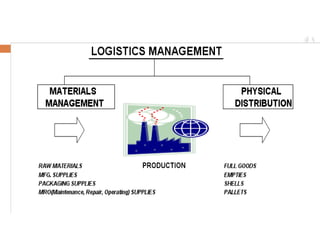
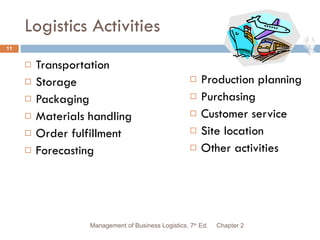
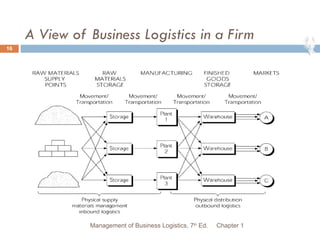
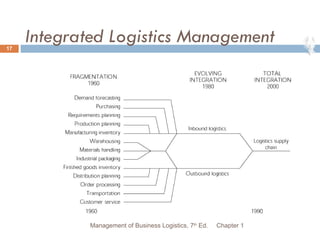
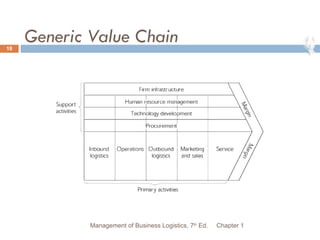
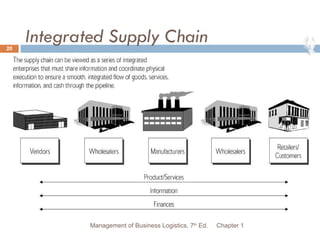
The document provides an overview of supply chain and logistics concepts for students. It defines key terms like supply chain management, logistics management, and physical distribution. It also outlines the typical flow of activities in a company's supply chain, from sales forecasting to order fulfillment. The goal is for students to understand the roles and importance of effective logistics and supply chain management.