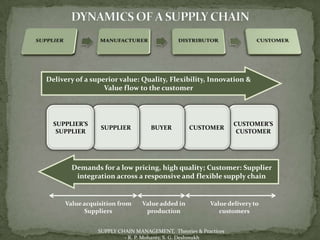
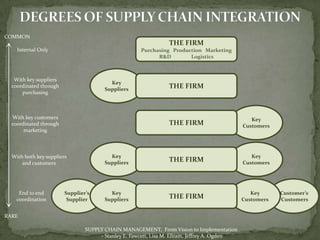
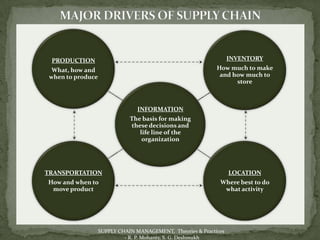
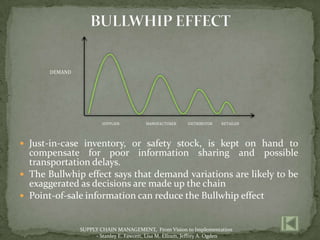
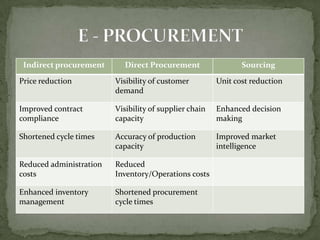
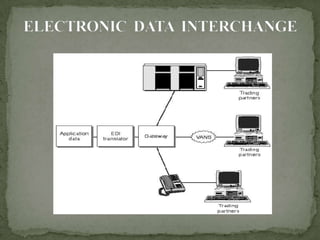
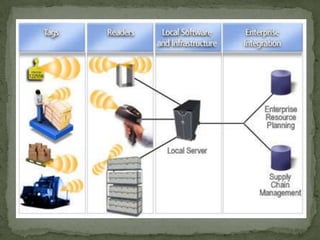
The document discusses the application of information technology in supply chain management. It covers topics such as the definition and dynamics of supply chain management, its components and degrees, the need for SCM, and the bullwhip effect. It also discusses how various IT tools can help address issues like quality, cost, time, technology and continuity of supply. Specific technologies covered include barcoding, RFID, e-commerce and EDI. The use of these technologies can help improve operational efficiency, reduce errors and cut costs in supply chain management.