Reprodinhumans 170322174812
•
0 likes•287 views
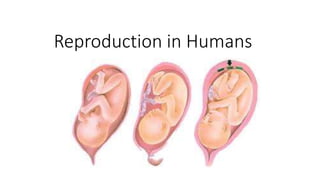
1. The male gamete (sperm) fuses with the female gamete (ova/egg) during fertilization to form a zygote. 2. The zygote develops into an embryo, which implants in the uterus and develops further into a fetus through the roles of the placenta and umbilical cord. 3. Childbirth occurs when contractions push the baby through the birth canal, after which the placenta detaches from the uterus and is delivered.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Human repro part2

1. The document discusses reproduction in humans, including ante-natal care for the mother during pregnancy and care for the newborn baby. It emphasizes the importance of diet, exercise, and avoiding harmful substances during pregnancy.
2. Breastfeeding is described as important for providing nutrients and antibodies to help the baby grow and avoid infection. Other topics covered include birth control methods and some common sexually transmitted infections.
Reprod in humans

1. The male gamete (sperm) fuses with the female gamete (ova/egg) during fertilization to form a zygote.
2. The zygote develops into an embryo that is implanted in the uterus and receives nutrients via the placenta and umbilical cord without mixing of the mother and embryo's blood.
3. Childbirth is triggered by contractions that open the cervix and push the baby through the birth canal, after which the placenta detaches and is delivered.
Human Reproduction

The male reproductive system produces and delivers sperm. The testes produce sperm in the seminiferous tubules which then travel through the epididymis, vas deferens and urethra. During ejaculation, sperm mix with fluids from the seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral glands to form semen. The female reproductive system prepares for possible pregnancy each month by releasing an egg. If fertilized, the uterus nourishes the embryo through gestation and birth. The menstrual and ovarian cycles coordinate to release an egg and prepare the uterus.
Ch.6.reproduction in humans

Puberty is the stage of development when the human body becomes capable of reproduction. During puberty, hormones cause physical changes like growth of sex organs and secondary sex characteristics. For females, this includes breast development and the start of menstruation. For males, changes involve growth of the penis and testes and facial/body hair. The document provides information about the male and female reproductive systems and their functions in sexual reproduction and childbirth.
Human reproduction

This document defines and describes human reproduction, including primary and secondary sex characteristics, reproductive cells, and the male and female reproductive systems. It explains that fertilization occurs when an ovum and sperm join to form a zygote, which implants in the uterus and becomes an embryo. Pregnancy is described, including the protective structures of the placenta, umbilical cord, and amniotic sac that develop. The stages of fetal development and labor are outlined, with labor involving dilation of the cervix, baby expulsion, and delivery of the afterbirth.
Human reproduction

Human reproduction occurs through sexual reproduction bringing male and female together. Primary sexual characteristics are present at birth and differ between males and females. During puberty, secondary sexual characteristics develop like breasts or facial hair. Reproductive cells called sperm and ova carry out reproduction. The male reproductive system includes testes, penis and other organs. The female system includes ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes and other organs. Fertilization happens when a sperm and ovum join to form a zygote. Pregnancy lasts 9 months as the embryo develops protective structures and into a fetus and baby over time. Birth occurs in three stages of dilation, expulsion, and delivery of the afterbirth.
Biology Sexual reproduction in mammals

The document provides information about the male and female reproductive systems. It describes the structure and function of the male reproductive organs, including the testes, penis, and accessory glands. It explains that testosterone controls the development of male secondary sex characteristics at puberty, such as facial hair and muscle growth. The document also outlines the structure and function of the female reproductive organs, including the ovaries, uterus, and vagina. It states that estrogen controls the development of female secondary sex characteristics, such as breast growth and menstruation. Finally, it summarizes the menstrual cycle and the roles of hormones like FSH, LH, estrogen and progesterone in regulating the cycle.
Human reproduction

The document provides information about the male and female reproductive systems:
- Both sexes have reproductive organs called genitals designed for intercourse and conception. The female reproductive organs include ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. The male reproductive organs include testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and penis.
- The ovaries hold and release eggs, while the testes produce sperm and testosterone. During ovulation, an egg is released from the ovaries and travels to the uterus through the fallopian tubes. If sperm fertilizes the egg, it may implant in the lining of the uterus.
Recommended
Human repro part2

1. The document discusses reproduction in humans, including ante-natal care for the mother during pregnancy and care for the newborn baby. It emphasizes the importance of diet, exercise, and avoiding harmful substances during pregnancy.
2. Breastfeeding is described as important for providing nutrients and antibodies to help the baby grow and avoid infection. Other topics covered include birth control methods and some common sexually transmitted infections.
Reprod in humans

1. The male gamete (sperm) fuses with the female gamete (ova/egg) during fertilization to form a zygote.
2. The zygote develops into an embryo that is implanted in the uterus and receives nutrients via the placenta and umbilical cord without mixing of the mother and embryo's blood.
3. Childbirth is triggered by contractions that open the cervix and push the baby through the birth canal, after which the placenta detaches and is delivered.
Human Reproduction

The male reproductive system produces and delivers sperm. The testes produce sperm in the seminiferous tubules which then travel through the epididymis, vas deferens and urethra. During ejaculation, sperm mix with fluids from the seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral glands to form semen. The female reproductive system prepares for possible pregnancy each month by releasing an egg. If fertilized, the uterus nourishes the embryo through gestation and birth. The menstrual and ovarian cycles coordinate to release an egg and prepare the uterus.
Ch.6.reproduction in humans

Puberty is the stage of development when the human body becomes capable of reproduction. During puberty, hormones cause physical changes like growth of sex organs and secondary sex characteristics. For females, this includes breast development and the start of menstruation. For males, changes involve growth of the penis and testes and facial/body hair. The document provides information about the male and female reproductive systems and their functions in sexual reproduction and childbirth.
Human reproduction

This document defines and describes human reproduction, including primary and secondary sex characteristics, reproductive cells, and the male and female reproductive systems. It explains that fertilization occurs when an ovum and sperm join to form a zygote, which implants in the uterus and becomes an embryo. Pregnancy is described, including the protective structures of the placenta, umbilical cord, and amniotic sac that develop. The stages of fetal development and labor are outlined, with labor involving dilation of the cervix, baby expulsion, and delivery of the afterbirth.
Human reproduction

Human reproduction occurs through sexual reproduction bringing male and female together. Primary sexual characteristics are present at birth and differ between males and females. During puberty, secondary sexual characteristics develop like breasts or facial hair. Reproductive cells called sperm and ova carry out reproduction. The male reproductive system includes testes, penis and other organs. The female system includes ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes and other organs. Fertilization happens when a sperm and ovum join to form a zygote. Pregnancy lasts 9 months as the embryo develops protective structures and into a fetus and baby over time. Birth occurs in three stages of dilation, expulsion, and delivery of the afterbirth.
Biology Sexual reproduction in mammals

The document provides information about the male and female reproductive systems. It describes the structure and function of the male reproductive organs, including the testes, penis, and accessory glands. It explains that testosterone controls the development of male secondary sex characteristics at puberty, such as facial hair and muscle growth. The document also outlines the structure and function of the female reproductive organs, including the ovaries, uterus, and vagina. It states that estrogen controls the development of female secondary sex characteristics, such as breast growth and menstruation. Finally, it summarizes the menstrual cycle and the roles of hormones like FSH, LH, estrogen and progesterone in regulating the cycle.
Human reproduction

The document provides information about the male and female reproductive systems:
- Both sexes have reproductive organs called genitals designed for intercourse and conception. The female reproductive organs include ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. The male reproductive organs include testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and penis.
- The ovaries hold and release eggs, while the testes produce sperm and testosterone. During ovulation, an egg is released from the ovaries and travels to the uterus through the fallopian tubes. If sperm fertilizes the egg, it may implant in the lining of the uterus.
Sexual reproduction in humans

Sexual reproduction in humans involves male and female reproductive systems. The male system includes testes that produce sperm and the female system includes ovaries that produce eggs. Fertilization occurs when a sperm fuses with an egg in the fallopian tube, forming a zygote. The zygote then implants in the uterus and develops into an embryo and fetus over nine months of gestation, until birth. If fertilization does not occur, the female undergoes menstruation and the cycle repeats every 28 days from puberty to menopause. Methods to prevent pregnancy include barrier methods, hormonal birth control, surgical sterilization, and IUDs.
Human reproduction

Human reproduction involves the combination of male and female reproductive cells or gametes. During puberty, physical changes like growth of body hair and changes in body shape prepare the bodies of boys and girls for reproduction. The male reproductive system produces millions of sperm cells daily in the testes, while the female system releases a mature egg once a month from the ovaries. Fertilization occurs when sperm fertilizes an egg, initiating pregnancy, which lasts about nine months until birth.
Reproduction in humans

The document summarizes human reproduction. It describes the key parts of the male and female reproductive systems and how they work together for fertilization and embryo development. The male system produces sperm in the testes, which travel through ducts and are stored in the seminal vesicles along with fluids. During sexual intercourse, sperm are ejaculated via the penis into the female's vagina. In the female, eggs mature and are released from the ovaries monthly if not fertilized. If sperm meet and fertilize an egg in the fallopian tubes, a zygote is formed and travels to implant in the uterus, leading to pregnancy and gestation, culminating in birth.
Human reproduction by Yulia

The document provides an overview of the human reproductive system and process of reproduction. It describes the male and female reproductive cells and systems, including the testes, ovaries, uterus and other organs. It explains fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm join in the fallopian tubes. Pregnancy involves development of the embryo and fetus over 9 months as it is nourished through the placenta. Labor concludes pregnancy in three phases as contractions widen the birth canal for delivery of the baby.
Presentación david human reproduction

Sexual reproduction allows human beings to have children. During puberty, males and females develop primary and secondary sex characteristics that distinguish their reproductive organs and bodies. Females produce eggs in their ovaries monthly while males continuously produce sperm in their testicles. Fertilization occurs when sperm fertilizes an egg during sexual intercourse, forming a zygote that develops into an embryo and fetus over nine months of pregnancy, ending with childbirth.
Reproduction lessson 1

This document discusses human reproduction. It describes that males produce millions of sperm cells that contain the father's genetic information and have a tail to help swim. Females produce a few hundred egg cells over their lifetime that contain the mother's genetic information. Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell meets an egg cell, and the joined cell begins dividing and growing into new cells to form an embryo.
7 b reproduction

The document is about the human reproductive system and process. It contains the following key points:
- Humans use sexual reproduction to produce offspring, which requires both male and female sex organs and sex cells.
- In females, eggs are produced in the ovaries and in males sperm is produced in the testes.
- Fertilization occurs when the sperm and egg meet during sexual intercourse, joining their nuclei.
- The fertilized egg implants in the uterus and forms the placenta, which exchanges gases and nutrients between the mother and developing fetus.
Human reproduction

Human reproduction involves the union of male and female reproductive cells. In humans, sexual reproduction occurs through the fertilization of an ovum by a spermatozoon within the female's reproductive tract. At puberty, females develop breasts and pubic hair and begin menstruating monthly due to the maturation of their ovaries and production of eggs and hormones. Males experience growth of pubic hair and facial hair at puberty along with a deepening voice due to increased hormone production by the testes. Fertilization usually occurs within the fallopian tubes after intercourse, when a sperm unites with an egg to form a zygote that implants in the uterus and develops into an embryo and eventually a fetus.
Human Reproduction 

The document discusses human reproduction, including the male and female reproductive systems and processes. Some key points:
1. It describes the major events in human sexual reproduction - gamete formation, puberty, fertilization, implantation, gestation, and parturition.
2. It provides an overview of the male reproductive system, including the testes, accessory ducts and glands, and external genitalia. Spermatogenesis and the role of hormones are also summarized.
3. The female reproductive system is outlined, including the ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, vagina, and external genitalia. Oogenesis and the menstrual cycle are briefly explained.
Human reproduction

Human reproduction involves internal fertilization where sperm from the male reproductive system containing the penis, testicles, and scrotum fertilizes an ovum from the female reproductive system containing the ovaries, uterus, Fallopian tubes, vagina, and vulva. This fertilization produces a zygote that develops into an embryo during pregnancy in the mother's uterus and is eventually birthed.
Reproduction and growth 

This document discusses several topics related to human reproduction and growth, including:
1. It outlines learning objectives on gamete formation, the menstrual cycle, early zygote development, and the role of science and technology in human reproduction.
2. It then provides details on gamete formation in males and females, explaining spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
3. The role of hormones in regulating the menstrual cycle is analyzed, outlining the hormones involved and how they influence follicle development, ovulation, and the endometrium throughout the cycle.
Reproduction In Human And Issues On Sex

The document summarizes sexual reproduction in animals. It describes the key differences between asexual and sexual reproduction, including that sexual reproduction involves two parents and produces offspring that are genetically different from the parents. It then provides details about the male and female reproductive systems, the process of fertilization, embryonic and fetal development, and childbirth.
Reproduction review lesson

Reproduction ensures the continuity of species. Sexual reproduction involves two parents and results in offspring that are genetically similar. It occurs through the fusion of male and female gametes. In plants, sexual reproduction involves flowers that have male anthers producing pollen and female stigma receiving pollen. Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains leading to fertilization where the sperm fuses with the egg. In humans, sexual reproduction involves the male reproductive system producing sperm and the female reproductive system containing ovaries and uterus. Contraceptive methods like condoms, IUDs, birth control pills and sterilization procedures prevent fertilization.
Sexual characteristics

Puberty is when the reproductive system matures, triggered by hormones from the pituitary gland, and results in secondary sexual characteristics developing between ages 11-15 such as lower voices and more muscle mass in boys and higher voices, breasts, and wider hips in girls. During puberty, one egg matures and is released each month through the Fallopian tubes, and if not fertilized by sperm, it leaves the body through the vagina along with some bleeding, known as menstruation or a period. The development of sexual organs both internally like ovaries and testes and externally like penises and vulvas enable human reproduction.
Humanreproductionsacha 130722032329-phpapp01-140307035250-phpapp02

Human reproduction occurs through sexual reproduction which involves both male and female sex cells. At puberty, individuals develop primary and secondary sexual characteristics that differentiate males and females. Sperm and ova are the reproductive cells in males and females respectively. The male reproductive system includes testes, penis and other organs that produce and transport sperm. The female system includes ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes and other organs involved in producing and housing an embryo. Fertilization happens when a sperm joins an ovum, forming a zygote that implants in the uterus. Pregnancy lasts 9 months as the embryo develops protected structures until birth.
Reproductive system

The document summarizes the male and female reproductive systems. It describes the key external and internal organs of each system, their functions, and the processes of reproduction. The male system includes the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and urethra. The female system includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. Sperm and eggs are produced and meet in the fallopian tubes, where fertilization can occur leading to embryo development in the uterus.
Human reproduction.

The document summarizes the key aspects of human reproduction. It describes puberty and the changes that occur during adolescence for both males and females. It then details the male and female reproductive systems and their functions. It explains the production of reproductive cells and the menstrual cycle. Finally, it outlines the processes of fertilization, pregnancy, and childbirth.
Human reproduction for grade 12

Human reproduction involves the joining of an ovum and spermatozoid through fertilization to form a zygote. The female reproductive system includes ovaries that produce ova and a uterus that supports embryo development. The male reproductive system includes testes that produce spermatozoa and accessory glands. During puberty, secondary sex characteristics like breast development and facial hair emerge due to hormonal changes. Fertilization is a multi-step process where a sperm penetrates an ovum in the fallopian tube, their genetic material combines, and an embryo is formed. The embryo implants in the uterus and develops over nine months of gestation into a fetus, preparing for birth.
BIOLOGY FORM 5 CHAPTER 4 - 4.1E FERTILISATION & DEVELOPMENT

The document summarizes the process of human reproduction from fertilization through embryonic and fetal development to childbirth. It describes how sperm and eggs are produced, fertilization in the fallopian tube, cleavage and formation of the morula and blastocyst. Implantation in the uterus and formation of the placenta and amniotic sac are explained. Stages of embryonic and fetal development through the trimesters are outlined. The roles of the placenta, umbilical cord and amniotic fluid are summarized. Childbirth and postnatal development including lactation are briefly described. Common topics like twins and congenital abnormalities are also covered at a high level.
Reproduction

Reproduction can occur through asexual or sexual means. Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring identical to the parent, while sexual reproduction involves two parents and produces offspring with genetic variation. The male reproductive system produces sperm in the testes which are transported through ducts. The female reproductive system produces eggs in the ovaries which pass to the uterus. Fertilization occurs when sperm and egg join together. In humans and most animals, reproduction occurs sexually through internal fertilization.
lesson 4.2 Human Reproduction

The male reproductive system produces sperm and testosterone. The testes produce sperm and are held in the scrotum outside of the body. During arousal, blood flows into the penis causing it to erect. The female reproductive system produces eggs and menstrual cycles. The ovaries produce eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes to the uterus. During ovulation, an egg is released and may be fertilized if sperm are present. Both systems undergo changes during puberty to support reproduction.
1 GNM anatomy Unit - 10 Repro System.pptx

By:
M. Thiru murugan
Unit – 10:
Structure and functions of the female reproductive system
Process of menstrual cycle, reproduction and menopause
Structure and functions of breasts
Structure and functions of the male reproductive system
Reproductive health
Reproductive system:
The organs involved in producing offspring (a person's child or children).
In women, this system includes the ovaries, the fallopian tubes, the uterus, and the vagina.
In men, it includes the prostate, the testes, and the penis.
The female reproductive system
The female reproductive system plays many vital functions that ensure the continuation of the human race
Located in the pelvic cavity
Parts:
It consist of
External genitalia
Internal genitalia
External genitalia:
Labia minora
Labia majora
Clitoris
Vaginal orifice
Internal genitalia:
Ovaries
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Vagina
Vagina:
A muscular tube, that extends from the cervix of the uterus to the outside of the body.
During intercourse, the vagina receives the male’s penis and semen.
Birth canal that the baby passes through in a normal delivery.
Ovaries:
Small almond-shaped glands that produce ova and the female sex hormones located on both sides of the uterus within the pelvic cavity.
In charge of ovulation and producing the female sex hormones.
The hormones are responsible for getting the lining of the uterus prepared for a fertilized ovum
Uterus:
Hollow organ (also called womb)
Fetus (unborn baby) develops and grows.
Contractions to the walls propels the baby during delivery through the birth canal in a normal delivery
Parts: fundus, body & cervix
The fundus is the broad curved upper area in which the fallopian tubes connect to the uterus;
The body, the main part of the uterus,
The cervix, extends downward and opens into the vagina.
Uterus has 3 layers:
The endometrium is the inner layer
The myometrium is the middle layer
The perimetrium is the outer layer
Function of uterus:
The uterus receives a fertilized egg and protects the fetus (baby) while it grows and develops.
The uterus contracts to push the baby out of the body during birth.
Every month, except when a woman is pregnant, the lining of the uterus grows and thickens in preparation for pregnancy.
If the woman doesn’t get pregnant, the lining is shed through the cervix into the vagina and out of the body. This is called menstruation.
The function of the female reproductive System:
The female reproductive system produces ova (the female reproductive cell)
Provides a location for fertilization
Growth of a fetus
Secretes female sex hormones
The breast produce milk to nourish the newborn.
Menstruation:
Menstruation, or period, is normal vaginal bleeding that occurs as part of a woman's monthly cycle.
Every month, your body prepares for pregnancy. If no pregnancy occurs, the uterus sheds its lining. The menstrual blood is partly blood and partly tissue from inside the uterus. It passes out of the body through the vagina.
Menstrual cycle:
Con
More Related Content
What's hot
Sexual reproduction in humans

Sexual reproduction in humans involves male and female reproductive systems. The male system includes testes that produce sperm and the female system includes ovaries that produce eggs. Fertilization occurs when a sperm fuses with an egg in the fallopian tube, forming a zygote. The zygote then implants in the uterus and develops into an embryo and fetus over nine months of gestation, until birth. If fertilization does not occur, the female undergoes menstruation and the cycle repeats every 28 days from puberty to menopause. Methods to prevent pregnancy include barrier methods, hormonal birth control, surgical sterilization, and IUDs.
Human reproduction

Human reproduction involves the combination of male and female reproductive cells or gametes. During puberty, physical changes like growth of body hair and changes in body shape prepare the bodies of boys and girls for reproduction. The male reproductive system produces millions of sperm cells daily in the testes, while the female system releases a mature egg once a month from the ovaries. Fertilization occurs when sperm fertilizes an egg, initiating pregnancy, which lasts about nine months until birth.
Reproduction in humans

The document summarizes human reproduction. It describes the key parts of the male and female reproductive systems and how they work together for fertilization and embryo development. The male system produces sperm in the testes, which travel through ducts and are stored in the seminal vesicles along with fluids. During sexual intercourse, sperm are ejaculated via the penis into the female's vagina. In the female, eggs mature and are released from the ovaries monthly if not fertilized. If sperm meet and fertilize an egg in the fallopian tubes, a zygote is formed and travels to implant in the uterus, leading to pregnancy and gestation, culminating in birth.
Human reproduction by Yulia

The document provides an overview of the human reproductive system and process of reproduction. It describes the male and female reproductive cells and systems, including the testes, ovaries, uterus and other organs. It explains fertilization occurs when an egg and sperm join in the fallopian tubes. Pregnancy involves development of the embryo and fetus over 9 months as it is nourished through the placenta. Labor concludes pregnancy in three phases as contractions widen the birth canal for delivery of the baby.
Presentación david human reproduction

Sexual reproduction allows human beings to have children. During puberty, males and females develop primary and secondary sex characteristics that distinguish their reproductive organs and bodies. Females produce eggs in their ovaries monthly while males continuously produce sperm in their testicles. Fertilization occurs when sperm fertilizes an egg during sexual intercourse, forming a zygote that develops into an embryo and fetus over nine months of pregnancy, ending with childbirth.
Reproduction lessson 1

This document discusses human reproduction. It describes that males produce millions of sperm cells that contain the father's genetic information and have a tail to help swim. Females produce a few hundred egg cells over their lifetime that contain the mother's genetic information. Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell meets an egg cell, and the joined cell begins dividing and growing into new cells to form an embryo.
7 b reproduction

The document is about the human reproductive system and process. It contains the following key points:
- Humans use sexual reproduction to produce offspring, which requires both male and female sex organs and sex cells.
- In females, eggs are produced in the ovaries and in males sperm is produced in the testes.
- Fertilization occurs when the sperm and egg meet during sexual intercourse, joining their nuclei.
- The fertilized egg implants in the uterus and forms the placenta, which exchanges gases and nutrients between the mother and developing fetus.
Human reproduction

Human reproduction involves the union of male and female reproductive cells. In humans, sexual reproduction occurs through the fertilization of an ovum by a spermatozoon within the female's reproductive tract. At puberty, females develop breasts and pubic hair and begin menstruating monthly due to the maturation of their ovaries and production of eggs and hormones. Males experience growth of pubic hair and facial hair at puberty along with a deepening voice due to increased hormone production by the testes. Fertilization usually occurs within the fallopian tubes after intercourse, when a sperm unites with an egg to form a zygote that implants in the uterus and develops into an embryo and eventually a fetus.
Human Reproduction 

The document discusses human reproduction, including the male and female reproductive systems and processes. Some key points:
1. It describes the major events in human sexual reproduction - gamete formation, puberty, fertilization, implantation, gestation, and parturition.
2. It provides an overview of the male reproductive system, including the testes, accessory ducts and glands, and external genitalia. Spermatogenesis and the role of hormones are also summarized.
3. The female reproductive system is outlined, including the ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, vagina, and external genitalia. Oogenesis and the menstrual cycle are briefly explained.
Human reproduction

Human reproduction involves internal fertilization where sperm from the male reproductive system containing the penis, testicles, and scrotum fertilizes an ovum from the female reproductive system containing the ovaries, uterus, Fallopian tubes, vagina, and vulva. This fertilization produces a zygote that develops into an embryo during pregnancy in the mother's uterus and is eventually birthed.
Reproduction and growth 

This document discusses several topics related to human reproduction and growth, including:
1. It outlines learning objectives on gamete formation, the menstrual cycle, early zygote development, and the role of science and technology in human reproduction.
2. It then provides details on gamete formation in males and females, explaining spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
3. The role of hormones in regulating the menstrual cycle is analyzed, outlining the hormones involved and how they influence follicle development, ovulation, and the endometrium throughout the cycle.
Reproduction In Human And Issues On Sex

The document summarizes sexual reproduction in animals. It describes the key differences between asexual and sexual reproduction, including that sexual reproduction involves two parents and produces offspring that are genetically different from the parents. It then provides details about the male and female reproductive systems, the process of fertilization, embryonic and fetal development, and childbirth.
Reproduction review lesson

Reproduction ensures the continuity of species. Sexual reproduction involves two parents and results in offspring that are genetically similar. It occurs through the fusion of male and female gametes. In plants, sexual reproduction involves flowers that have male anthers producing pollen and female stigma receiving pollen. Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains leading to fertilization where the sperm fuses with the egg. In humans, sexual reproduction involves the male reproductive system producing sperm and the female reproductive system containing ovaries and uterus. Contraceptive methods like condoms, IUDs, birth control pills and sterilization procedures prevent fertilization.
Sexual characteristics

Puberty is when the reproductive system matures, triggered by hormones from the pituitary gland, and results in secondary sexual characteristics developing between ages 11-15 such as lower voices and more muscle mass in boys and higher voices, breasts, and wider hips in girls. During puberty, one egg matures and is released each month through the Fallopian tubes, and if not fertilized by sperm, it leaves the body through the vagina along with some bleeding, known as menstruation or a period. The development of sexual organs both internally like ovaries and testes and externally like penises and vulvas enable human reproduction.
Humanreproductionsacha 130722032329-phpapp01-140307035250-phpapp02

Human reproduction occurs through sexual reproduction which involves both male and female sex cells. At puberty, individuals develop primary and secondary sexual characteristics that differentiate males and females. Sperm and ova are the reproductive cells in males and females respectively. The male reproductive system includes testes, penis and other organs that produce and transport sperm. The female system includes ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes and other organs involved in producing and housing an embryo. Fertilization happens when a sperm joins an ovum, forming a zygote that implants in the uterus. Pregnancy lasts 9 months as the embryo develops protected structures until birth.
Reproductive system

The document summarizes the male and female reproductive systems. It describes the key external and internal organs of each system, their functions, and the processes of reproduction. The male system includes the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and urethra. The female system includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. Sperm and eggs are produced and meet in the fallopian tubes, where fertilization can occur leading to embryo development in the uterus.
Human reproduction.

The document summarizes the key aspects of human reproduction. It describes puberty and the changes that occur during adolescence for both males and females. It then details the male and female reproductive systems and their functions. It explains the production of reproductive cells and the menstrual cycle. Finally, it outlines the processes of fertilization, pregnancy, and childbirth.
Human reproduction for grade 12

Human reproduction involves the joining of an ovum and spermatozoid through fertilization to form a zygote. The female reproductive system includes ovaries that produce ova and a uterus that supports embryo development. The male reproductive system includes testes that produce spermatozoa and accessory glands. During puberty, secondary sex characteristics like breast development and facial hair emerge due to hormonal changes. Fertilization is a multi-step process where a sperm penetrates an ovum in the fallopian tube, their genetic material combines, and an embryo is formed. The embryo implants in the uterus and develops over nine months of gestation into a fetus, preparing for birth.
BIOLOGY FORM 5 CHAPTER 4 - 4.1E FERTILISATION & DEVELOPMENT

The document summarizes the process of human reproduction from fertilization through embryonic and fetal development to childbirth. It describes how sperm and eggs are produced, fertilization in the fallopian tube, cleavage and formation of the morula and blastocyst. Implantation in the uterus and formation of the placenta and amniotic sac are explained. Stages of embryonic and fetal development through the trimesters are outlined. The roles of the placenta, umbilical cord and amniotic fluid are summarized. Childbirth and postnatal development including lactation are briefly described. Common topics like twins and congenital abnormalities are also covered at a high level.
Reproduction

Reproduction can occur through asexual or sexual means. Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring identical to the parent, while sexual reproduction involves two parents and produces offspring with genetic variation. The male reproductive system produces sperm in the testes which are transported through ducts. The female reproductive system produces eggs in the ovaries which pass to the uterus. Fertilization occurs when sperm and egg join together. In humans and most animals, reproduction occurs sexually through internal fertilization.
What's hot (20)
Humanreproductionsacha 130722032329-phpapp01-140307035250-phpapp02

Humanreproductionsacha 130722032329-phpapp01-140307035250-phpapp02
BIOLOGY FORM 5 CHAPTER 4 - 4.1E FERTILISATION & DEVELOPMENT

BIOLOGY FORM 5 CHAPTER 4 - 4.1E FERTILISATION & DEVELOPMENT
Similar to Reprodinhumans 170322174812
lesson 4.2 Human Reproduction

The male reproductive system produces sperm and testosterone. The testes produce sperm and are held in the scrotum outside of the body. During arousal, blood flows into the penis causing it to erect. The female reproductive system produces eggs and menstrual cycles. The ovaries produce eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes to the uterus. During ovulation, an egg is released and may be fertilized if sperm are present. Both systems undergo changes during puberty to support reproduction.
1 GNM anatomy Unit - 10 Repro System.pptx

By:
M. Thiru murugan
Unit – 10:
Structure and functions of the female reproductive system
Process of menstrual cycle, reproduction and menopause
Structure and functions of breasts
Structure and functions of the male reproductive system
Reproductive health
Reproductive system:
The organs involved in producing offspring (a person's child or children).
In women, this system includes the ovaries, the fallopian tubes, the uterus, and the vagina.
In men, it includes the prostate, the testes, and the penis.
The female reproductive system
The female reproductive system plays many vital functions that ensure the continuation of the human race
Located in the pelvic cavity
Parts:
It consist of
External genitalia
Internal genitalia
External genitalia:
Labia minora
Labia majora
Clitoris
Vaginal orifice
Internal genitalia:
Ovaries
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Vagina
Vagina:
A muscular tube, that extends from the cervix of the uterus to the outside of the body.
During intercourse, the vagina receives the male’s penis and semen.
Birth canal that the baby passes through in a normal delivery.
Ovaries:
Small almond-shaped glands that produce ova and the female sex hormones located on both sides of the uterus within the pelvic cavity.
In charge of ovulation and producing the female sex hormones.
The hormones are responsible for getting the lining of the uterus prepared for a fertilized ovum
Uterus:
Hollow organ (also called womb)
Fetus (unborn baby) develops and grows.
Contractions to the walls propels the baby during delivery through the birth canal in a normal delivery
Parts: fundus, body & cervix
The fundus is the broad curved upper area in which the fallopian tubes connect to the uterus;
The body, the main part of the uterus,
The cervix, extends downward and opens into the vagina.
Uterus has 3 layers:
The endometrium is the inner layer
The myometrium is the middle layer
The perimetrium is the outer layer
Function of uterus:
The uterus receives a fertilized egg and protects the fetus (baby) while it grows and develops.
The uterus contracts to push the baby out of the body during birth.
Every month, except when a woman is pregnant, the lining of the uterus grows and thickens in preparation for pregnancy.
If the woman doesn’t get pregnant, the lining is shed through the cervix into the vagina and out of the body. This is called menstruation.
The function of the female reproductive System:
The female reproductive system produces ova (the female reproductive cell)
Provides a location for fertilization
Growth of a fetus
Secretes female sex hormones
The breast produce milk to nourish the newborn.
Menstruation:
Menstruation, or period, is normal vaginal bleeding that occurs as part of a woman's monthly cycle.
Every month, your body prepares for pregnancy. If no pregnancy occurs, the uterus sheds its lining. The menstrual blood is partly blood and partly tissue from inside the uterus. It passes out of the body through the vagina.
Menstrual cycle:
Con
B.1 male & female reproductive anatomy

The document provides an overview of the male and female reproductive systems. It describes the key organs of each system, including their functions and common diseases. For males, it outlines the testes, penis, scrotum and other internal organs. For females, it details the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina and other organs. It also provides timelines of puberty and reproductive lifespan for each sex. Finally, it lists some common disorders that can affect the reproductive systems, such as cancers, infections and other conditions.
FEMALE & MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 2.pptx

The document summarizes the key parts of the male and female reproductive systems. It describes the external and internal organs of both systems, including their functions in reproduction and sexual response. The female system includes organs like the ovaries, uterus, vagina, and vulva. The male system includes the penis, testicles, seminal vesicles, and prostate gland. Both systems are described in detail with diagrams to enhance understanding of human anatomy and physiology.
Reproduction and issues on sex 2014

This document covers topics related to human reproduction, including:
1. It defines asexual and sexual reproduction, and describes the roles of gametes and fertilization in sexual reproduction.
2. It outlines the male and female reproductive systems, labeling and describing the functions of key organs like the testes, ovaries, uterus and more.
3. It discusses puberty, the menstrual cycle regulated by hormones, sexual intercourse, fertilization, embryo development, fetal development, and the roles of the amniotic sac, amniotic fluid, placenta and umbilical cord in pregnancy.
Human reproduction by Maria

This document discusses the human reproductive system. It describes the primary and secondary sexual characteristics that differentiate males and females. It then explains the female reproductive system including the ovaries, uterus, Fallopian tubes, and vagina. The male reproductive system includes the testicles, vas deferens, urethra, seminal vesicles, and prostate. Fertilization occurs when an ovum and sperm join to form a zygote. Pregnancy lasts about 9 months as the embryo develops into a fetus and eventually a baby ready for birth. Labor involves three phases of dilation, expulsion, and delivery of the afterbirth.
Human reproduction

This document summarizes human reproduction. It describes the primary and secondary sex characteristics of males and females. It explains that reproduction requires both female egg cells and male sperm cells. It then details the female reproductive system including the external genitalia, internal organs, menstrual cycle, and pregnancy. It also outlines the male reproductive system including the penis, testicles, and role of semen. Fertilization occurs when a sperm cell joins with an egg cell to form a zygote, leading to pregnancy and eventual birth.
Human biology3a3b reproduction

The document summarizes the human reproductive system and processes of both males and females. It describes the male and female reproductive organs and their functions. It explains gamete production, fertilization, embryonic development, fetal development and stages of pregnancy. It also discusses puberty, maternal changes during pregnancy, labor and delivery.
4to 9 human reproduction for students

The document summarizes key aspects of sexual and asexual reproduction. It describes several methods of asexual reproduction including binary fission, budding, spore formation, and fragmentation. It then contrasts asexual and sexual reproduction, noting that sexual reproduction involves two gametes (sperm and egg) fusing to form a zygote. The document proceeds to provide details about the male and female reproductive systems in humans, the process of fertilization, embryonic and fetal development, and the role of the placenta in nutrient exchange.
reproductive system.pptx

The document summarizes the male and female reproductive systems. It describes that both systems produce gametes (sperm and eggs) and have organs that work together for fertilization and pregnancy. The male system includes testes that produce sperm and the female includes ovaries that release eggs and a uterus that nourishes a developing fetus during pregnancy. Fertilization occurs when sperm meets an egg in the fallopian tubes, leading to cell division and eventual childbirth.
The human body and reproduction

This document describes the human reproductive system and process of reproduction from puberty through birth. It explains that during adolescence, boys and girls undergo puberty where their reproductive organs mature. It then outlines the male and female reproductive systems and their function. It details the process of fertilization where sperm and egg unite, and describes pregnancy in three trimesters. Finally, it summarizes the three stages of birth: dilation, expulsion, and delivery of the placenta.
Unit 3 (2)

This document summarizes the key stages of human reproduction. It describes the differences between male and female reproductive systems and sex cells. The male sex cell is sperm, while the female is the ovum or egg cell. Fertilization occurs when a sperm fertilizes an ovum to form a zygote. The zygote then develops into an embryo and fetus over a period of 8-9 months, receiving nutrients from the mother in the uterus. Birth occurs after 9 months of development. The document also briefly describes the menstrual cycle in females.
Unit 3 (2)

This document summarizes the key stages of human reproduction. It describes the differences between male and female reproductive systems and sex cells. The male sex cell is sperm, while the female is the ovum or egg cell. Fertilization occurs when a sperm fertilizes an ovum to form a zygote. The zygote then develops into an embryo and fetus over a period of 8-9 months, receiving nutrients from the mother in the uterus. Birth occurs after 9 months of development. The document also briefly describes the menstrual cycle in females.
Sexual reproduction in animals ppt

Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes to produce offspring that contain a mix of characteristics from both parents. This allows for more variations in offspring, which is advantageous for species survival when environmental conditions change. Variations in offspring increase the chance that some will possess traits making them resistant to new threats. Sexual reproduction requires contributions from both sexes through their different gametes - sperm from males and eggs from females.
Sexual reproduction in Human methods and techniques

The placenta functions to exchange nutrients and waste between the mother and fetus. It attaches to the uterine wall and connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord. The placenta allows oxygen, glucose, amino acids and salts to pass from the mother's bloodstream to the fetus's bloodstream, while carbon dioxide and urea pass in the opposite direction, into the mother's bloodstream. This exchange occurs across the thin walls of the blood vessels without the bloodstreams directly mixing. The placenta regulates this exchange and protects the fetus from high blood pressure.
Human reproduction completed

This document provides an overview of human reproduction for both males and females. It describes the internal and external anatomy of both the male and female reproductive systems. For females, it explains the menstrual cycle, hormones involved, ovulation and how fertilization occurs if the egg is fertilized by sperm. For males, it describes sperm production and ejaculation. If fertilization is successful, it describes the process of implantation and early fetal development. It also briefly discusses birth, breastfeeding and the possibility of twins.
Human development and sex determination 

1) Fertilization occurs when a sperm joins an egg, forming a zygote with 46 chromosomes - 23 from each parent. This determines the new individual as either 46,XX (female) or 46,XY (male).
2) The zygote undergoes cell division and develops into an embryo over a series of stages. By the end of the first trimester, all major organ systems have formed.
3) Sexual differentiation is determined by chromosomes, gonads, and hormone exposure. The presence of the SRY gene on the Y chromosome triggers testes development; its absence leads to ovaries. Subsequent hormone secretions shape internal and external genitalia along male or female lines.
Reproductive system science7

The male reproductive system consists of external organs like the penis and scrotum which contains the testes, and internal organs like the vas deferens. The testes produce sperm and testosterone. Sperm contains genetic information and a tail that propels it. In females, the ovaries produce eggs and the uterus nourishes embryo development. During ovulation, an egg is released and must be fertilized within 24 hours. If not fertilized, menstruation occurs through the cervix and vagina. The menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones and usually occurs monthly from puberty to menopause.
Human reproduction ppt

The document provides information about human reproduction:
- It describes the male and female reproductive systems and the journey of sperm and egg through the systems. The sperm fertilizes the egg in the fallopian tubes.
- It explains the process of fertilization and the early stages of development from zygote to embryo to fetus. The fetus develops over nine months before birth.
- Key parts of the male system that are mentioned include the testes, penis, and sperm. The female system includes the ovaries, uterus, fallopian tubes, and vagina.
humanembryonicdevelopment-141015070629-conversion-gate02 (1).pdf

The stages of pregnancy and development include fertilization, embryonic development, fetal growth and development, and childbirth. Key events include zygote formation within a few days of conception, implantation in the uterus around 1 week, and formation of the three primary germ layers and development of organ systems by 8 weeks. The fetus continues to grow and differentiate over the next 5 months, nearly doubling in size each month. Birth occurs around 9 months after internal and external changes prepare the fetus for life outside the womb.
Similar to Reprodinhumans 170322174812 (20)
Sexual reproduction in Human methods and techniques

Sexual reproduction in Human methods and techniques
humanembryonicdevelopment-141015070629-conversion-gate02 (1).pdf

humanembryonicdevelopment-141015070629-conversion-gate02 (1).pdf
More from Maria Teresa Asprella Libonati
Reprod in humans

The document describes human reproduction. It explains that sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes. The male system produces sperm in the testes and transfers them via the sperm ducts. The female system contains ovaries which hold eggs from birth. At ovulation, an egg is released into the fallopian tubes where fertilization by sperm may occur, forming a zygote. The zygote implants in the uterus and develops via the placenta and umbilical cord until birth.
Rep plants part 3

This document summarizes the processes of plant reproduction, including pollination and fertilization. It discusses:
- How pollen is transferred from the stamen to the carpel during pollination.
- The pollen tube grows and transfers the male gamete to the ovule contained in the ovary. Fertilization occurs when the male and female gametes fuse.
- After fertilization, the zygote develops into an embryo inside the seed. The ovary develops into fruit, protecting the seed until conditions allow for germination.
Rep in plants 2

The document describes the structure and function of flower parts, including that flowers produce male and female gametes. Sepals protect the developing flower, petals attract insects for cross-pollination, the nectary produces nectar, the carpel contains ovules for female gamete production, and the stamen contains pollen grains with male gametes. Pollination is the transfer of pollen and can occur through insect-pollination, where insects carry pollen between flowers, or wind-pollination. Fertilization happens when pollen nuclei fuse with ovule nuclei.
Repr in plants

Plants can reproduce both asexually and sexually. Asexual reproduction involves mitosis and results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in offspring with a unique combination of genes from both parents. Gametes are haploid cells that are formed through meiosis in the parent organism in order to combine and form a diploid zygote.
Homeostasis pt2

The hypothalamus regulates body temperature through negative feedback by sensing blood temperature and sending signals to alter processes like shivering, sweating and blood vessel constriction/dilation. The pancreas and liver also use negative feedback to keep blood glucose levels steady by secreting insulin and glucagon which signal the liver to store or release glucose as needed. Diabetes occurs when this process is disrupted, resulting in dangerous fluctuations in blood glucose.
Homeostasis

Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of a constant internal environment in the body, keeping factors such as temperature, water concentration, and glucose levels stable despite changes in the external environment. This allows cells to function efficiently and prevents damage. Endothermic animals like mammals and birds internally regulate their body temperature, while ectothermic animals like reptiles rely on external temperatures. The skin plays an important role in homeostasis through its structure - the epidermis contains cells that protect the body and produce melanin and keratin, while the dermis contains sweat glands, blood vessels, and nerves that help regulate temperature.
Drugs

This document discusses various drugs and their effects on the human body. It provides information on antibiotics and how bacteria are evolving resistance. It also discusses opioids like heroin and their addictive properties. The document covers alcohol consumption and alcoholism. It addresses anabolic steroids used for muscle growth and the health risks. Finally, it summarizes the harmful effects of smoking tobacco, including increased cancer and heart disease risks.
Endocrine system

The endocrine system communicates messages via hormones released directly into the bloodstream from ductless glands. Hormones are carried throughout the body and affect target organs. Important endocrine glands include the adrenal glands, which secrete adrenaline in response to stress signals from the brain, causing effects like increased heart rate and breathing. Plants also respond to stimuli through hormones like auxin, which is produced in shoot tips and causes phototropism by stimulating faster growth on the shady side of shoots, bending them towards light sources.
Coordination2

This document summarizes several parts of the eye and vision system. It describes the main sense organs including the eye, ear, nose, tongue, and skin. It then focuses on the eye, explaining that the retina contains rod and cone cells that are receptors sensitive to light. The iris controls the size of the pupil to regulate the amount of light entering the eye. The lens focuses light onto the retina, where it is transmitted via the optic nerve to the brain to create an image.
Coordination(1)

The document discusses coordination between receptors and effectors in the body. It describes how stimuli are detected by receptors and responses are carried out by effectors, such as muscles and glands. There are two pathways for coordination - the nervous system, which uses nerves and electrical impulses, and the endocrine system, which uses hormones. The nervous system allows for very fast coordination, which is important for functions like hunting and avoiding predators. It then describes the basic anatomy and processes of the nervous system in more detail.
Unit 12

The human excretory system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine via tiny tubules called nephrons. The urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters and into the bladder, where it is stored until excretion through the urethra. For those with kidney failure, dialysis provides an artificial filtration of the blood to remove waste, while transplantation involves surgically implanting a donor kidney to replace non-functioning ones.
Excretion

Excretion is the removal of waste products from an organism. These waste products include the byproducts of metabolism like urea and ammonia, as well as toxic materials and substances in excess. Egestion refers specifically to the passing out of undigested food through the anus, whereas excretion removes metabolic waste products. In mammals, excess protein is broken down into urea in the liver through a process called deamination and then transported to the kidneys for excretion in urine. The liver plays an important role in metabolizing nutrients and filtering waste from the bloodstream.
Respiration

The respiratory system allows for gas exchange in humans. Air enters through the nose or mouth and passes through the trachea into the lungs. In the lungs, the bronchi branch into smaller tubes called bronchioles that end in alveoli, which are tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs. Oxygen from the inhaled air passes into the bloodstream, and carbon dioxide passes from the bloodstream into the alveoli to be exhaled. Breathing is driven by the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contracting and relaxing to expand and contract the lungs and chest.
Resp intro

This document discusses respiration and gas exchange. It explains that aerobic respiration uses oxygen to break down glucose, releasing carbon dioxide and water. Anaerobic respiration in yeast breaks down glucose into alcohol and carbon dioxide without oxygen. Anaerobic respiration in humans produces lactic acid instead of alcohol when oxygen cannot be supplied fast enough to muscles during vigorous exercise.
Immunity2

The document discusses how the immune system responds to pathogens. When a pathogen enters the body, lymphocytes recognize it and produce antibodies specific to that pathogen. The antibodies coat the pathogen and recruit phagocytes to destroy it. Memory cells remain after an infection to allow for a faster response if the same pathogen is encountered again. It takes time for antibodies to be produced and for the pathogen to be eliminated, during which time the pathogen may continue to reproduce. Vaccination provides active immunity by exposing the body to dead or weakened pathogens to stimulate memory cell production without causing disease.
Immunity

A British woman visiting India was bitten by a dog but did not seek medical treatment. Seven weeks later back in Britain, she fell ill and doctors could not diagnose her mild symptoms. She was eventually taken to a specialist tropical diseases hospital where it was discovered she had rabies from the dog bite in India. Rabies is a viral disease transmitted through infected animal bites that is almost always fatal if left untreated.
Unit 9 transport in animals

The document discusses the circulatory system and blood transport in animals. It describes single and double circulatory systems. In a single circulation, blood travels from the heart to the gills to absorb oxygen and then to the organs before returning to the heart. In a double circulation, there are two circuits - one where blood passes from the heart to the lungs to absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide, and another where blood passes from the heart to the organs and tissues to deliver oxygen before returning to the heart. A double circulation has evolved to create more pressure to pump blood around the system and separate oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood.
Unit 7 digestion

The document discusses the process of digestion. It begins with an overview of the alimentary canal and its parts, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. It then covers the stages of digestion - ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion. Specific topics covered include the roles and locations of enzymes in breaking down food, as well as the functions of organs like the liver, gallbladder and pancreas in digestion.
Unit 7 animal nutrition - diet

This document provides information about animal nutrition and balanced diets. It defines what a balanced diet is and lists the seven major types of nutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, water, and fiber. It describes the sources and functions of these nutrients and explains that an unbalanced diet can lead to deficiency diseases. Specific nutrient deficiencies that are discussed include vitamin C (scurvy), vitamin D (rickets), vitamin A (night blindness), calcium, and iron (anemia). The document also covers malnutrition conditions like marasmus and kwashiorkor that can result from poor nutrition.
More from Maria Teresa Asprella Libonati (20)
Recently uploaded
How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method

Odoo provides an option for creating a module by using a single line command. By using this command the user can make a whole structure of a module. It is very easy for a beginner to make a module. There is no need to make each file manually. This slide will show how to create a module using the scaffold method.
clinical examination of hip joint (1).pdf

described clinical examination all orthopeadic conditions .
The History of Stoke Newington Street Names

Presented at the Stoke Newington Literary Festival on 9th June 2024
www.StokeNewingtonHistory.com
Main Java[All of the Base Concepts}.docx

This is part 1 of my Java Learning Journey. This Contains Custom methods, classes, constructors, packages, multithreading , try- catch block, finally block and more.
ANATOMY AND BIOMECHANICS OF HIP JOINT.pdf

it describes the bony anatomy including the femoral head , acetabulum, labrum . also discusses the capsule , ligaments . muscle that act on the hip joint and the range of motion are outlined. factors affecting hip joint stability and weight transmission through the joint are summarized.
How to Add Chatter in the odoo 17 ERP Module

In Odoo, the chatter is like a chat tool that helps you work together on records. You can leave notes and track things, making it easier to talk with your team and partners. Inside chatter, all communication history, activity, and changes will be displayed.
Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat

Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat
Exploiting Artificial Intelligence for Empowering Researchers and Faculty, In...

Exploiting Artificial Intelligence for Empowering Researchers and Faculty, In...Dr. Vinod Kumar Kanvaria
Exploiting Artificial Intelligence for Empowering Researchers and Faculty,
International FDP on Fundamentals of Research in Social Sciences
at Integral University, Lucknow, 06.06.2024
By Dr. Vinod Kumar KanvariaHow to Fix the Import Error in the Odoo 17

An import error occurs when a program fails to import a module or library, disrupting its execution. In languages like Python, this issue arises when the specified module cannot be found or accessed, hindering the program's functionality. Resolving import errors is crucial for maintaining smooth software operation and uninterrupted development processes.
RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3

RPMS Template 2023-2024 by: Irene S. Rueco
The simplified electron and muon model, Oscillating Spacetime: The Foundation...

Discover the Simplified Electron and Muon Model: A New Wave-Based Approach to Understanding Particles delves into a groundbreaking theory that presents electrons and muons as rotating soliton waves within oscillating spacetime. Geared towards students, researchers, and science buffs, this book breaks down complex ideas into simple explanations. It covers topics such as electron waves, temporal dynamics, and the implications of this model on particle physics. With clear illustrations and easy-to-follow explanations, readers will gain a new outlook on the universe's fundamental nature.
The Diamonds of 2023-2024 in the IGRA collection

A review of the growth of the Israel Genealogy Research Association Database Collection for the last 12 months. Our collection is now passed the 3 million mark and still growing. See which archives have contributed the most. See the different types of records we have, and which years have had records added. You can also see what we have for the future.
Executive Directors Chat Leveraging AI for Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion

Let’s explore the intersection of technology and equity in the final session of our DEI series. Discover how AI tools, like ChatGPT, can be used to support and enhance your nonprofit's DEI initiatives. Participants will gain insights into practical AI applications and get tips for leveraging technology to advance their DEI goals.
How to Make a Field Mandatory in Odoo 17

In Odoo, making a field required can be done through both Python code and XML views. When you set the required attribute to True in Python code, it makes the field required across all views where it's used. Conversely, when you set the required attribute in XML views, it makes the field required only in the context of that particular view.
Walmart Business+ and Spark Good for Nonprofits.pdf

"Learn about all the ways Walmart supports nonprofit organizations.
You will hear from Liz Willett, the Head of Nonprofits, and hear about what Walmart is doing to help nonprofits, including Walmart Business and Spark Good. Walmart Business+ is a new offer for nonprofits that offers discounts and also streamlines nonprofits order and expense tracking, saving time and money.
The webinar may also give some examples on how nonprofits can best leverage Walmart Business+.
The event will cover the following::
Walmart Business + (https://business.walmart.com/plus) is a new shopping experience for nonprofits, schools, and local business customers that connects an exclusive online shopping experience to stores. Benefits include free delivery and shipping, a 'Spend Analytics” feature, special discounts, deals and tax-exempt shopping.
Special TechSoup offer for a free 180 days membership, and up to $150 in discounts on eligible orders.
Spark Good (walmart.com/sparkgood) is a charitable platform that enables nonprofits to receive donations directly from customers and associates.
Answers about how you can do more with Walmart!"
Recently uploaded (20)
How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method

How to Build a Module in Odoo 17 Using the Scaffold Method
Liberal Approach to the Study of Indian Politics.pdf

Liberal Approach to the Study of Indian Politics.pdf
Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat

Azure Interview Questions and Answers PDF By ScholarHat
Exploiting Artificial Intelligence for Empowering Researchers and Faculty, In...

Exploiting Artificial Intelligence for Empowering Researchers and Faculty, In...
RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3

RPMS TEMPLATE FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2023-2024 FOR TEACHER 1 TO TEACHER 3
The simplified electron and muon model, Oscillating Spacetime: The Foundation...

The simplified electron and muon model, Oscillating Spacetime: The Foundation...
Executive Directors Chat Leveraging AI for Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion

Executive Directors Chat Leveraging AI for Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
Walmart Business+ and Spark Good for Nonprofits.pdf

Walmart Business+ and Spark Good for Nonprofits.pdf
Reprodinhumans 170322174812
- 2. Human Reproductive • Sexual Reproductive. • Male gamete fuses with female gamete to form a zygote
- 3. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female
- 4. Thumbnail.
- 5. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female • OVARIES • Two ovaries contain ova (eggs). Ova = female gametes • Women have these cells in their bodies from birth, whereas men produce new sperm continually = meaning once the ova are finished, the female can no longer reproduce
- 6. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female • OVARIES • Two ovaries contain ova (eggs). Ova = female gametes • Women have these cells in their bodies from birth, whereas men produce new sperm continually = meaning once the ova are finished, the female can no longer reproduce
- 8. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female • OVIDUCTS or FALLOPIAN TUBES • From each ovary is an oviduct/fallopian tube. • The oviduct is lined with ciliated cells. Every month, an ovum (egg) develops and becomes mature, and is released from an ovary. The cilia move the ovum along the oviduct and into the uterus.
- 10. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female • UTERUS or WOMB • The uterus is a muscular bag with a soft lining. • It is where a baby develops until its birth. • The cervix is a ring of muscle at the lower end of the uterus. It keeps the baby in place while the woman is pregnant.
- 12. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female • VAGINA • The vagina is a muscular tube that leads from the cervix to the outside of the woman's body. The bladder opening, urethra, it is separate from the vagina. It passes urine out of the body from the bladder.
- 14. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Male
- 16. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Male • SPERM DUCT and GLANDS • The sperm pass through the sperm ducts, and mix with fluids produced by glands. • The fluids provide the sperm cells with nutrients. This mixture is called semen.
- 18. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Male • SPERM DUCT and GLANDS • The sperm pass through the sperm ducts, and mix with fluids produced by glands. • The fluids provide the sperm cells with nutrients. This mixture is called semen.
- 20. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Sperm Production • Sperm develop in the testis, by meiosis. • From puberty, sperm is produced continuously until death. • QUESTION? • Why are the testes on the outside of the body? • Sperm production is sensitive to heat. Too hot and cells will not develop.
- 21. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Egg Production • Girl is already born with all her eggs. At puberty, some begin to mature. (one at a time) • Ovulation = when the egg is mature, it will burst from the ovary into the oviduct. • PUBERTY = "stage of development during which sexual maturity is reached"
- 22. Fertilization and development of the embryo • Fertilisation is the fusion of the nucleus of a male gamete with the nucleus of a female gamete, producing a new cell called a zygote. This then matures into an embryo.
- 24. Fertilization and development of the embryo • Fertilisation • The egg is released from the ovary and moves toward the oviduct. • A sperm has been ejaculated into the vagina and is travelling up the cervix. (Using their tails to swim)
- 25. Fertilization and development of the embryo • Fertilisation • The egg and sperm meet at the oviduct and the process of fertilisation begins. Only the head of the one sperm enters the egg. After entry, the egg membrane becomes impenetrable to other sperm
- 27. Fertilization and development of the embryo • Fertilisation • Now a zygote has formed. • The zygote moves slowly down the oviducts. Dividing by mitosis, to form an embryo. • NB. Cilia in oviduct "sweep" the embryo along the tube. (peristalsis) • EMBRYO = an immature organism before all the organs have formed • This embryo is fed from yolk of the egg.
- 28. Fertilization and development of the embryo • Implantation • After several hours, the embryo reaches the uterus • It sinks into the spongy lining of the wall.
- 30. The roles of the placenta • The Placenta • After fertilisation, the newly-formed zygote divides repeatedly to form a ball of cells called an embryo. This becomes implanted in the wall of the uterus. • After 11 weeks of development, the embryo is called a fetus. The amniotic sac produces amniotic fluid, which surrounds and protects the developing embryo.
- 32. The roles of the placenta • The Placenta • A placenta, connected by an umbilical cord, develops from the embryo. The placenta anchors the embryo in the uterus. • Umbilical cord:- • nutrients and oxygen to move from the mother to the embryo • waste materials and carbon dioxide to move from the embryo to the mother • There is no connection between the circulatory systems of the embryo and its mother, so their blood doesn’t mix. • (Separated by the placenta wall) • These materials pass from one to the other by diffusion. (wall is thin)
- 34. The roles of the placenta • The Placenta • As the fetus grows, so does the placenta • At birth the placenta is a flat disc 12cm x 3cm
- 36. The roles of the placenta • Development of the embryo/fetus • Zygote Embryo Fetus • At fertilisation Simple ball of cells Cells develop into different types (identical cells) (10-11 Weeks, all organs in place) (6 Weeks, organs begin to form) (8 Weeks, muscles move) (10-38 Weeks, continues to develop) (38 Weeks, ready to be born)
- 38. The roles of the placenta • BIRTH • Birth begins with strong muscle contractions in uterus wall. Stretching the cervix open. • Amniotic sac breaks When cervix is wide enough, muscles push the baby down through the cervix and out of the vagina The baby is still attached by the umbilical cord and placenta. Placenta no longer needed (baby can breath for itself) The placenta detaches from the uterus wall and passes through the vagina (afterbirth) Umbilical cord is cut, painless because there are no nerves. Stump forms the baby's navel A few weeks before birth the fetus usually turns over, so head is next to cervix
- 39. The roles of the placenta • BIRTH • Birth begins with strong muscle contractions in uterus wall. Stretching the cervix open. • Amniotic sac breaks When cervix is wide enough, muscles push the baby down through the cervix and out of the vagina The baby is still attached by the umbilical cord and placenta. Placenta no longer needed (baby can breath for itself) The placenta detaches from the uterus wall and passes through the vagina (afterbirth) Umbilical cord is cut, painless because there are no nerves. Stump forms the baby's navel A few weeks before birth the fetus usually turns over, so head is next to cervix
- 40. • 1 Which statement about sex cells is correct? • Sperm are male gametes • Ova are male gametes • Sperm are female gametes • 2 In reproduction, what is fertilisation? • When a male and female gamete join • When a farmer puts manure on farmland • When plants drop seeds onto the ground QUESTIONS
- 41. • 3 What is a zygote? • A cell formed when two embryos join, which will develop into a gamete • A cell formed when two gametes join, which will develop into an embryo • A cell formed when two gametes join, which will develop into a gland • 4 Which of the following is not a part of the male reproductive system? • Penis • Testes • Uterus QUESTIONS
- 42. • 5 Where are the female sex cells contained? • In the uterus • In the ovaries • In the ova • 6 What is ovulation? • The release of a mature egg cell • The loss of the lining of the uterus • The joining of a male sex cell and a female sex cell QUESTIONS
- 43. • 7 Which way does blood normally pass across the placenta? • From the mother to the foetus • From the foetus to the mother • Blood does not pass across the placenta QUESTIONS