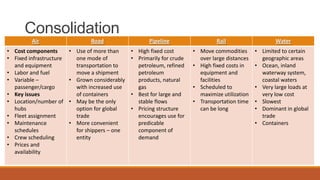
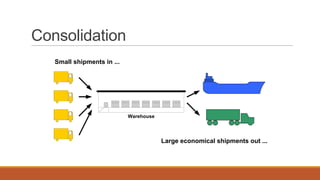
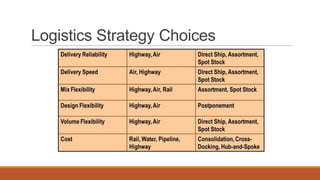
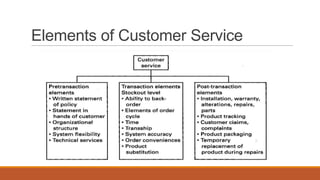
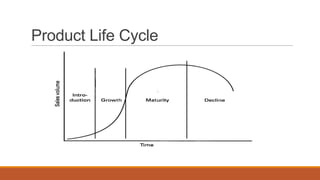
The document discusses key topics in logistics strategy and planning, including reasons for increased interest in logistics such as deregulation and globalization. It covers major logistics decision areas like transportation modes and warehousing approaches. Transportation modes discussed include road, water, rail, air and pipeline. The document also addresses consolidation, customer service, logistics products, pricing logistics, and risks associated with products.