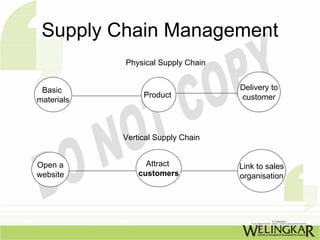
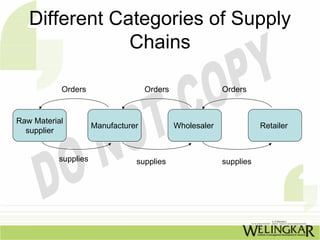
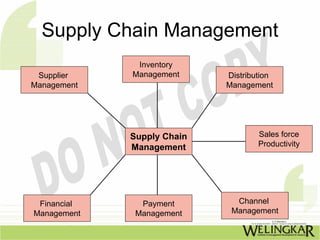
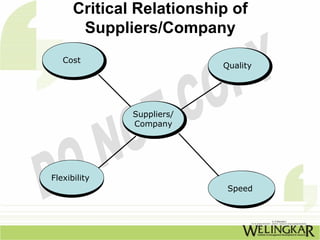
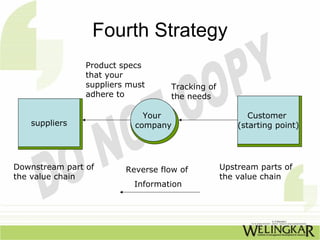
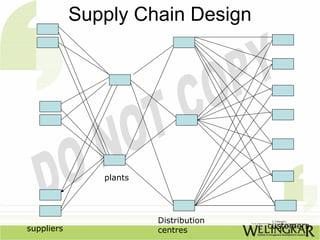
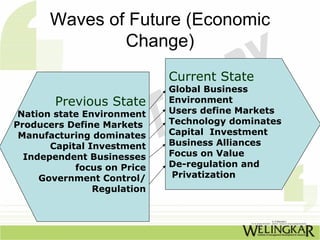
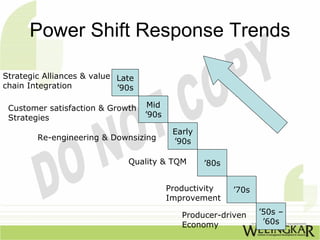
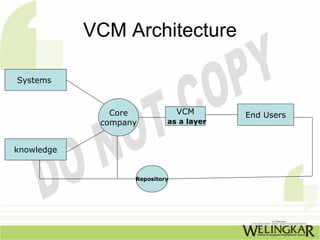
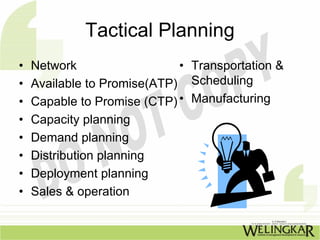
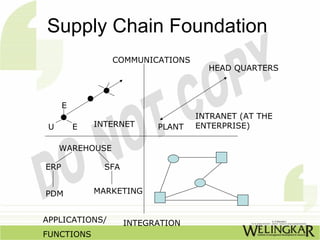
The document discusses supply chain management (SCM) and its essential components, benefits, and goals, emphasizing cost reduction, improved customer relationships, and competitive advantage. It outlines characteristics of SCM, such as global sourcing, real-time information processing, and integration of processes, as well as challenges such as data disparities and proprietary standards. The text also highlights various tools and strategies for effective supply chain planning and communication.