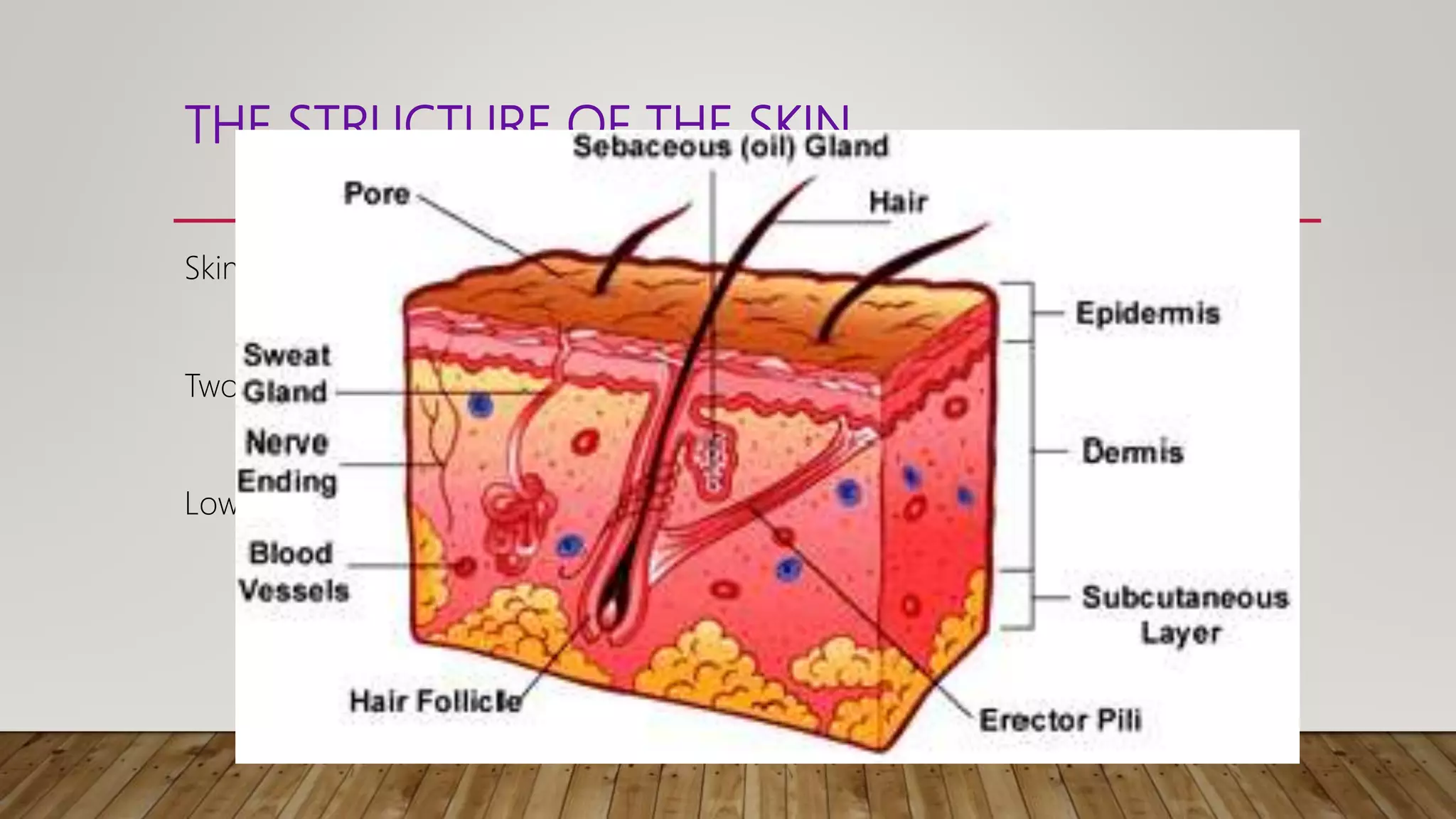
Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of a constant internal environment in the body, keeping factors such as temperature, water concentration, and glucose levels stable despite changes in the external environment. This allows cells to function efficiently and prevents damage. Endothermic animals like mammals and birds internally regulate their body temperature, while ectothermic animals like reptiles rely on external temperatures. The skin plays an important role in homeostasis through its structure - the epidermis contains cells that protect the body and produce melanin and keratin, while the dermis contains sweat glands, blood vessels, and nerves that help regulate temperature.