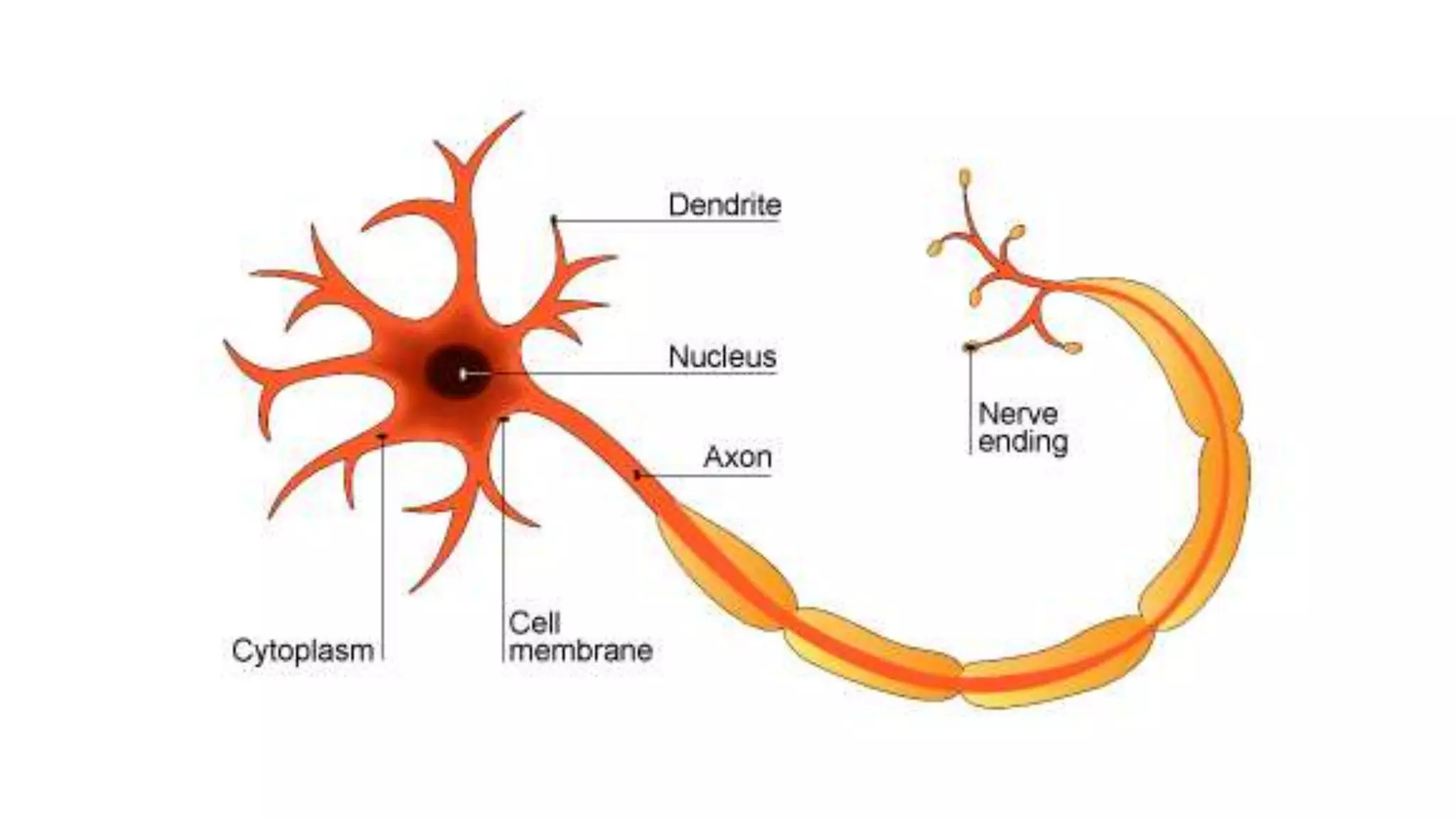
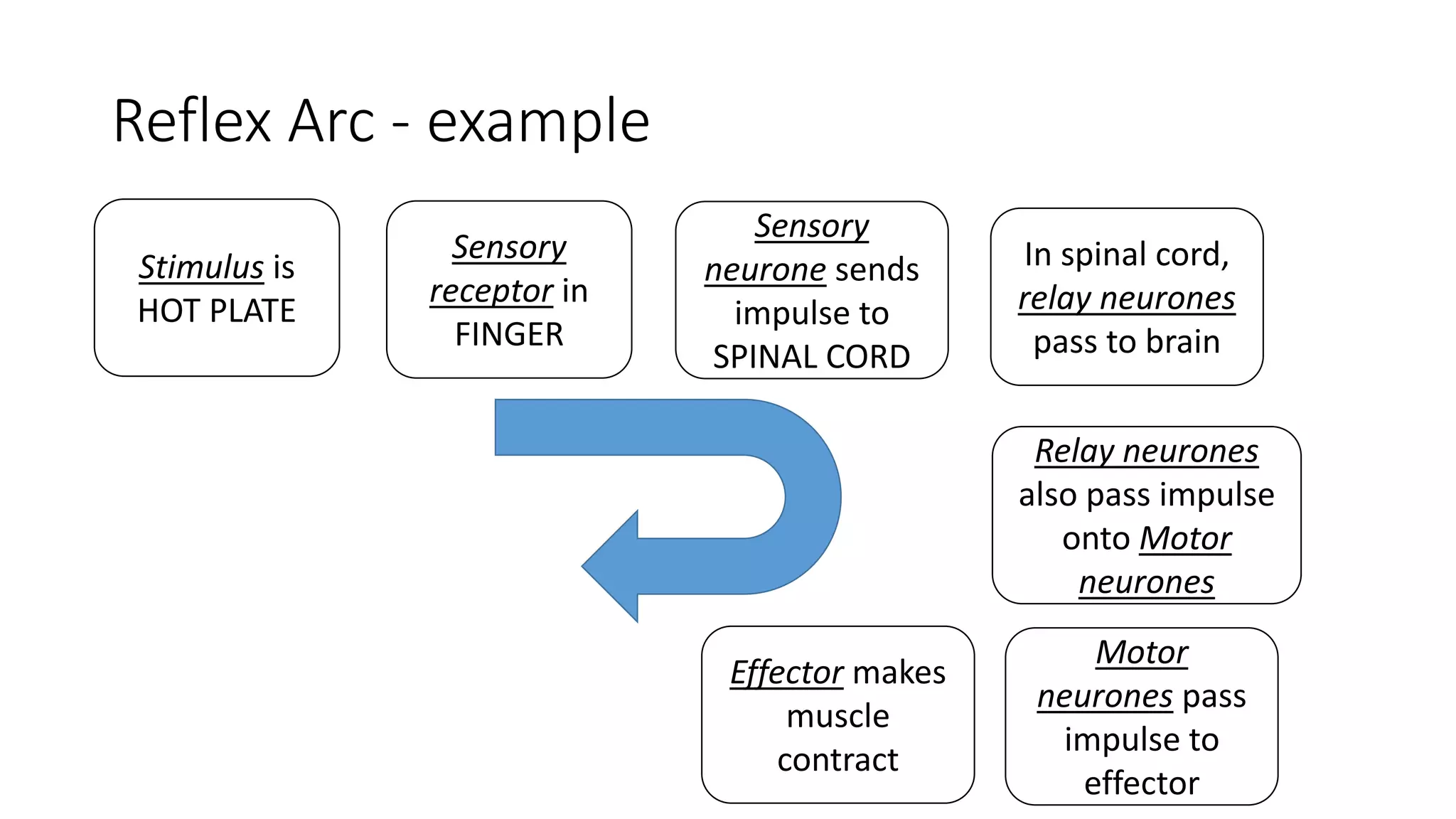
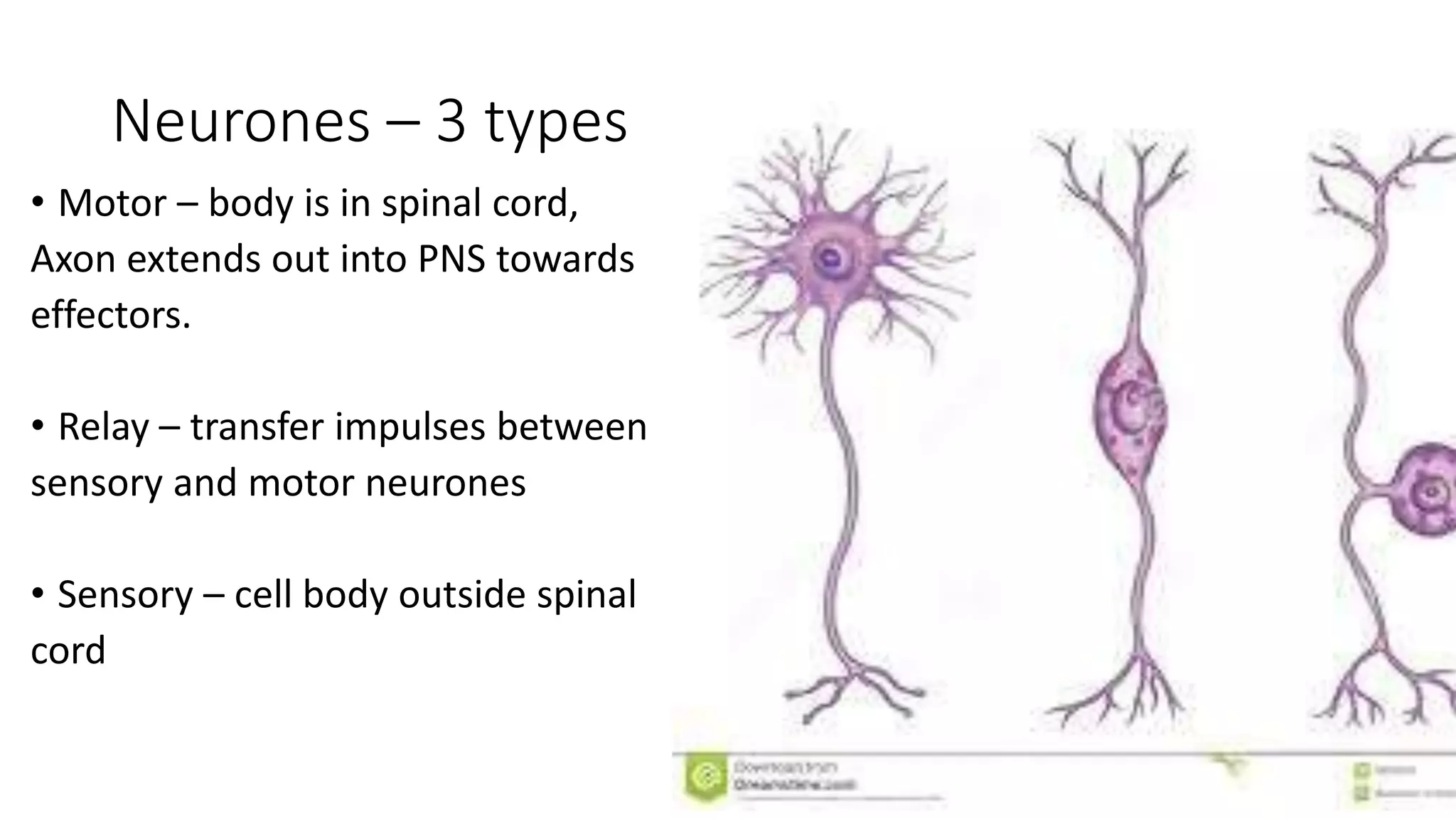
The document discusses coordination between receptors and effectors in the body. It describes how stimuli are detected by receptors and responses are carried out by effectors, such as muscles and glands. There are two pathways for coordination - the nervous system, which uses nerves and electrical impulses, and the endocrine system, which uses hormones. The nervous system allows for very fast coordination, which is important for functions like hunting and avoiding predators. It then describes the basic anatomy and processes of the nervous system in more detail.