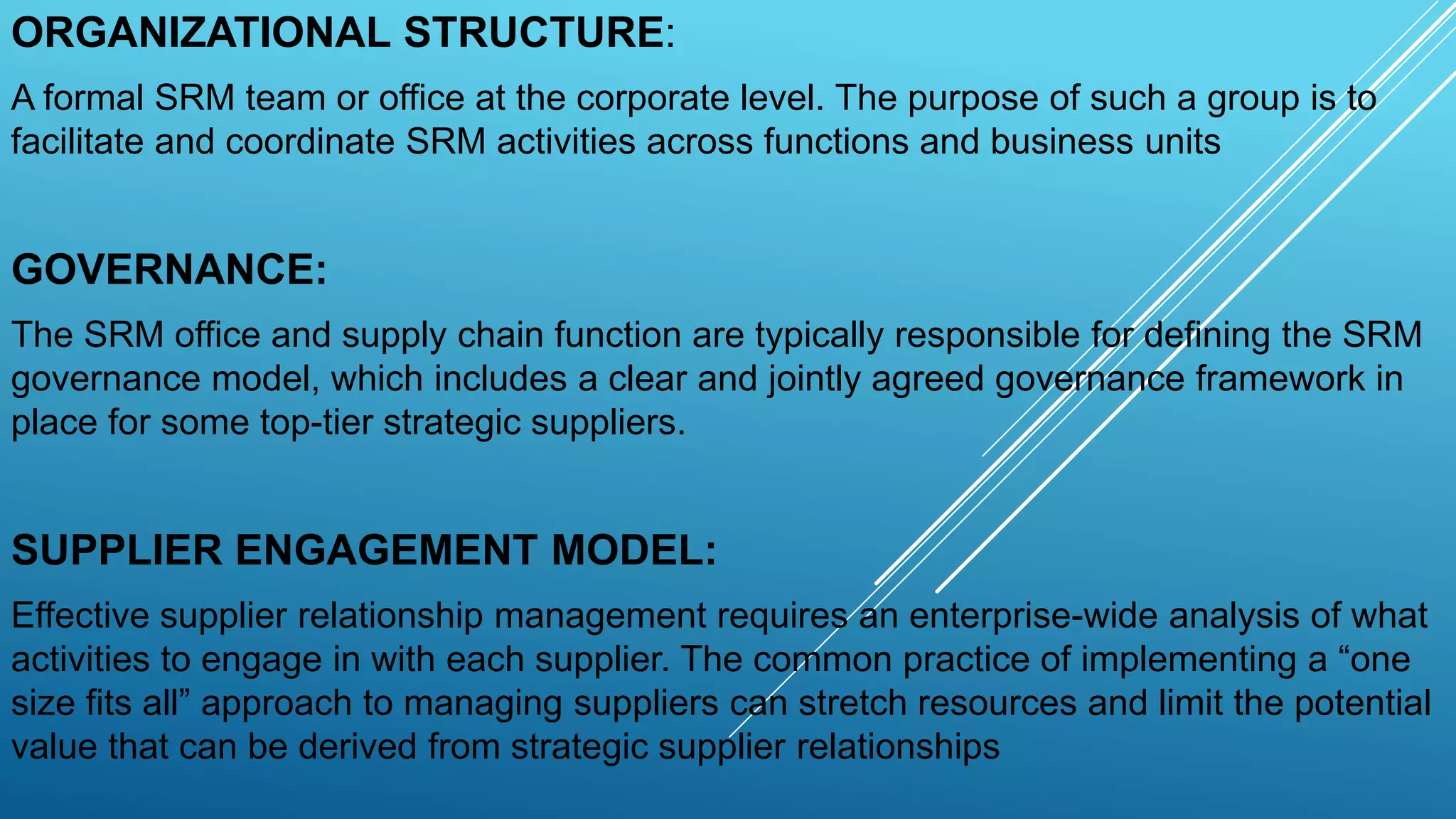
This document discusses supplier relationship management (SRM). SRM involves strategically managing interactions with third-party suppliers to maximize value. There are five key components of SRM: organizational structure, governance, supplier engagement model, value measurement, and technology and systems. Effective SRM requires establishing a formal SRM team, governance framework, tailored supplier engagement approaches, metrics to measure added value, and technology to track supplier performance data.