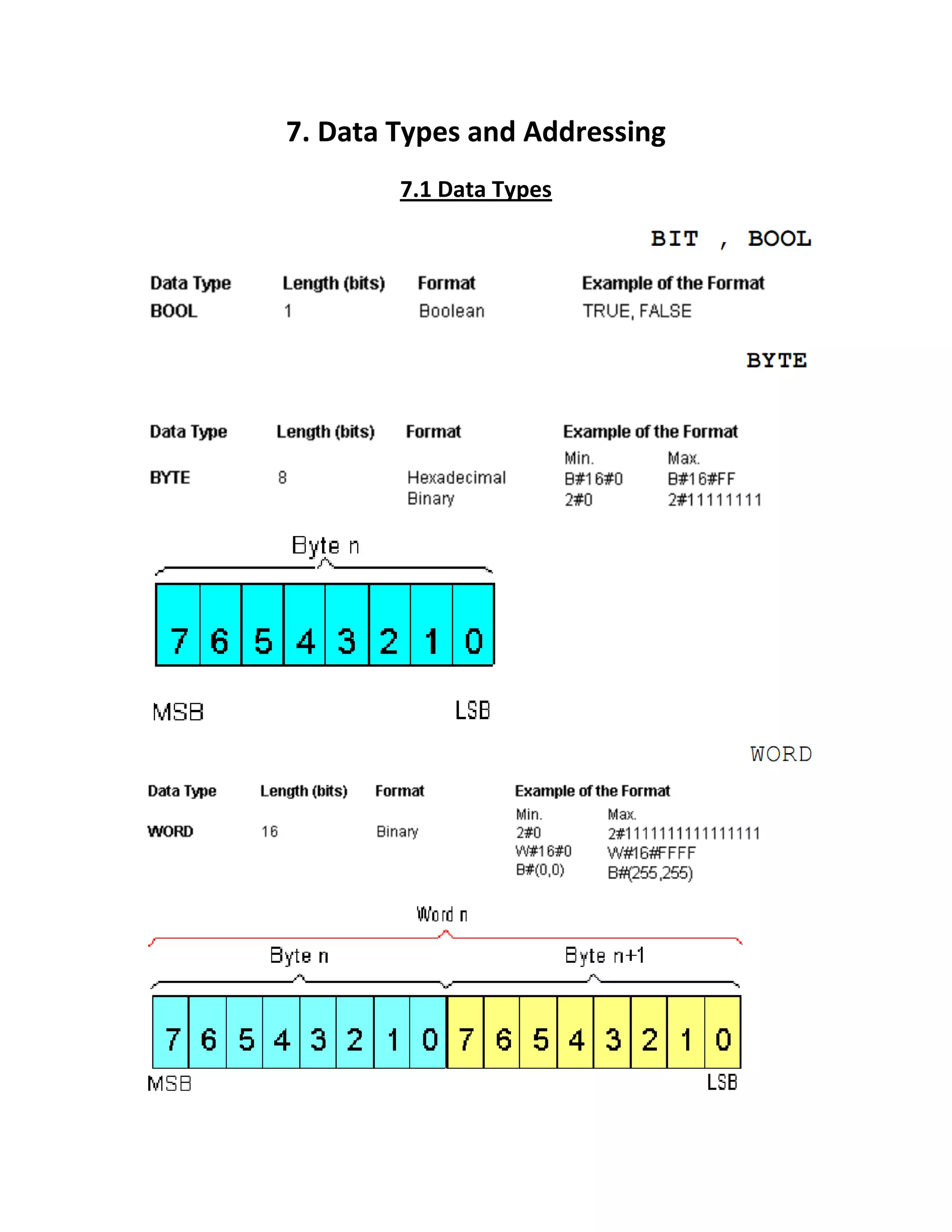
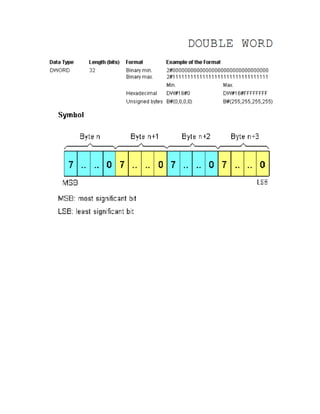
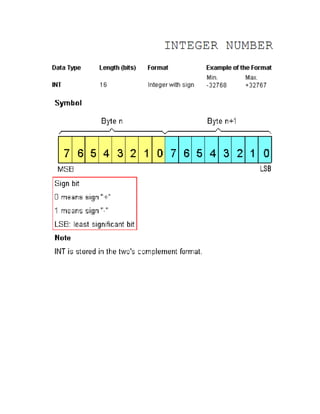
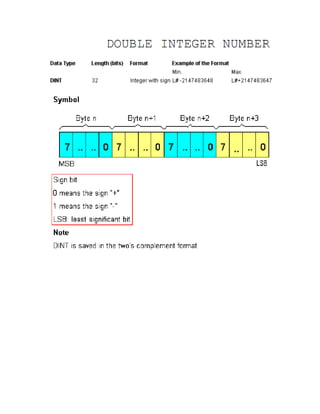
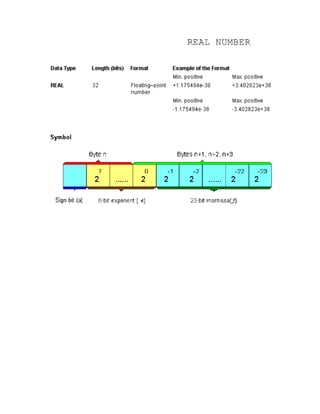
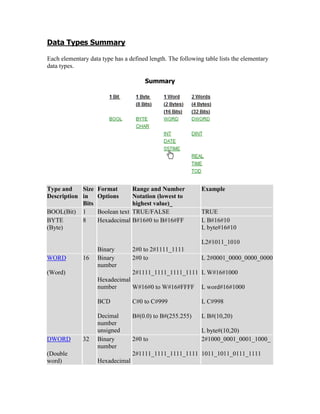
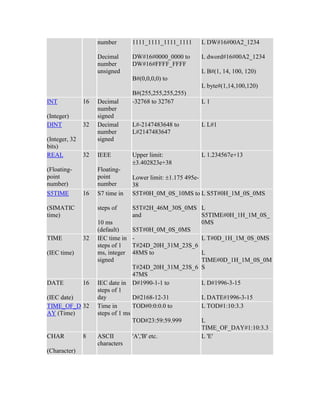
The document details various elementary data types including their sizes, formats, and ranges, such as boolean, byte, word, dword, integer, and real numbers. It also outlines the addressing method for storage areas like inputs, outputs, timers, counters, and memory, specifying how to reference them by byte and bit addresses. Examples illustrate how these types and addresses are applied in practical contexts.