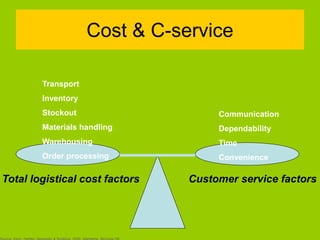
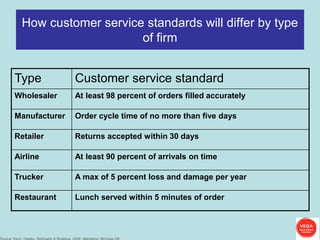
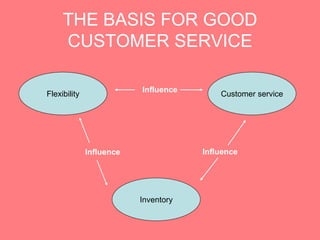
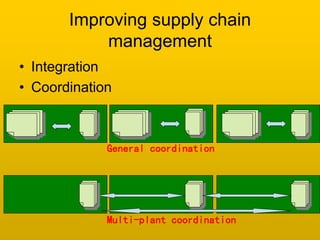
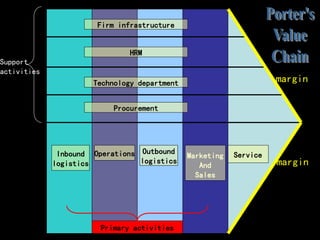
The document discusses objectives and principles of logistics and supply chain management. The key objectives are to minimize costs while maximizing customer service. Principles discussed include increasing communication along the supply chain to ensure smooth flow, controlling costs through inventory reduction while maintaining service levels, and standardizing parts. Metrics and data collection on factors like quality, delivery, flexibility, and cost are important for benchmarking performance. Customer service standards will differ depending on the type of firm.