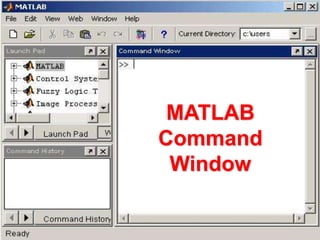
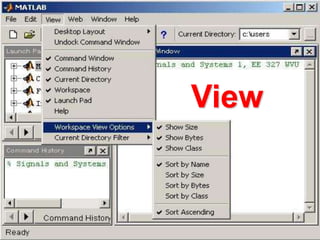
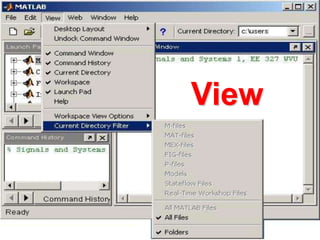
This document provides an introduction and overview of MATLAB. It discusses what MATLAB is, the basic MATLAB interface and environment, variables and data types, basic math and logical operations, built-in functions, and some examples of basic MATLAB operations. MATLAB stands for Matrix Laboratory and is designed for matrix operations. It allows technical computing problems to be solved quickly using matrices and vectors. The MATLAB environment is command-based and results are displayed in the command window. Help is accessible through the help menu or typing help commands.










![38
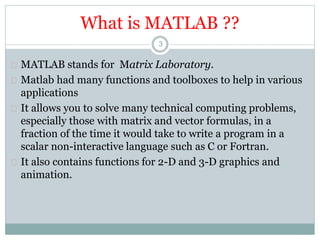
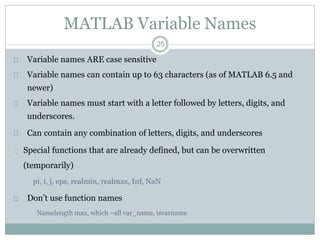
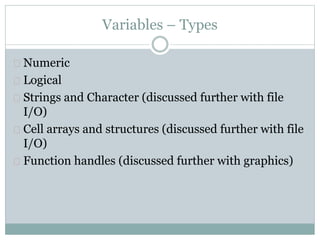
Numbers and variables and similar in
Matlab
2.4e-12 is 2.4*10-12
pi is the variable with defined name.
i or j is complex unit (it can be overwritten).
For trigonometric functions [rad] is used.
clear all, clears all defined variables.
close all, closes all graphical windows.
clear all, close all, very usefull combination!
clc, clears the screen, but nothing else.
CRTL+C stop the execution of the program in Matlab.
dir, current directory.
who, list of all defined variables.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabintroduction-141220042711-conversion-gate02/85/Matlab-introduction-38-320.jpg)
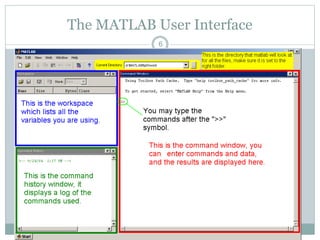
![Basic Matlab Operations
>> % This is a comment, it starts with a “%”
>> y = 5*3 + 2^2; % simple arithmetic
>> x = [1 2 4 5 6]; % create the vector “x”
>> x1 = x.^2; % square each element in x
>> E = sum(abs(x).^2); % Calculate signal energy
>> P = E/length(x); % Calculate av signal power
>> x2 = x(1:3); % Select first 3 elements in x
>> z = 1+i; % Create a complex number
>> a = real(z); % Pick off real part
>> b = imag(z); % Pick off imaginary part](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabintroduction-141220042711-conversion-gate02/85/Matlab-introduction-39-320.jpg)