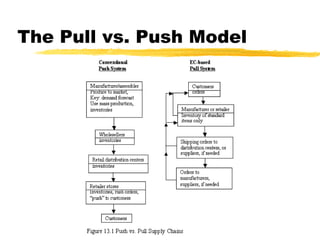
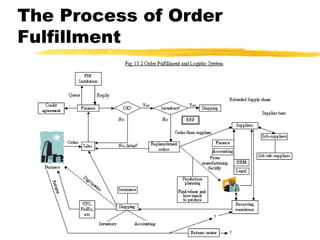
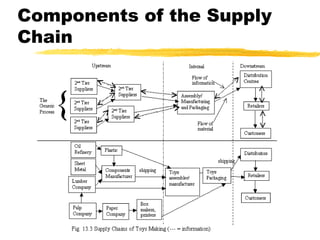
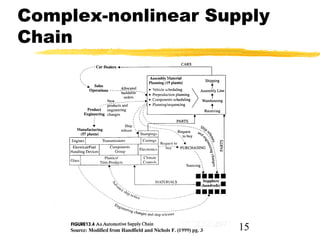
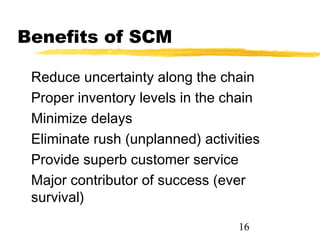
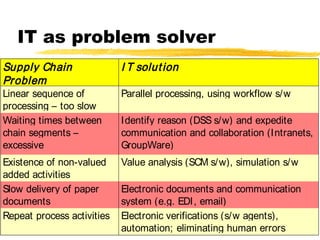
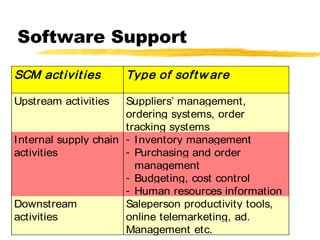
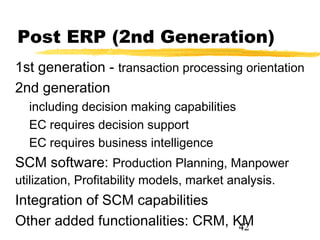
This chapter discusses order fulfillment, logistics, and supply chain management. It describes the process of order fulfillment and the major concepts of front office operations, back office operations, logistics, and the supply chain. The chapter outlines the steps in order fulfillment and discusses challenges like meeting demand, customized products, and the pull vs push models. It emphasizes the importance of integration along the supply chain.