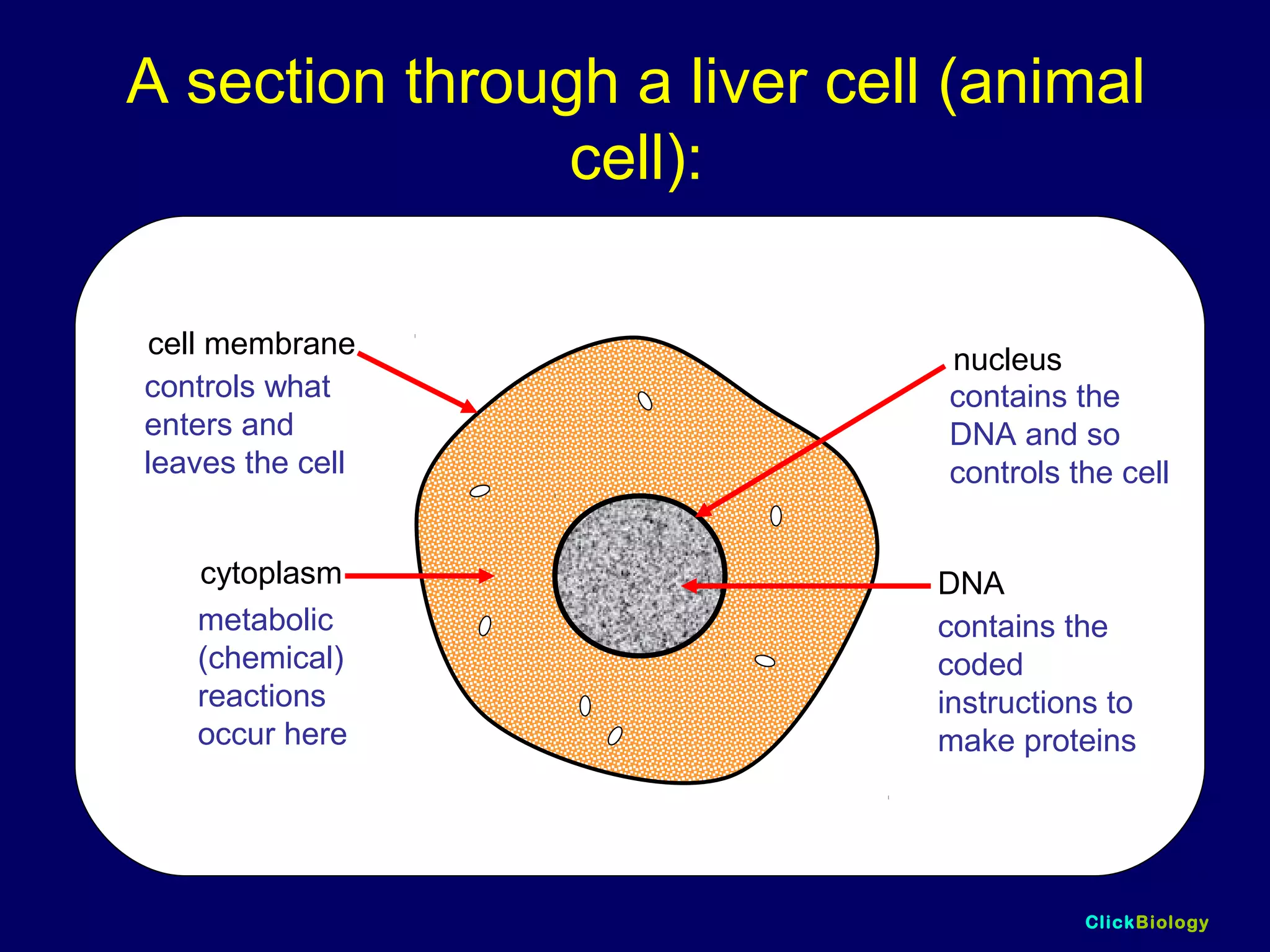
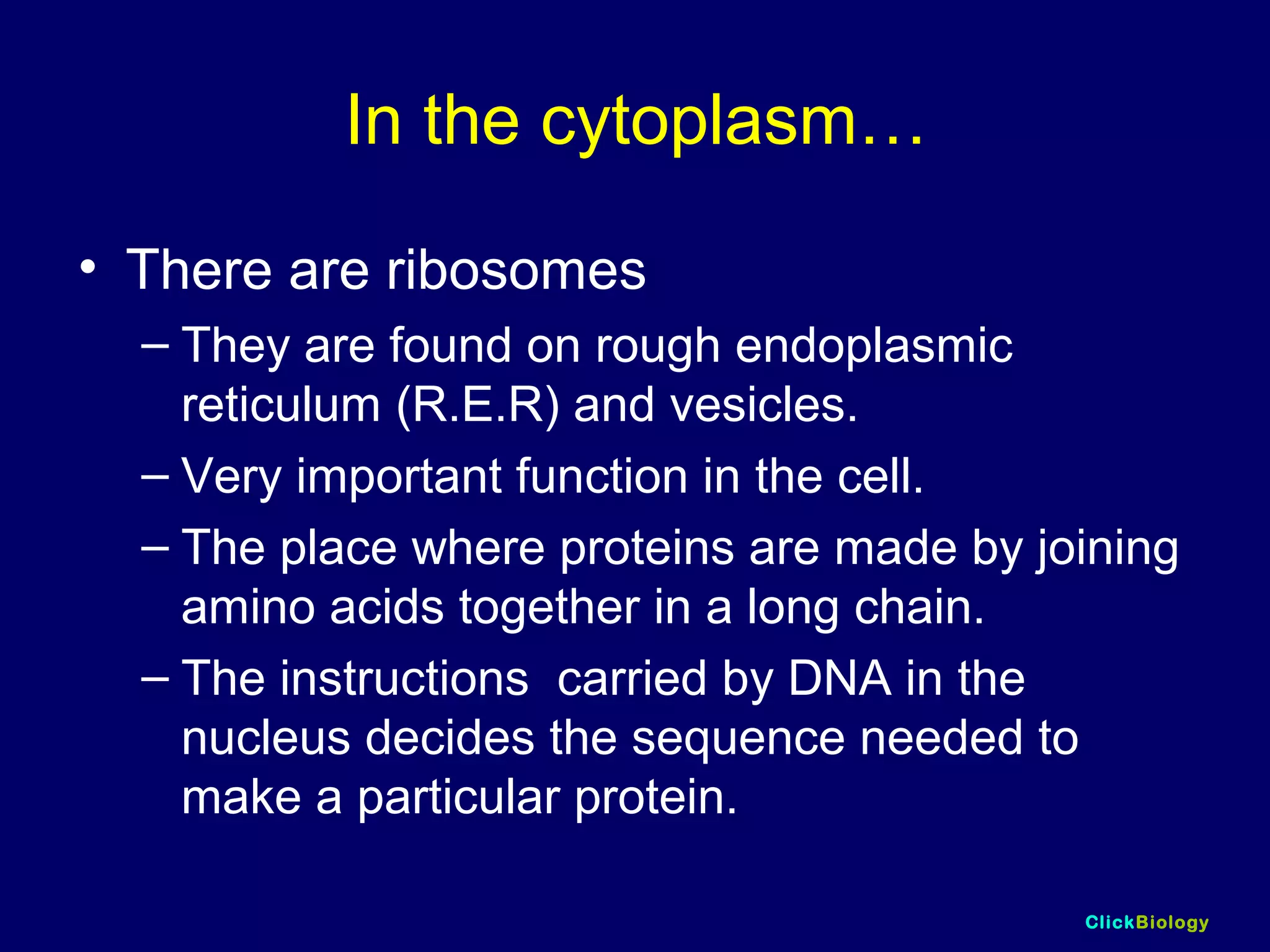
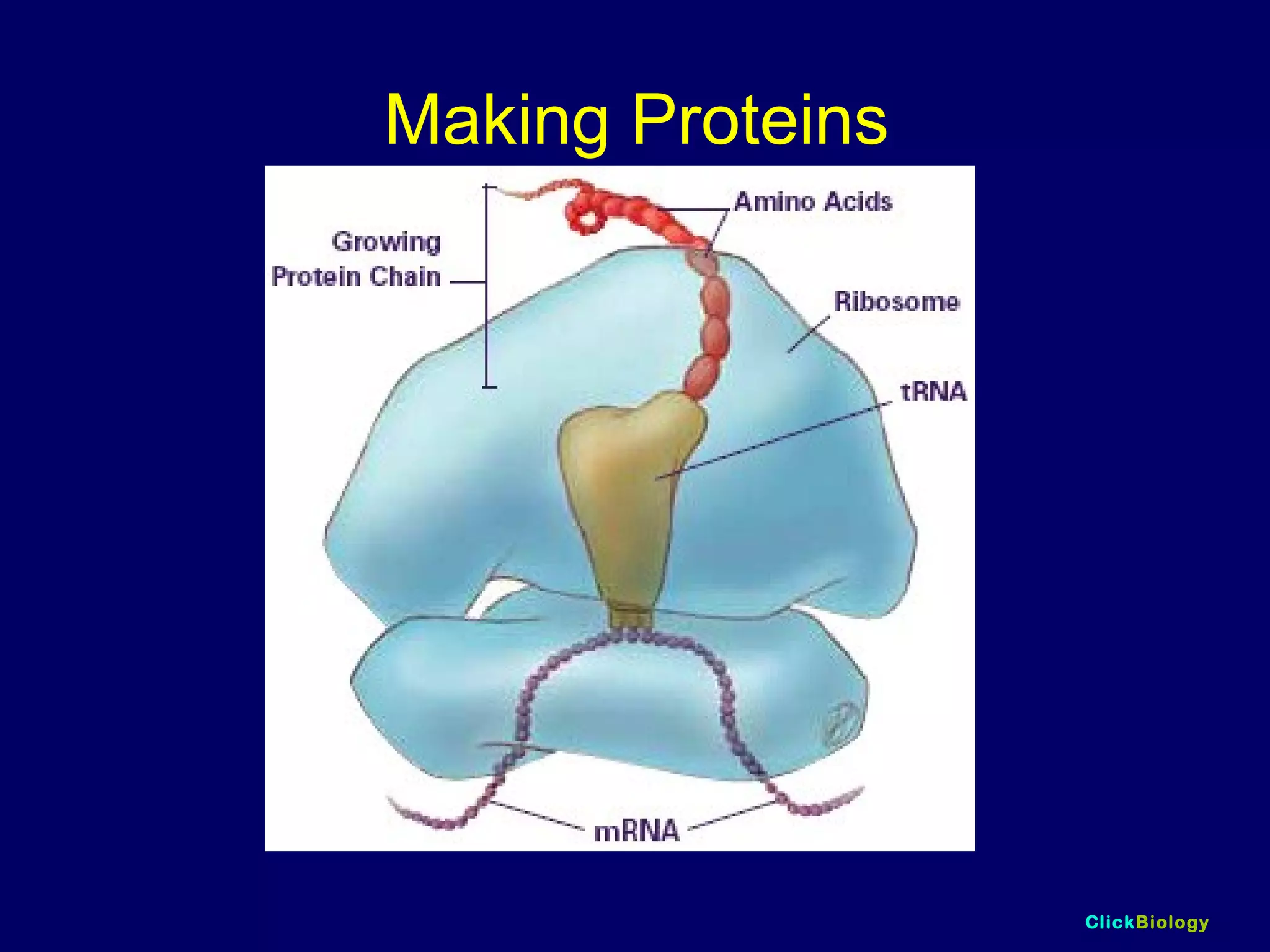
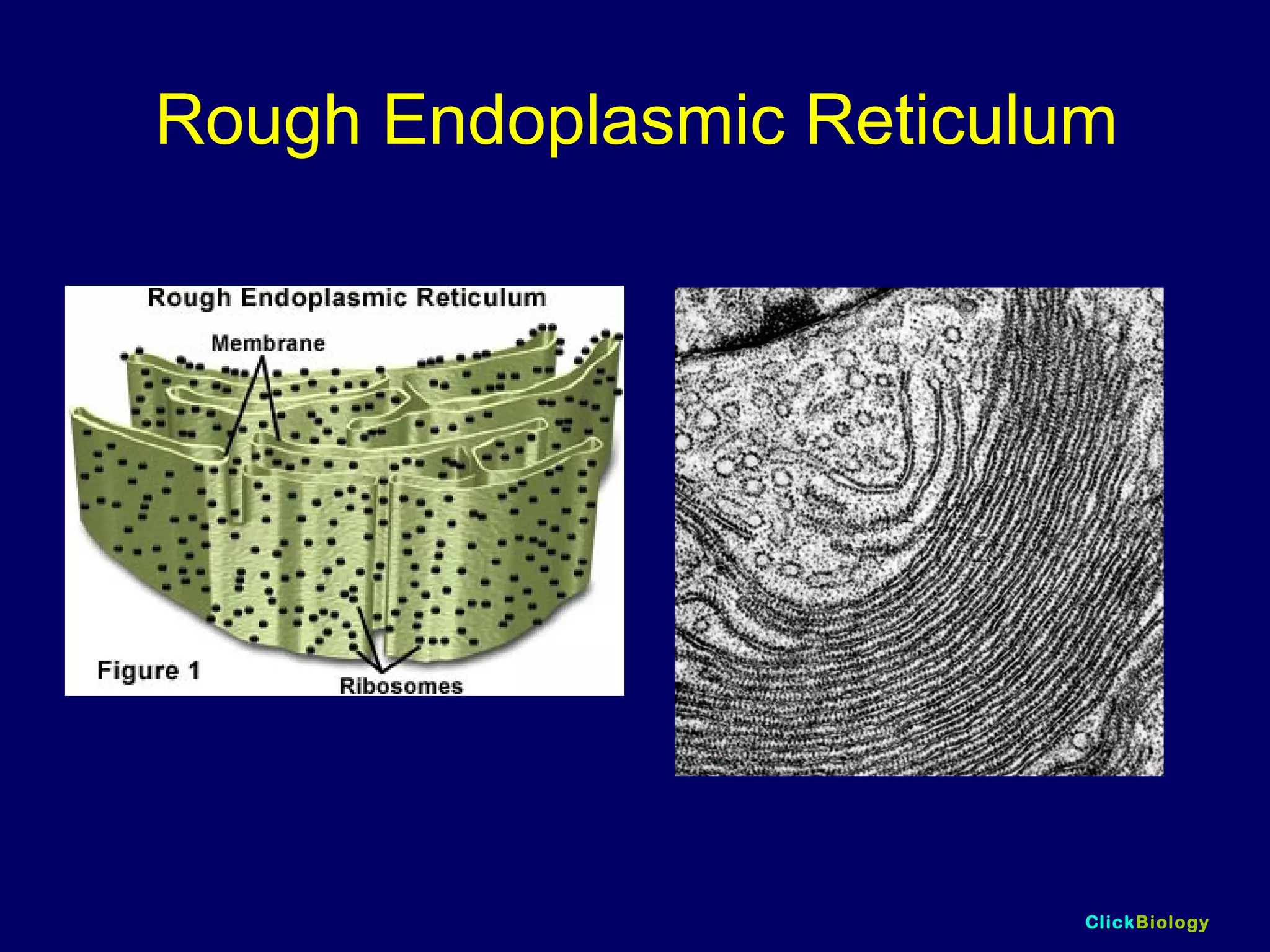
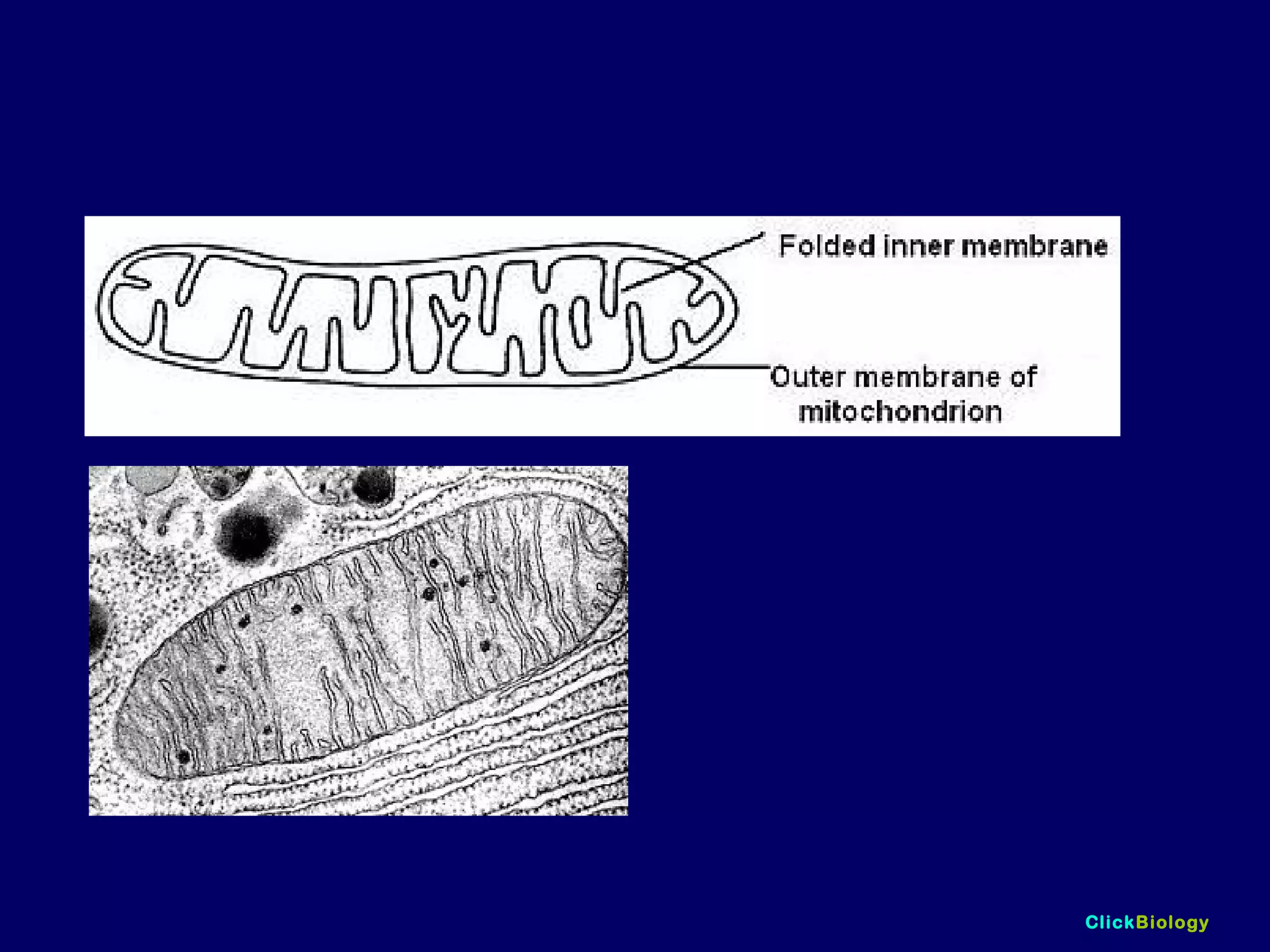
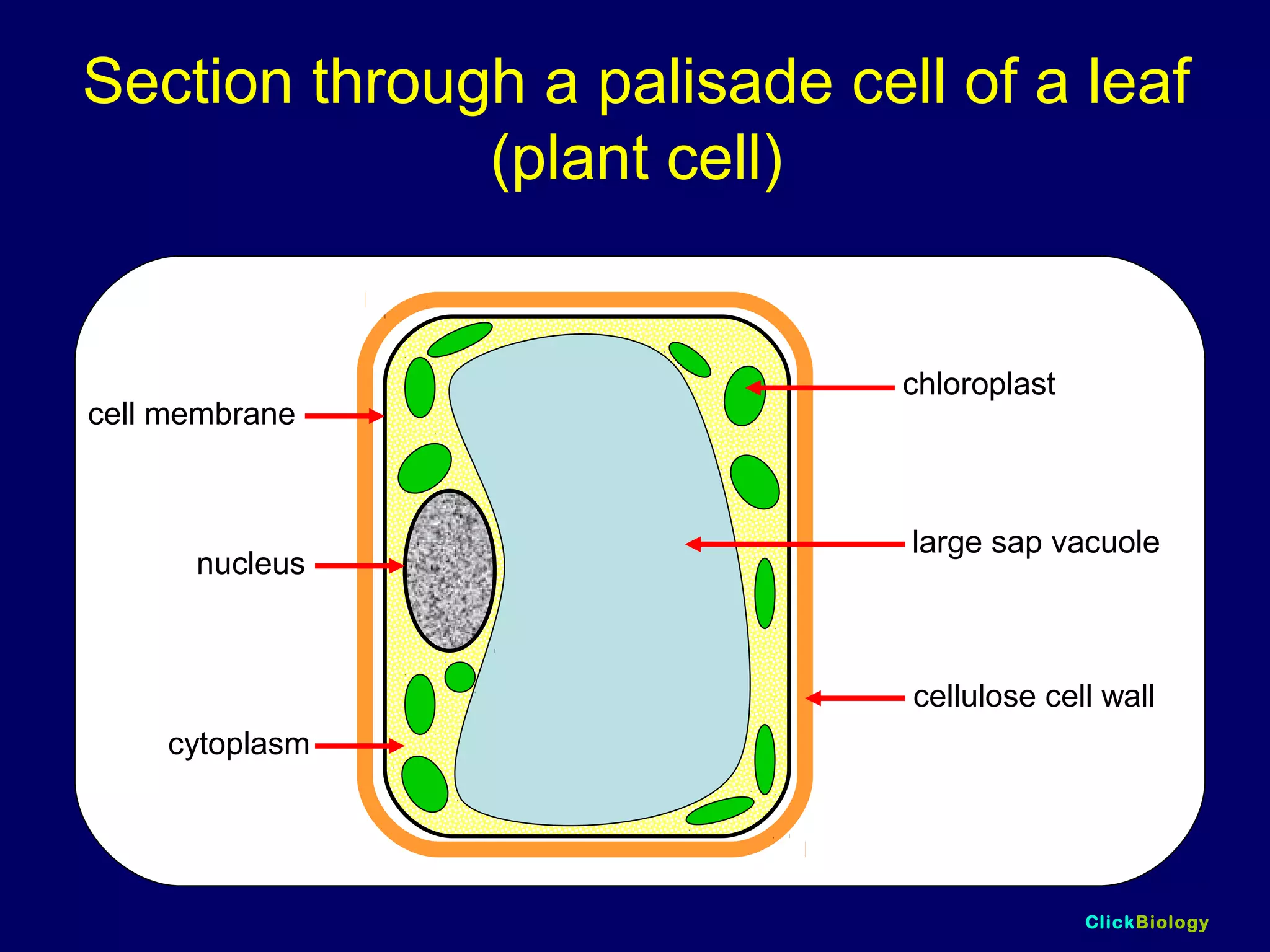
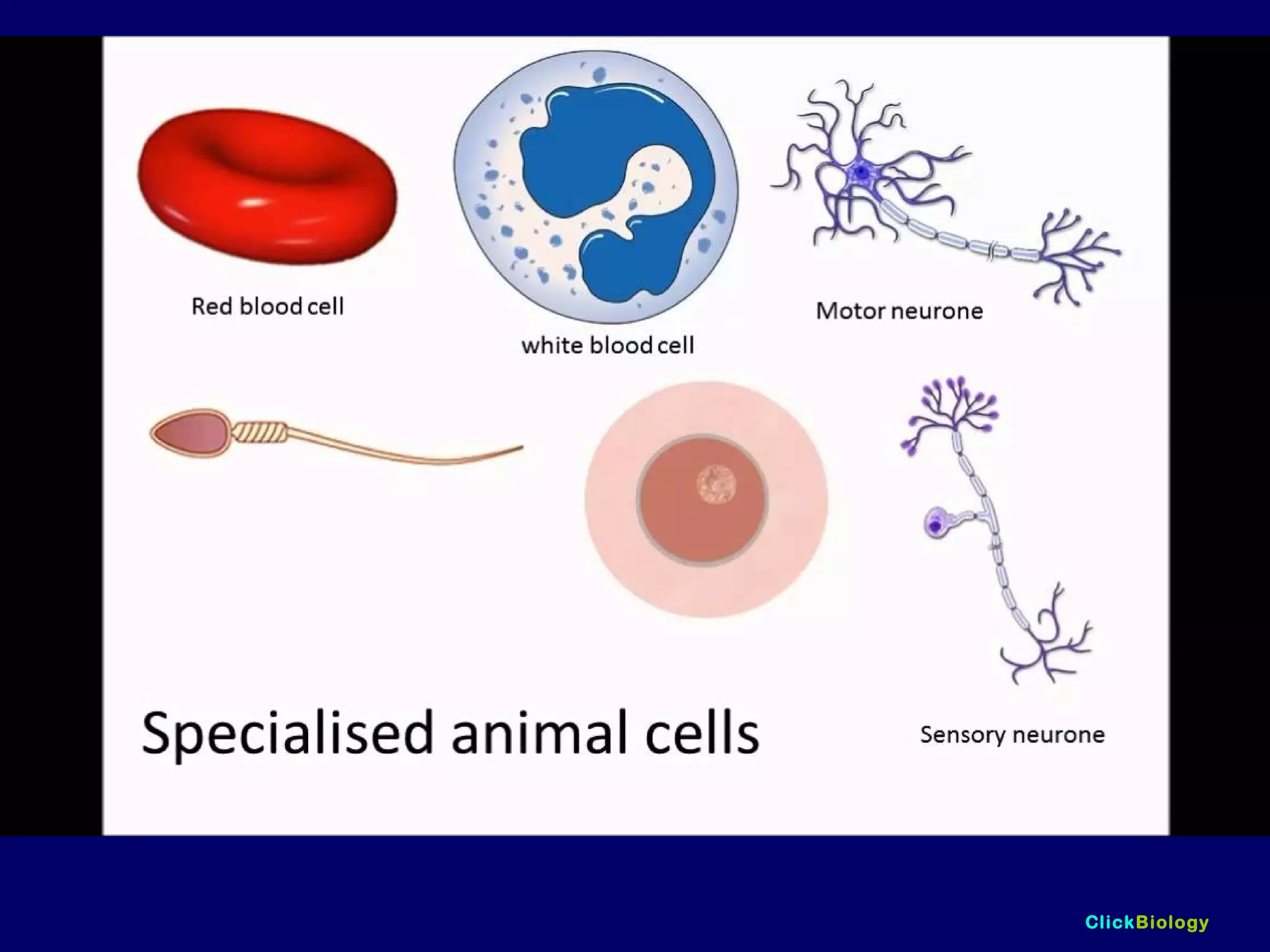
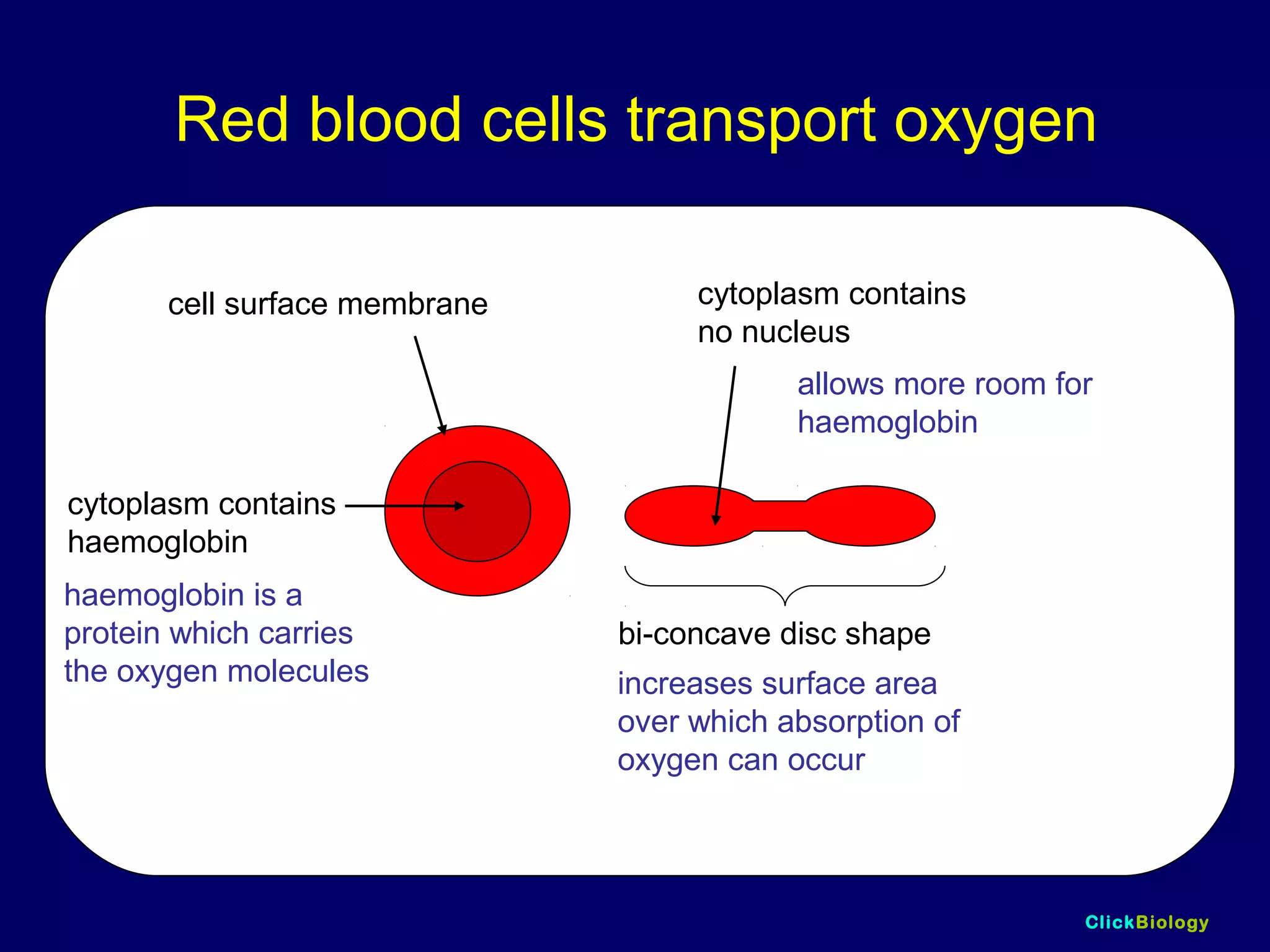
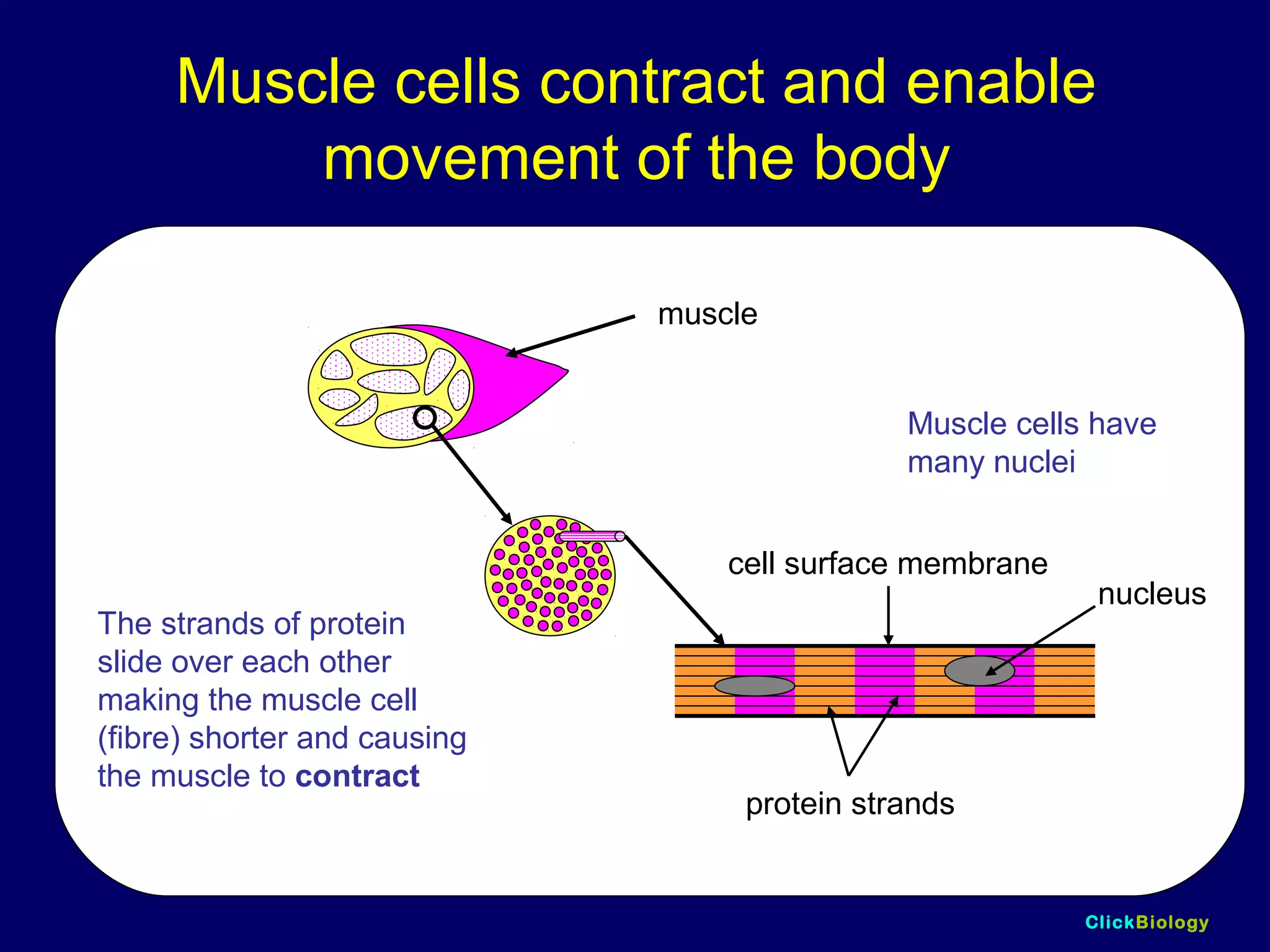
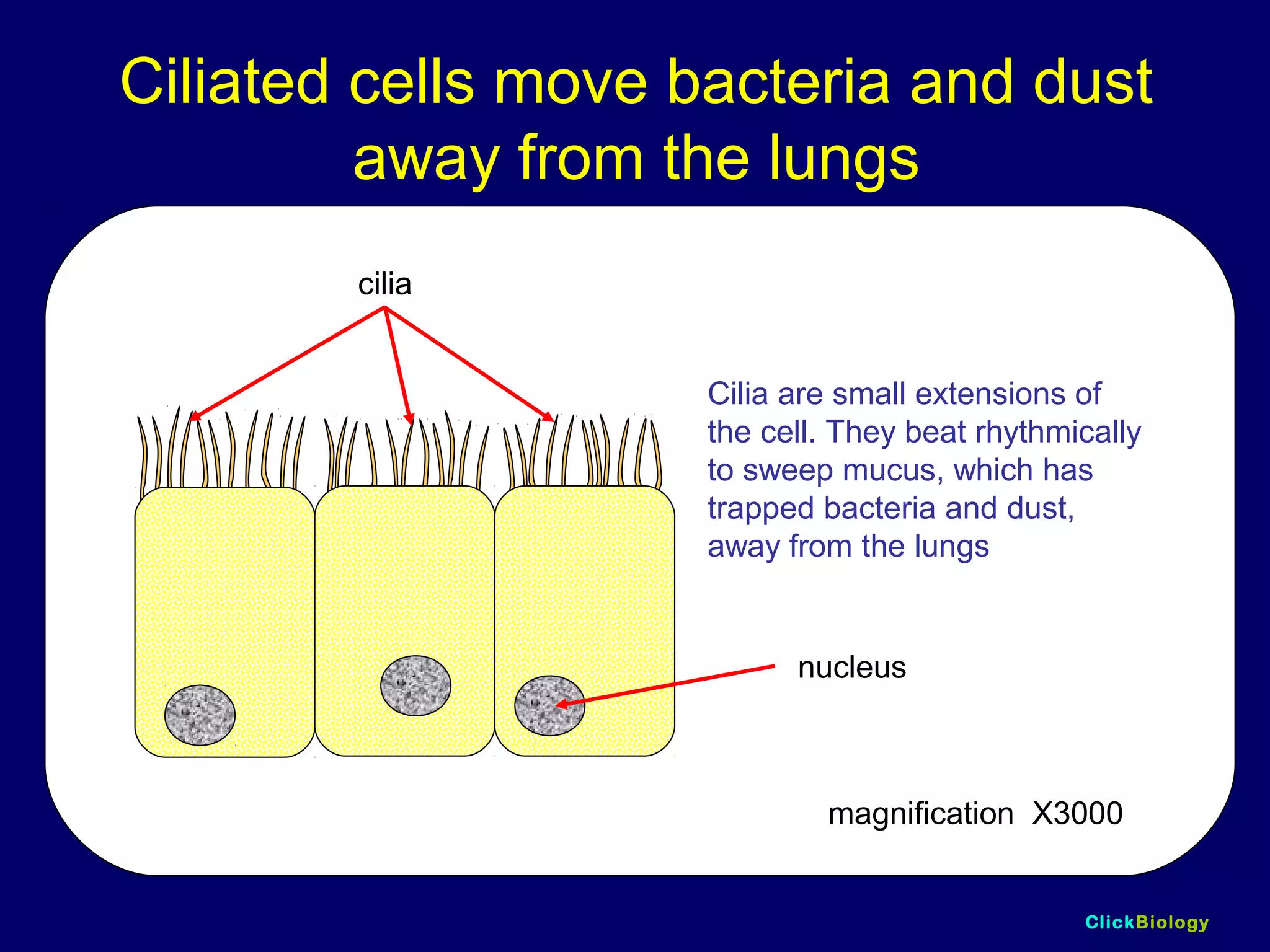
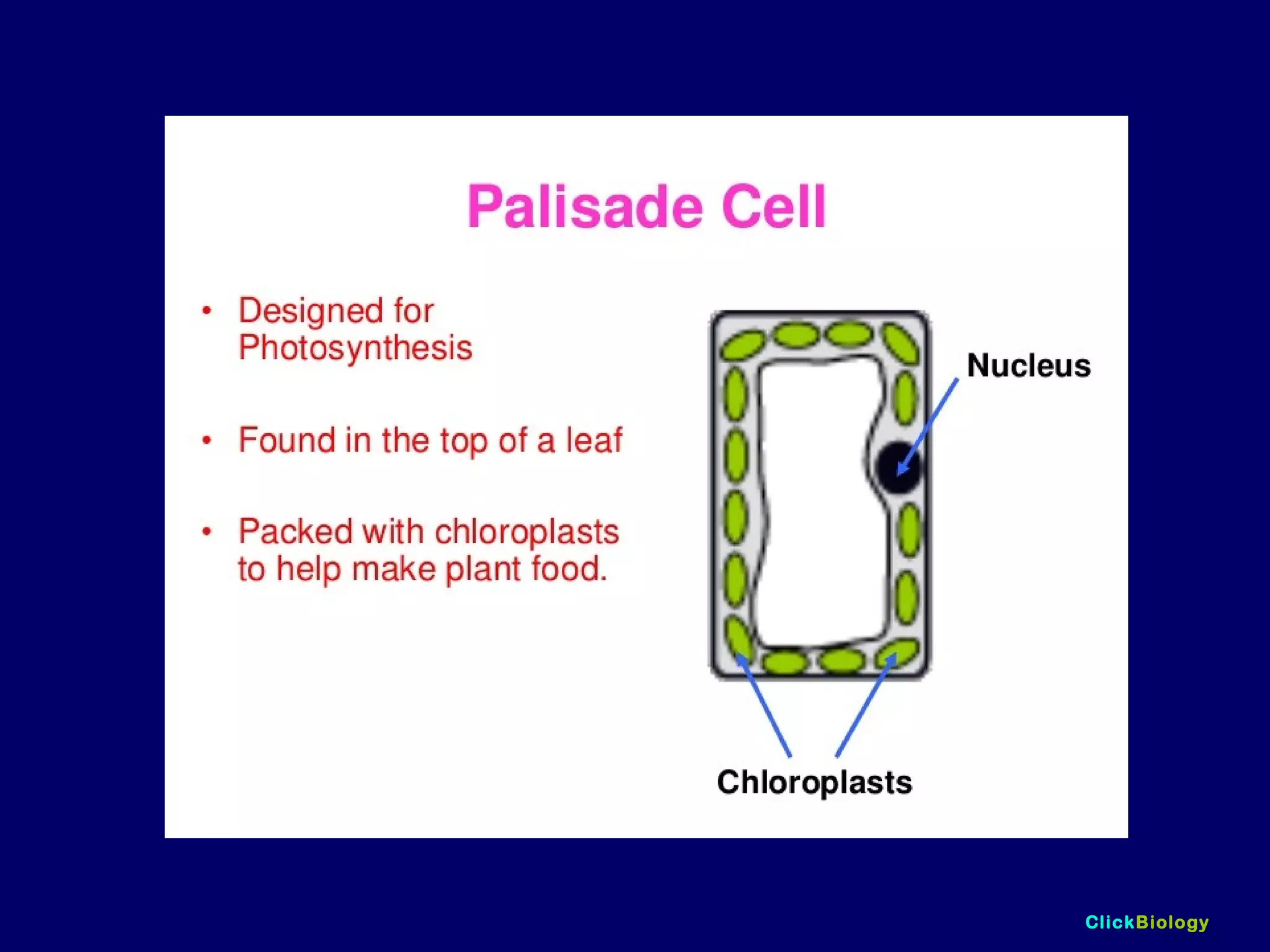
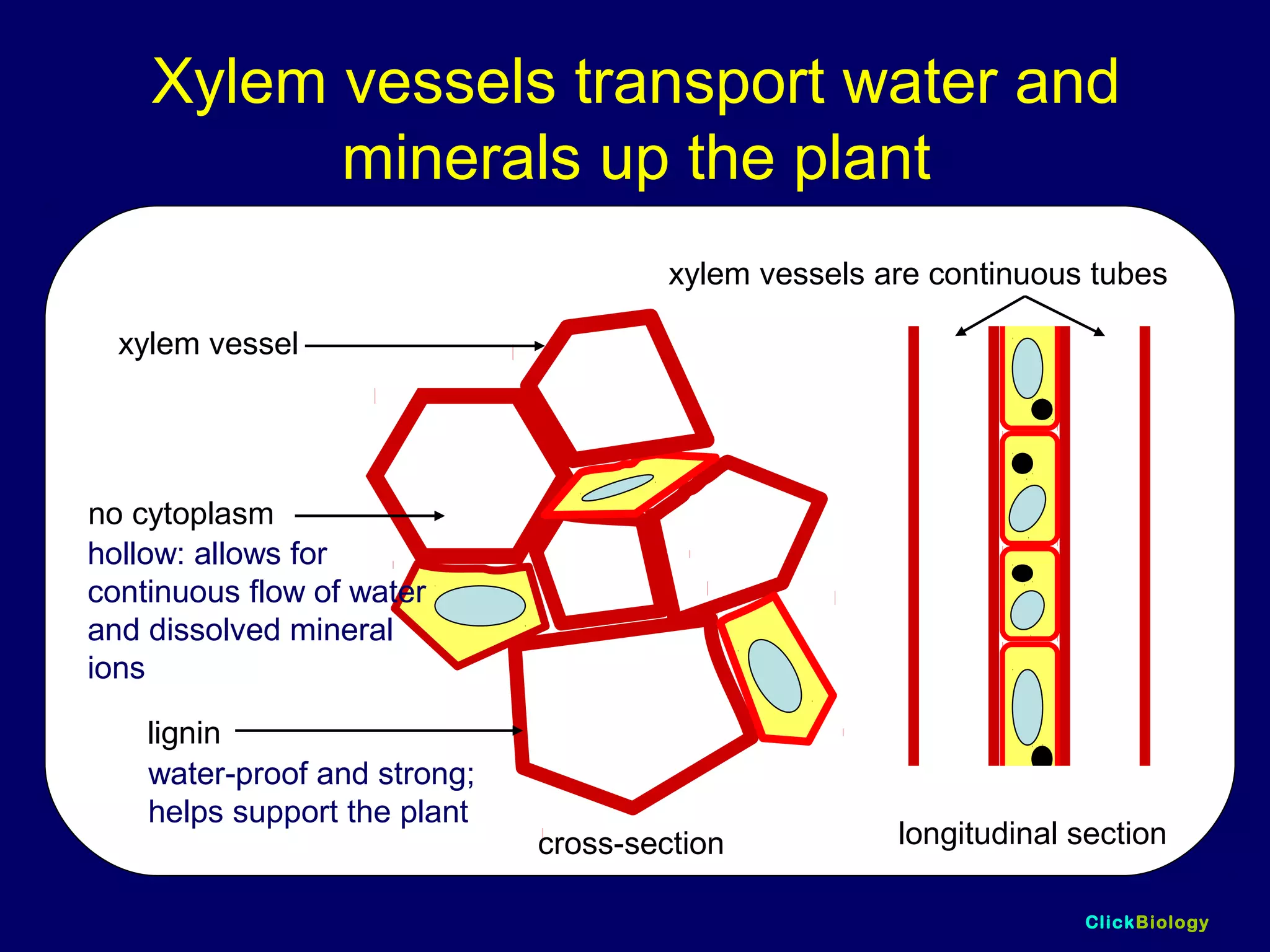
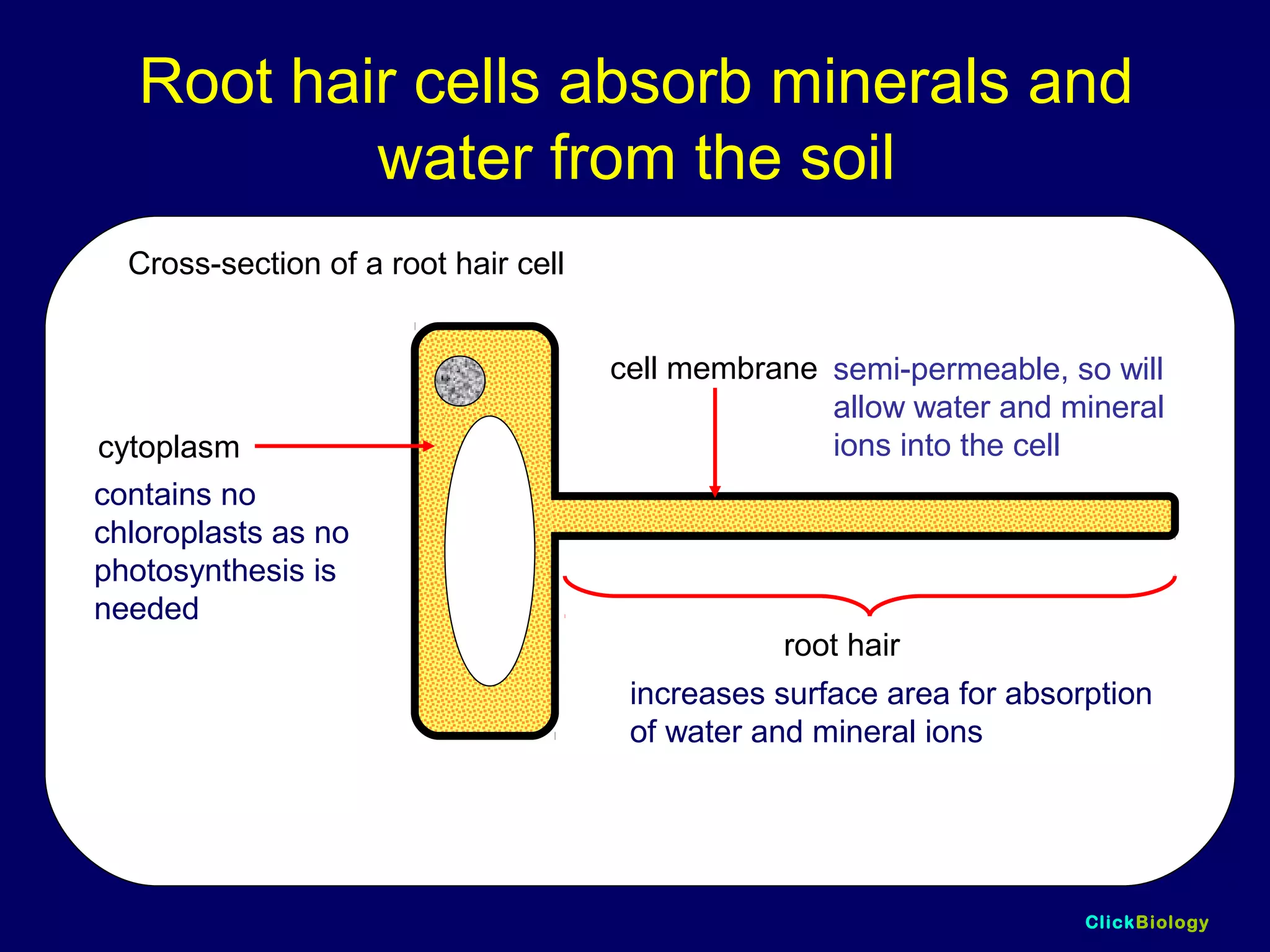
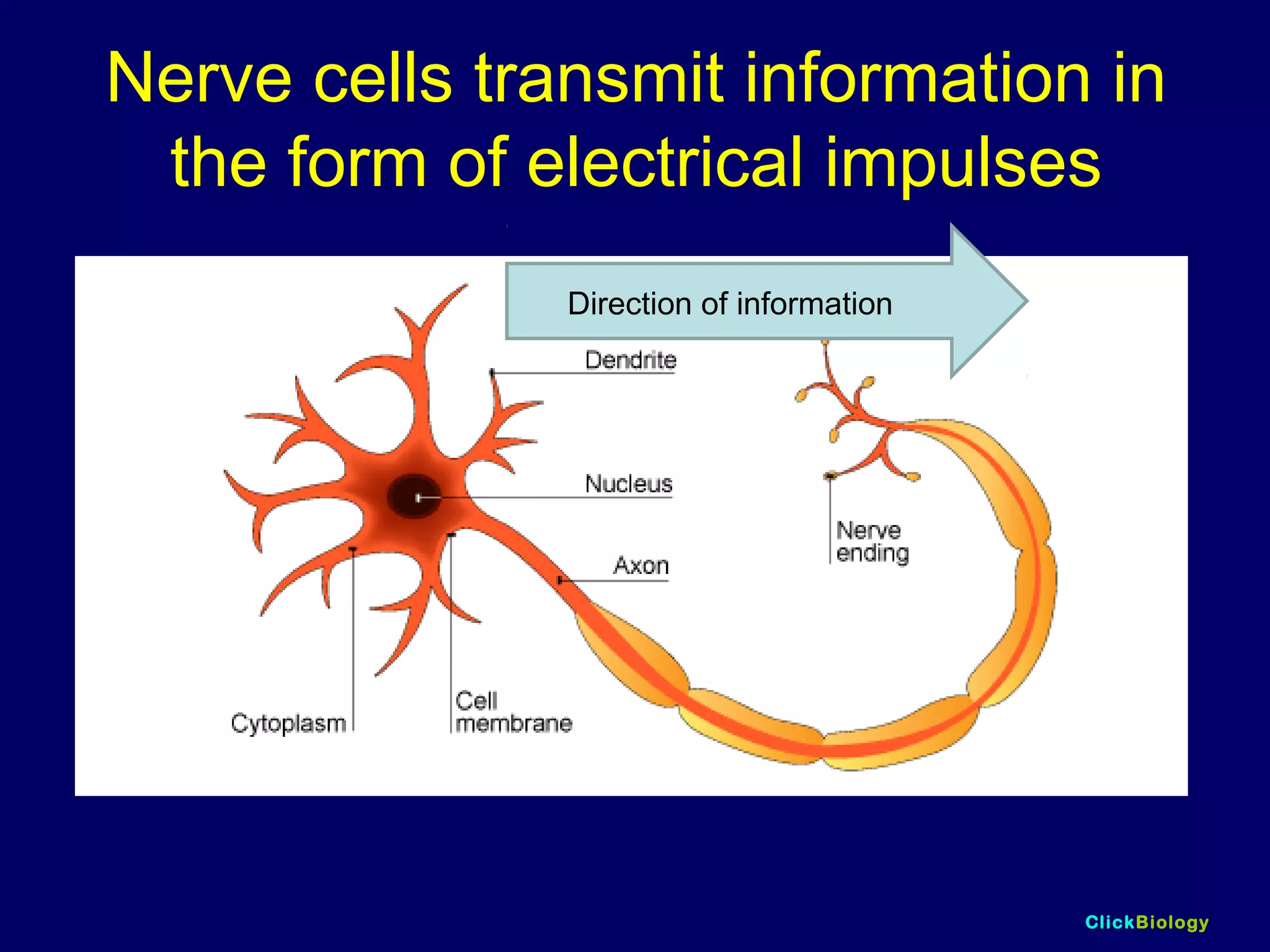
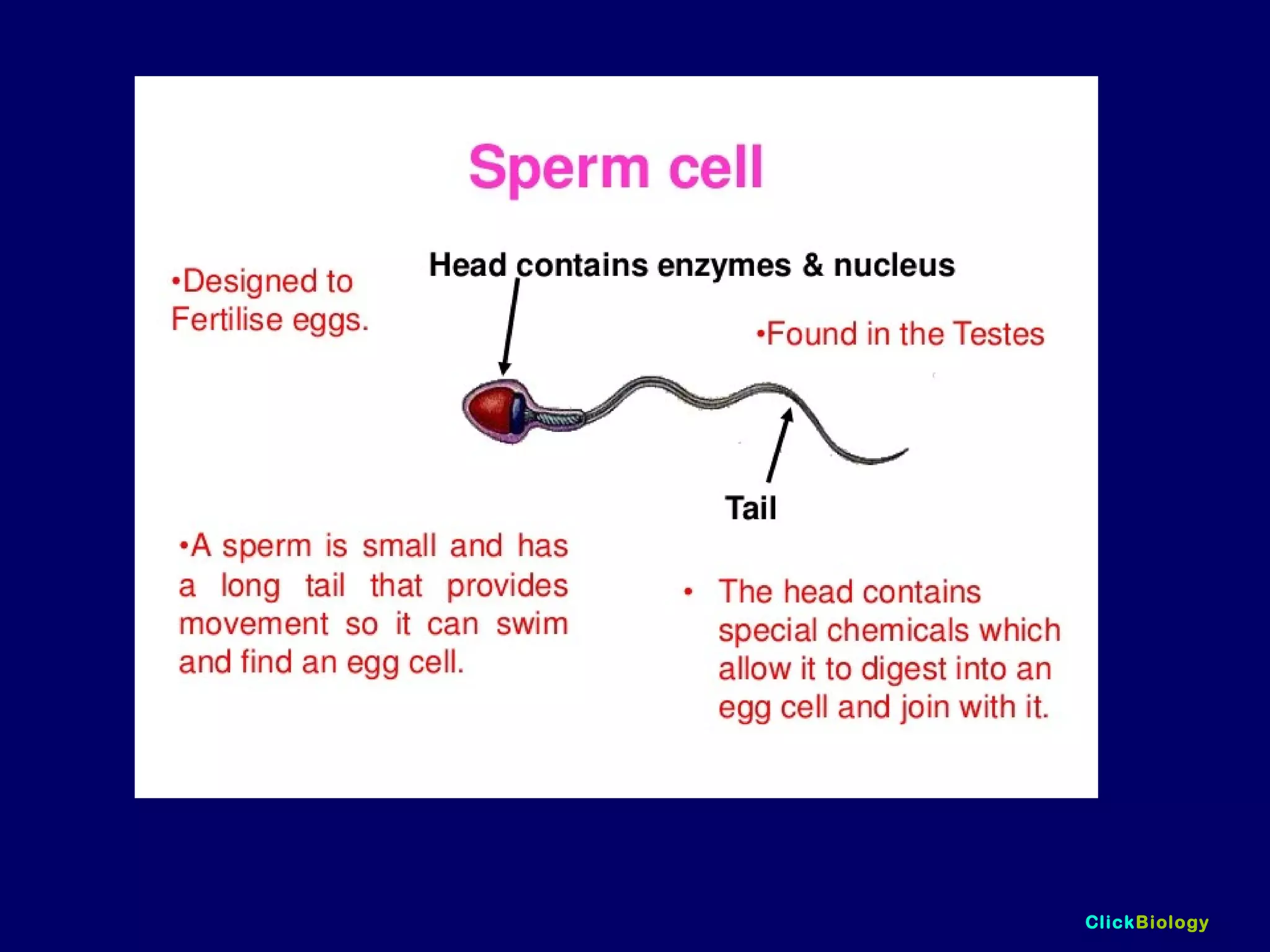
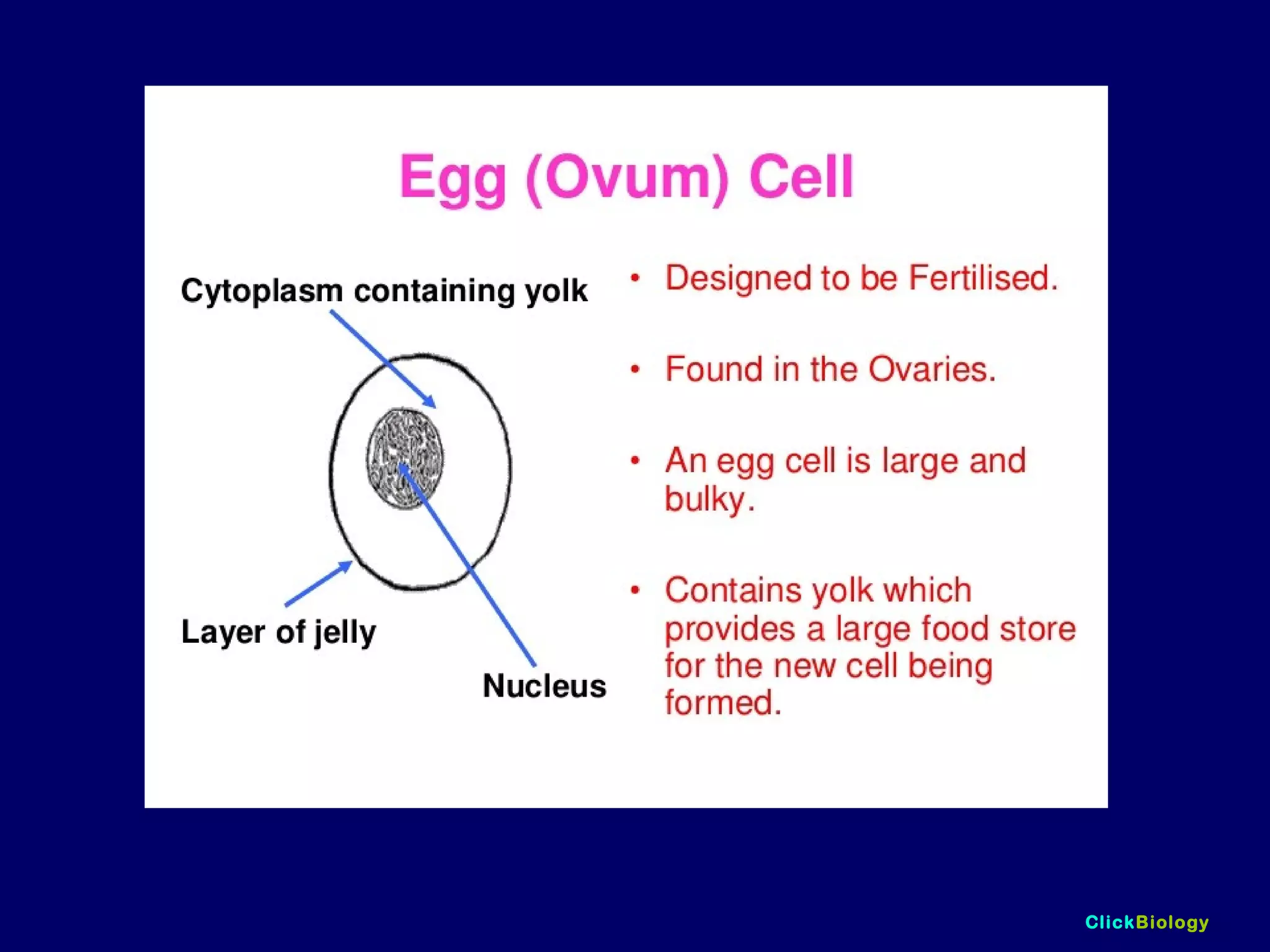
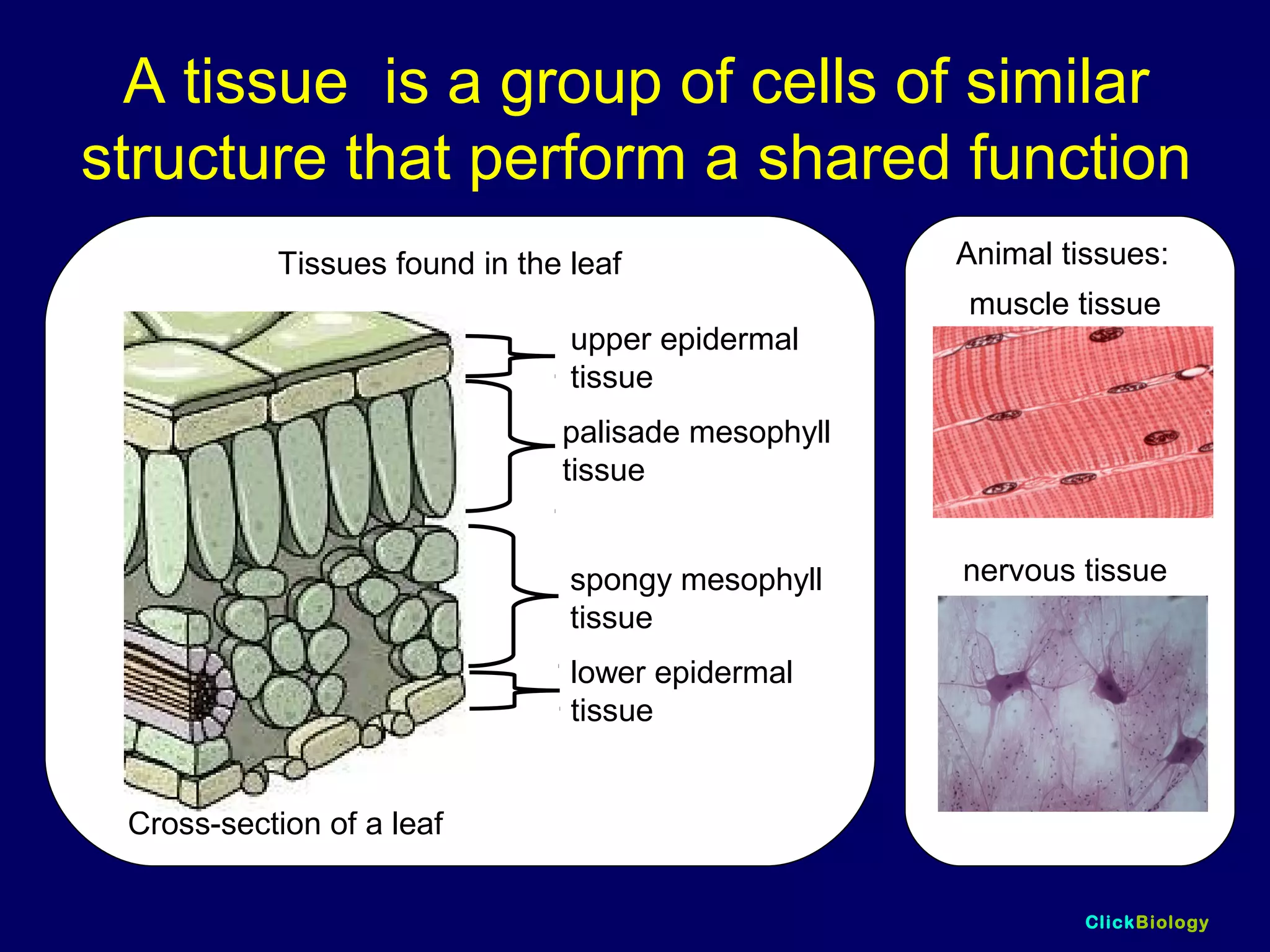
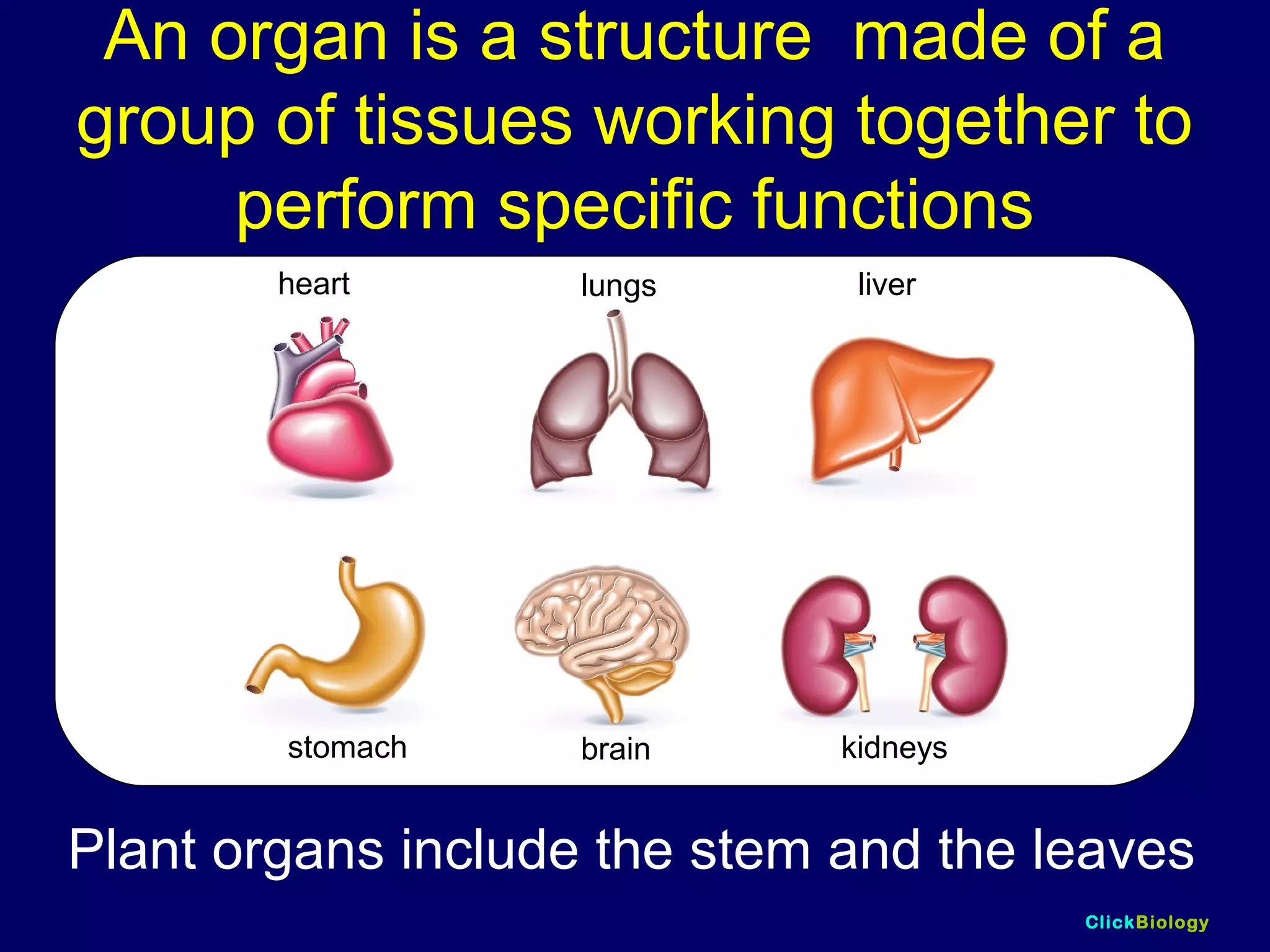
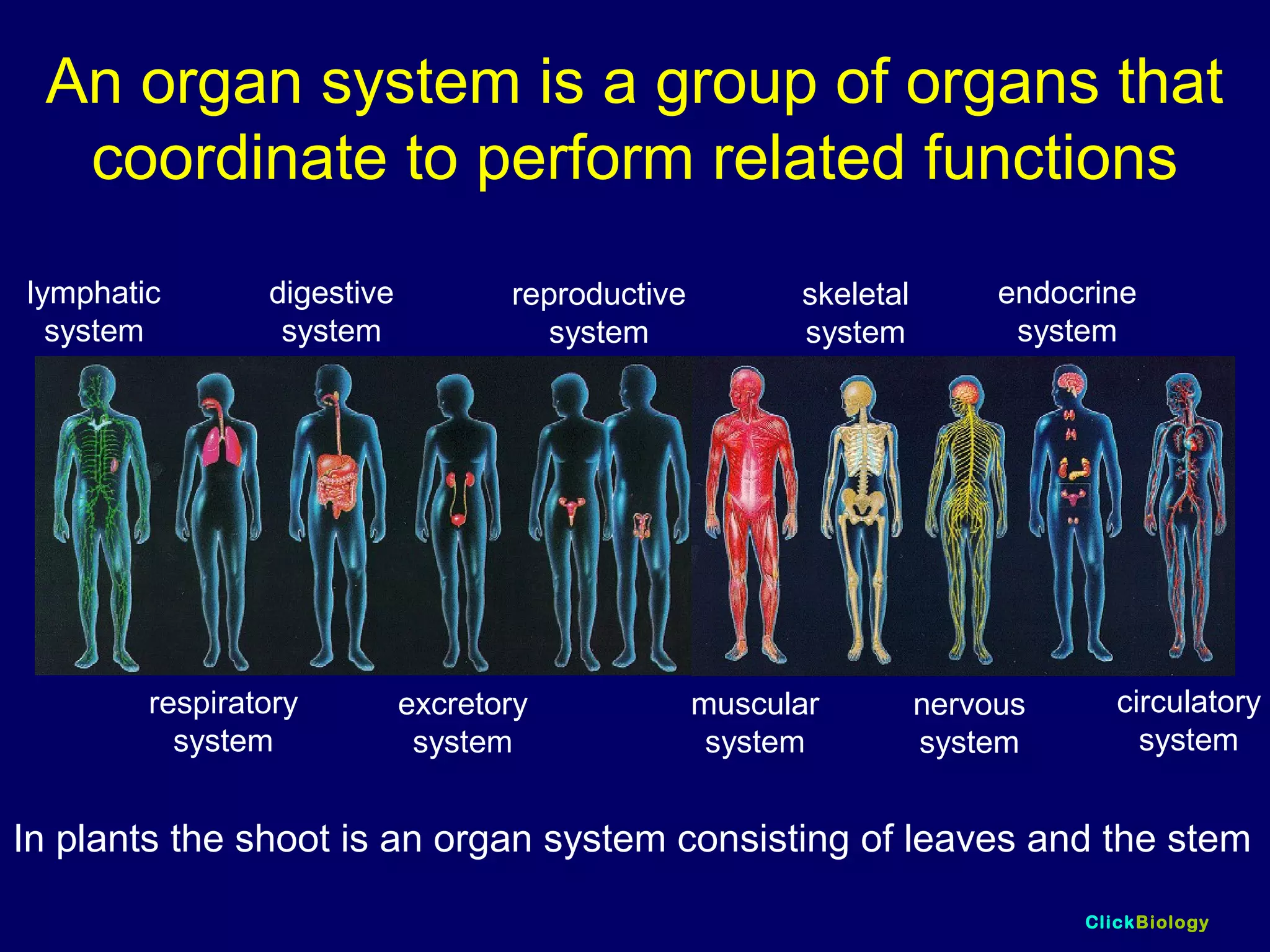
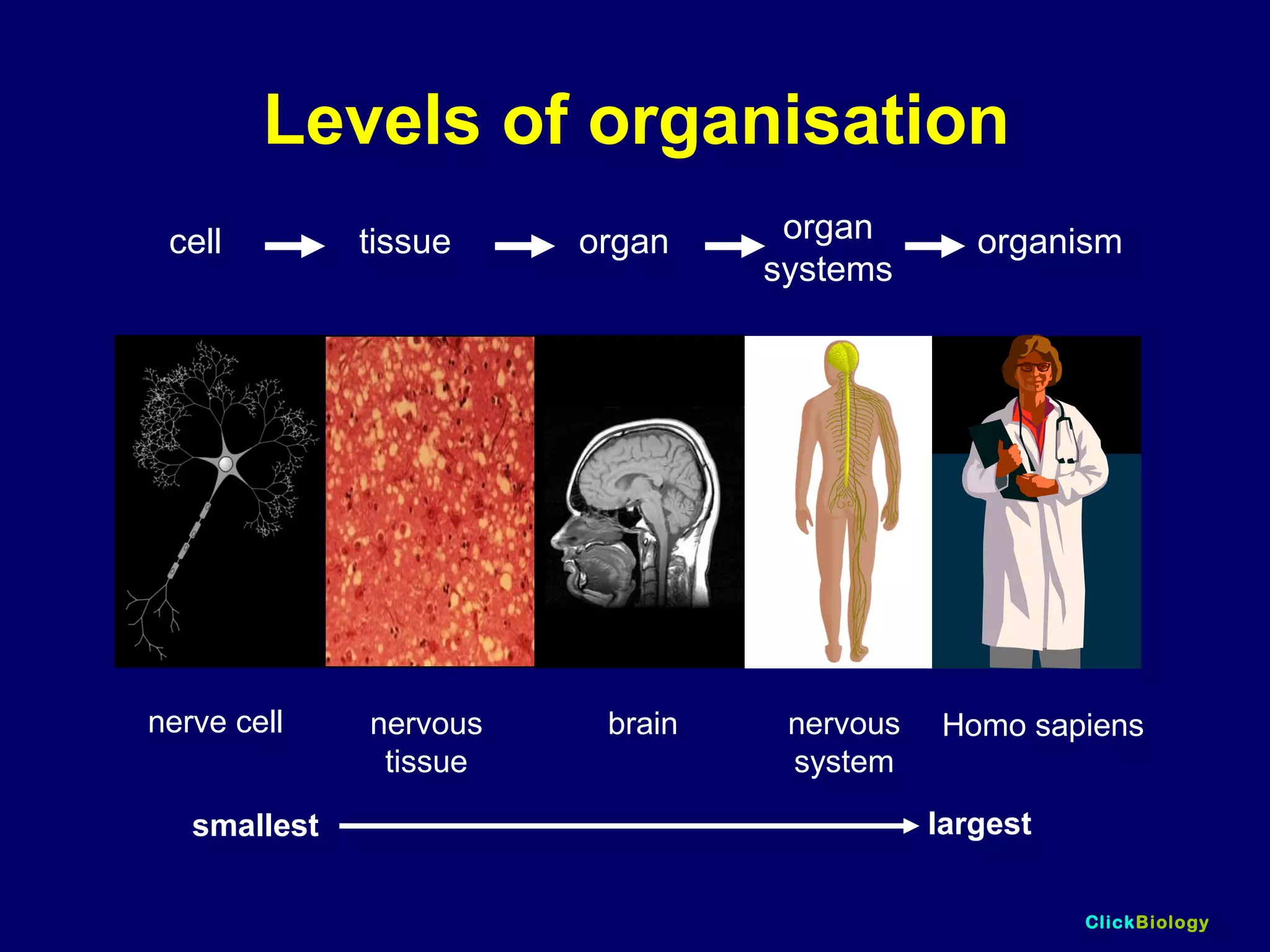
The document discusses cells and their structures. It describes the structures of plant and animal cells, including their cell membranes, nuclei, cytoplasm, chloroplasts in plant cells, and cell walls in plant cells. It also explains the functions of cell organelles like ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and vacuoles. Specialized cell structures and functions are described for red blood cells, muscle cells, ciliated cells, xylem vessels, and root hair cells. Finally, it defines tissues as groups of similar cells, organs as structures of multiple tissue types, and organ systems as groups of organs that work together.