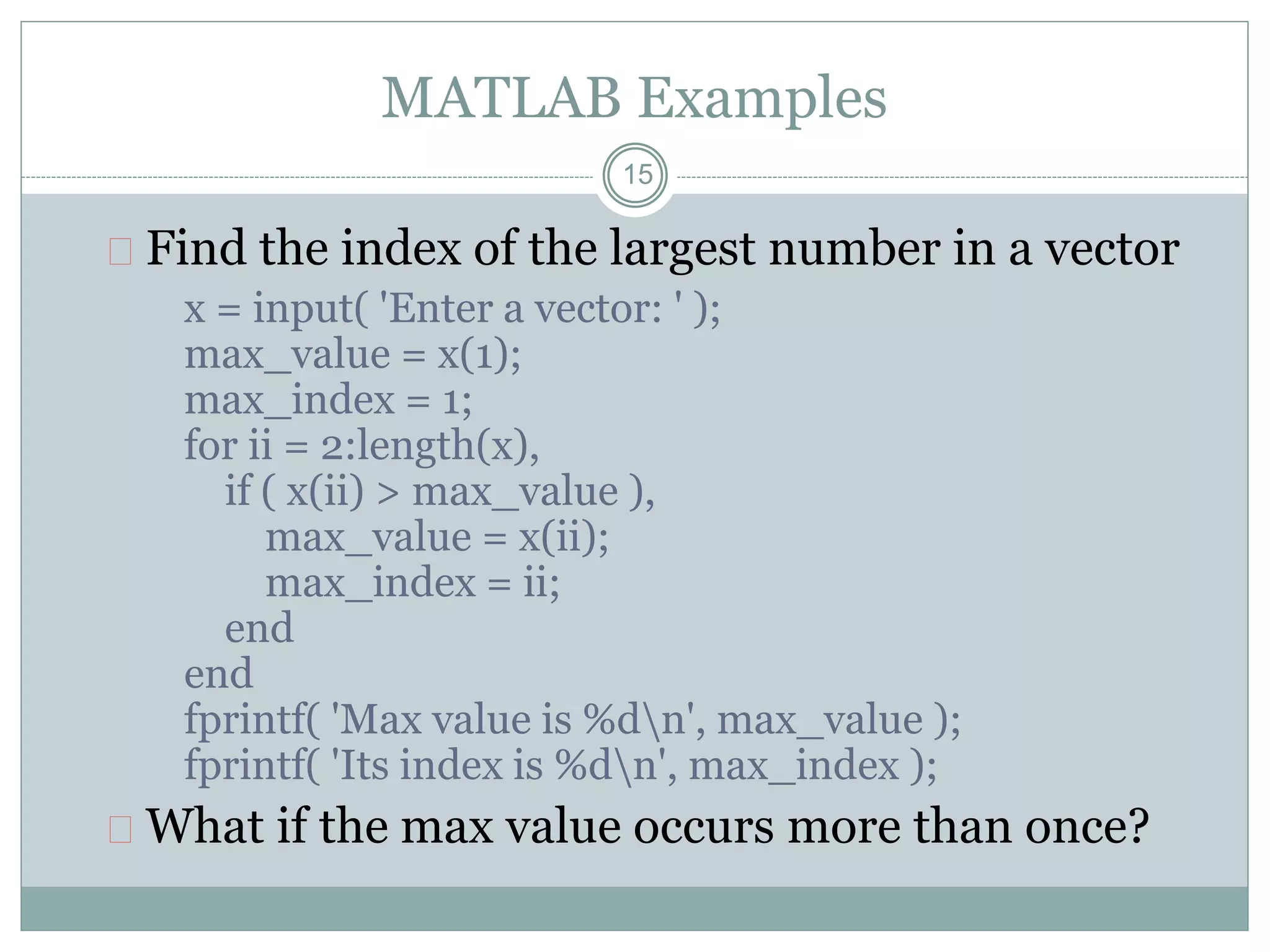
The document discusses MATLAB files and functions. It describes that:
1) Functions and scripts are stored in .m files. The MATLAB workspace can be saved in .mat files for easy loading and efficient access. Plots can be saved in .fig files.
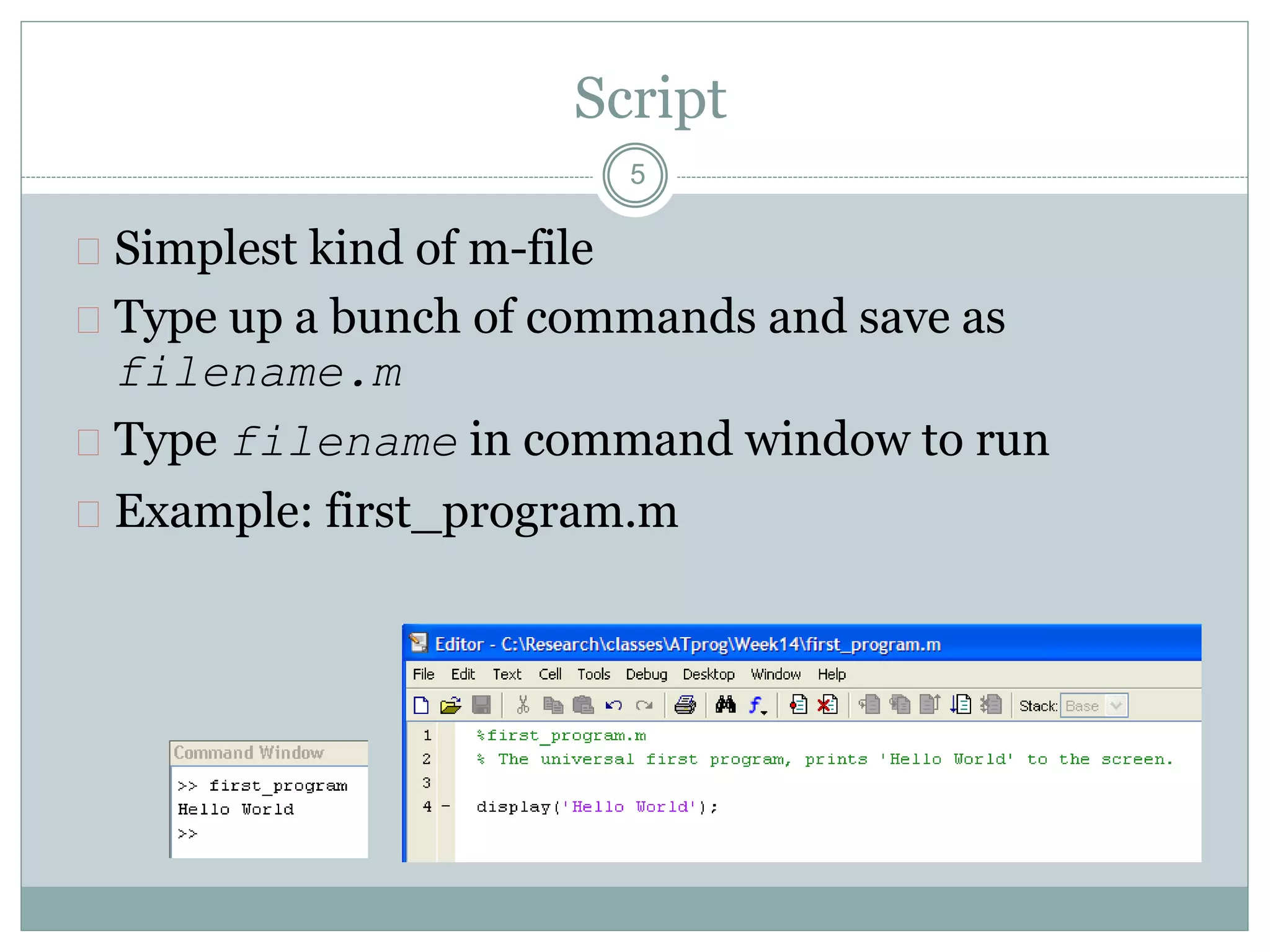
2) Scripts contain commands that run when the file is run. Functions have their own variables, accept inputs, and return outputs.
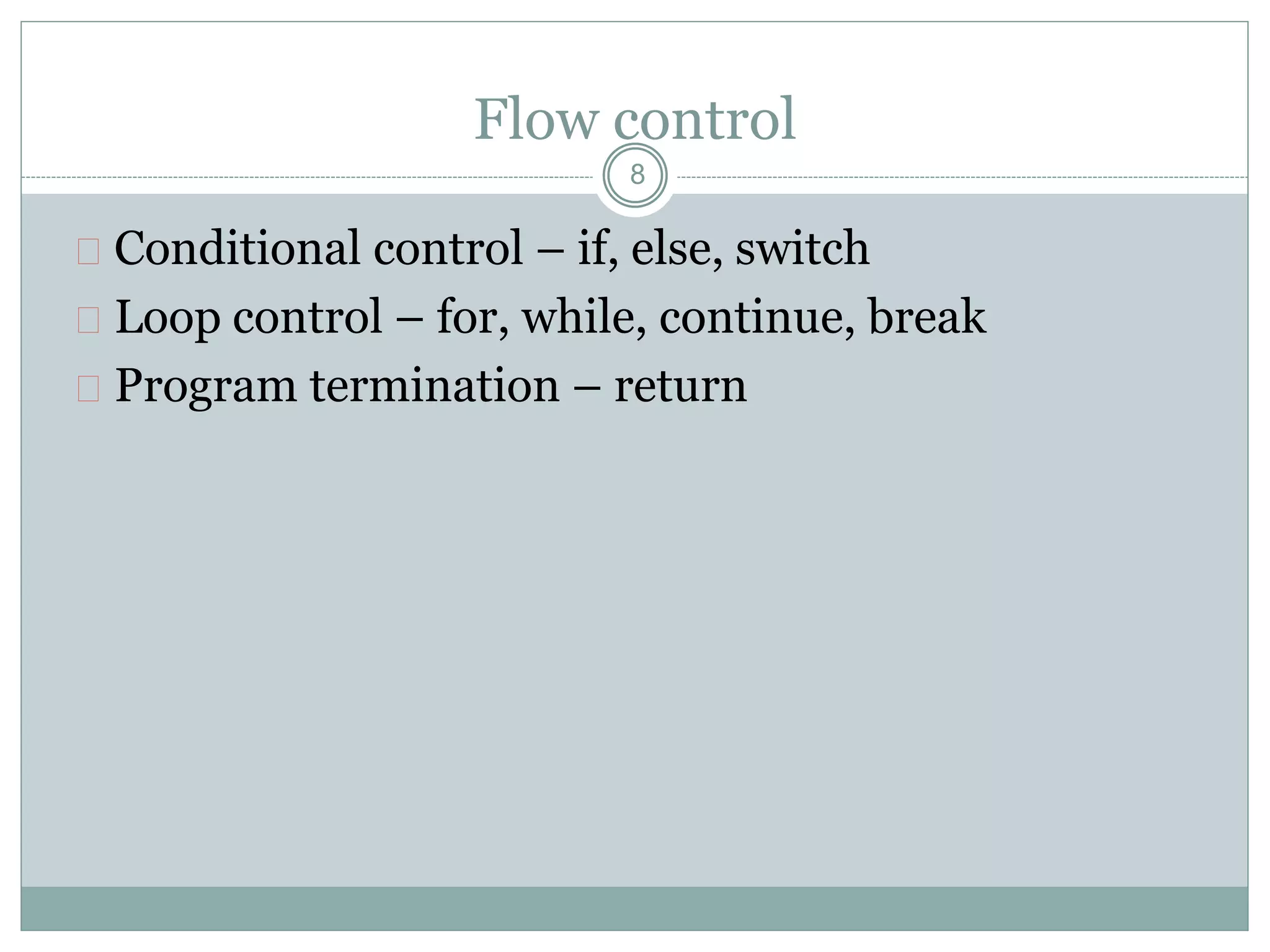
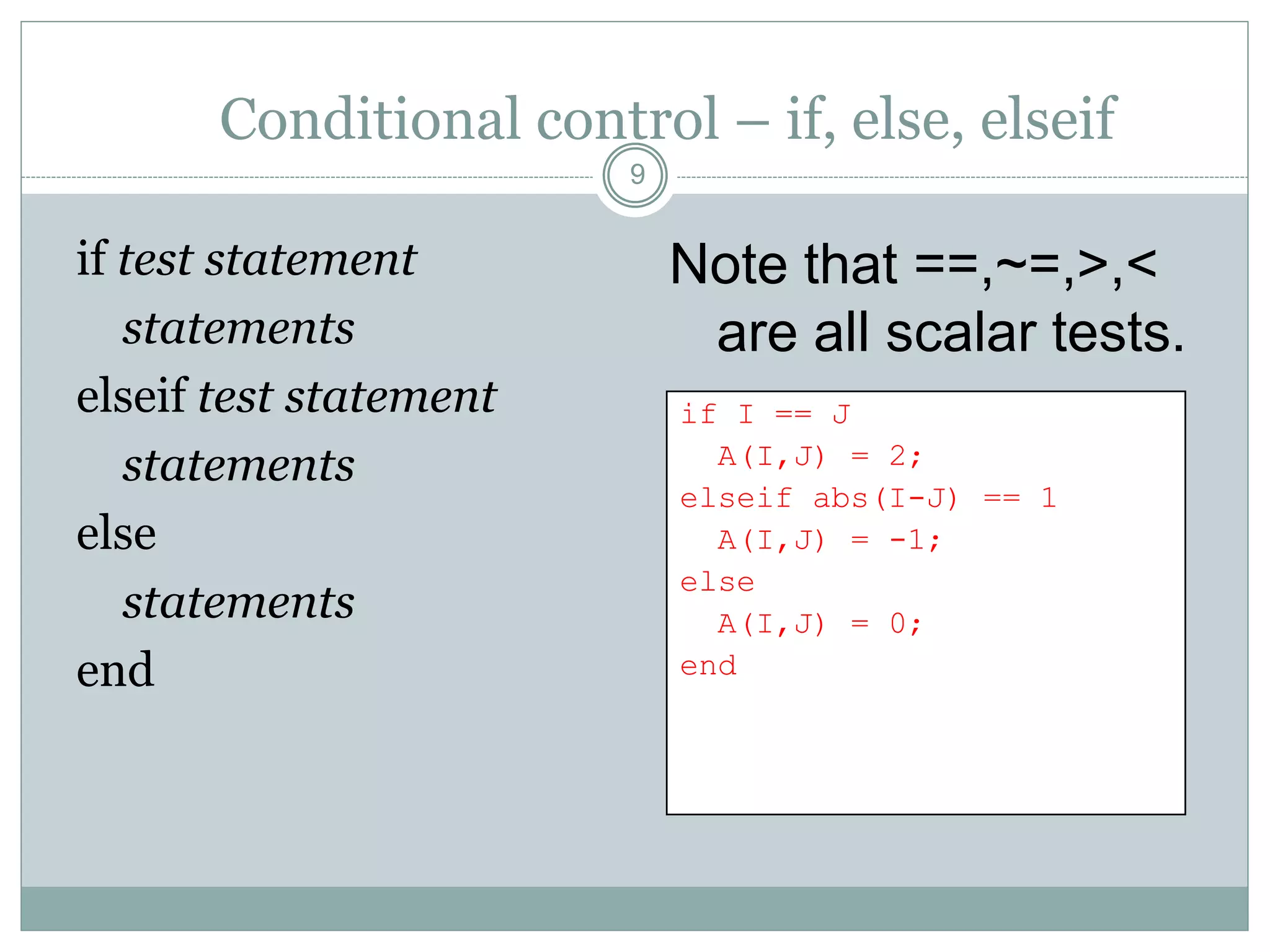
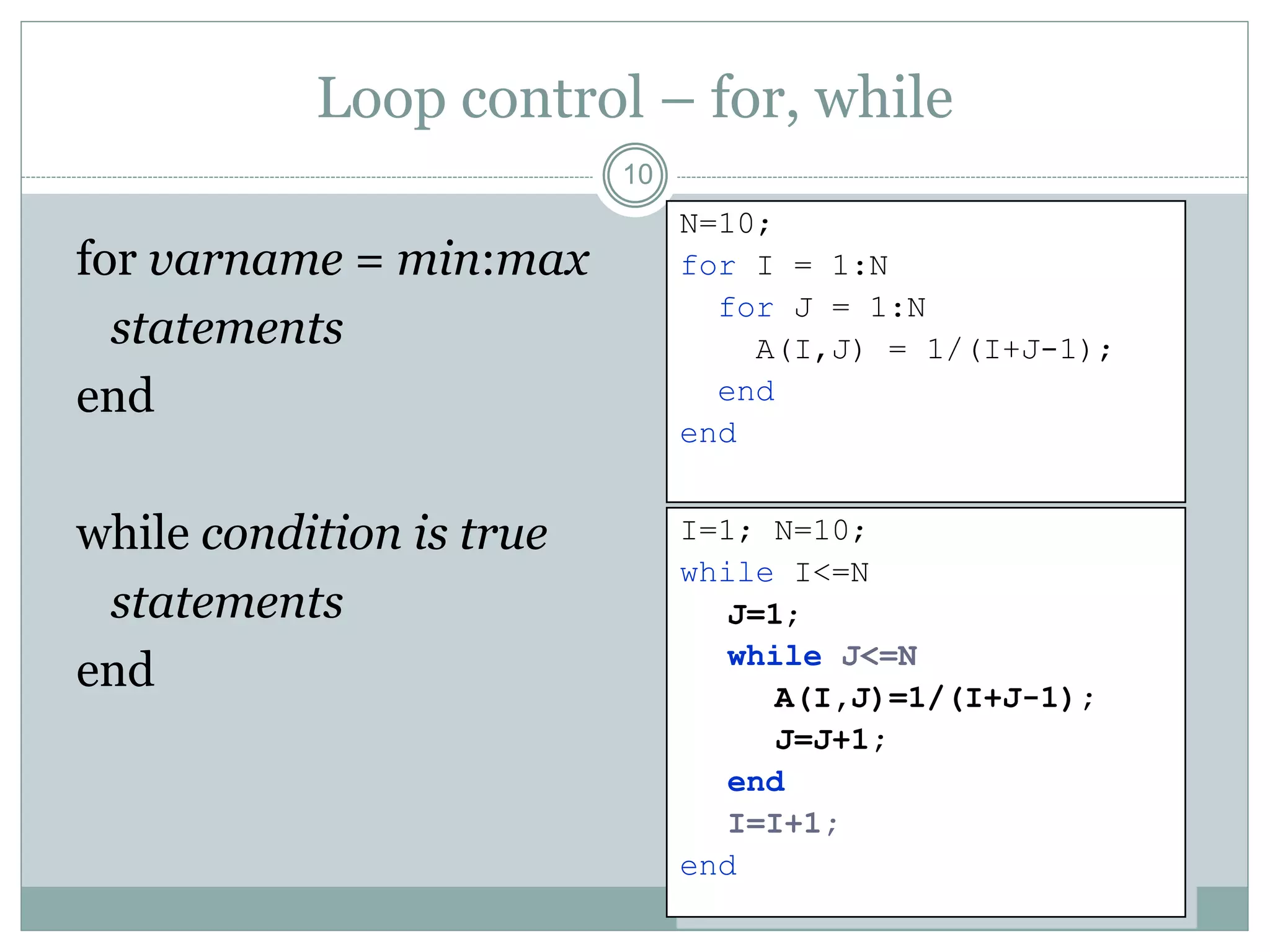
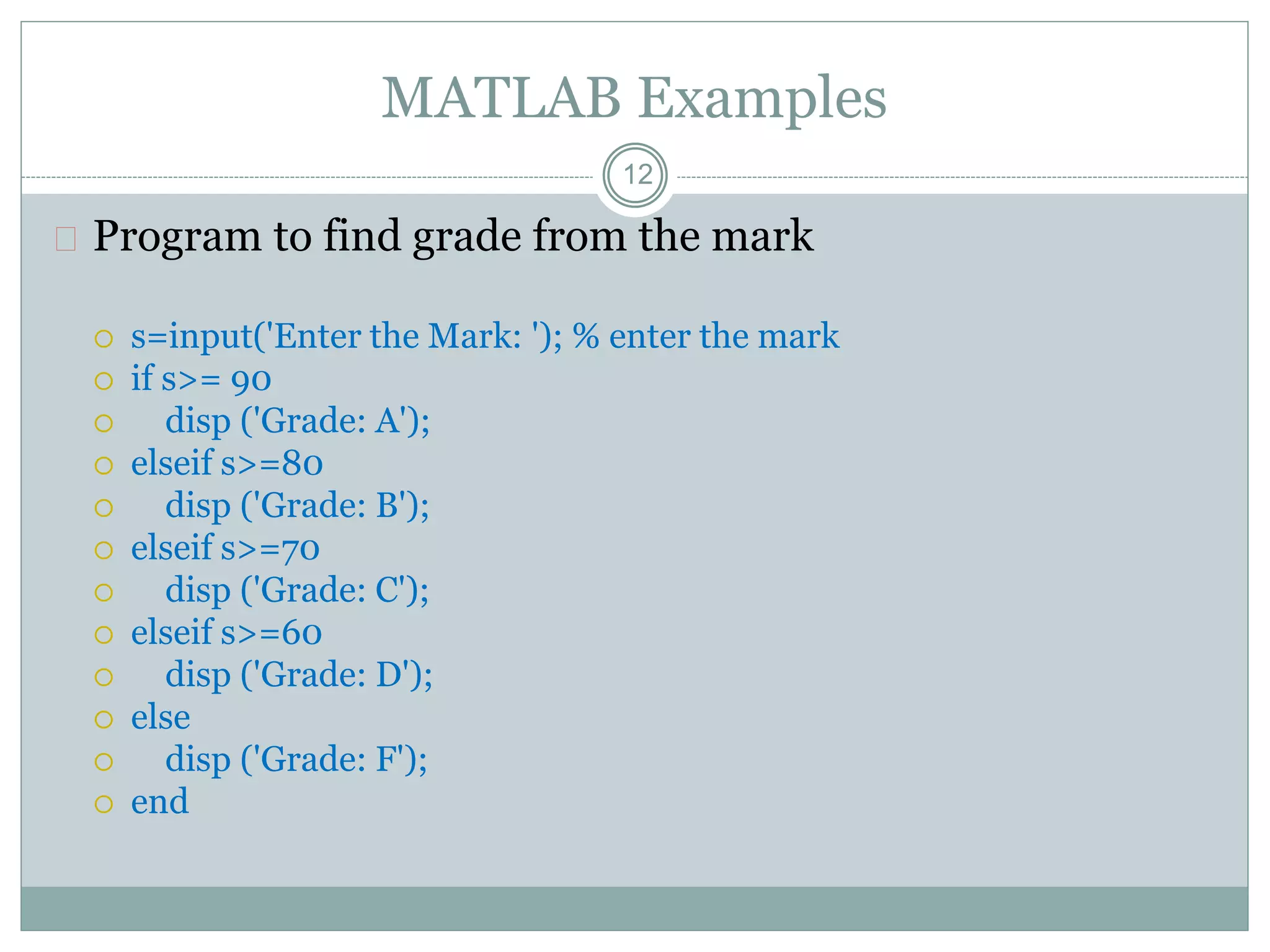
3) Comments start with % and help document code. Control flow includes conditional (if/else) and loop (for/while) statements. Functions terminate with return.