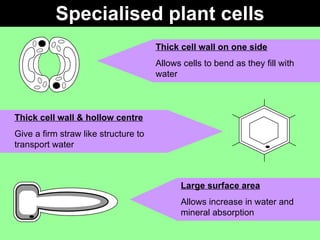
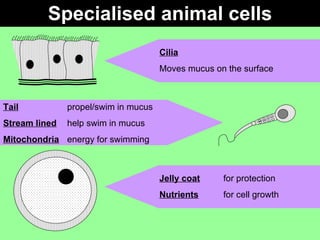
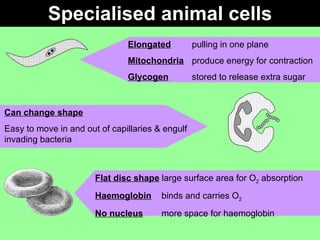
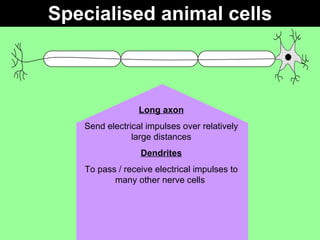
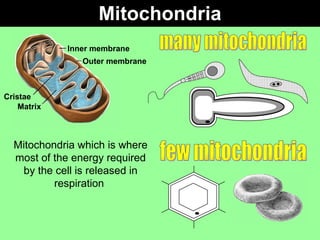
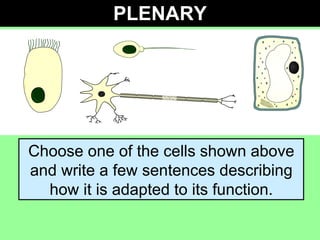
This document discusses specialized cells and their functions. It provides examples of specialized plant cells like those with thick cell walls that allow bending as they fill with water and have large surface areas for absorbing water and minerals. Specialized animal cells discussed include cilia for moving mucus, elongated muscle cells for contraction, flat disc-shaped red blood cells for oxygen transport, and nerve cells with long axons and dendrites for transmitting electrical signals. Students are asked to order complexity from cell to organism and describe cellular adaptations and functions.