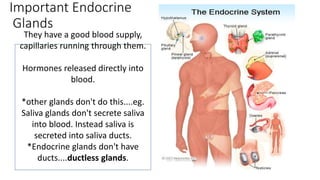
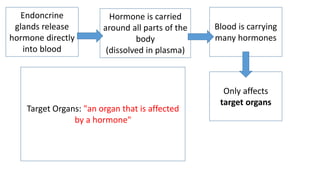
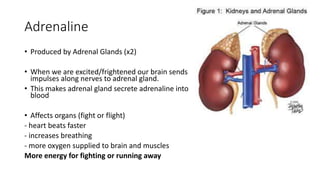
The endocrine system communicates messages via hormones released directly into the bloodstream from ductless glands. Hormones are carried throughout the body and affect target organs. Important endocrine glands include the adrenal glands, which secrete adrenaline in response to stress signals from the brain, causing effects like increased heart rate and breathing. Plants also respond to stimuli through hormones like auxin, which is produced in shoot tips and causes phototropism by stimulating faster growth on the shady side of shoots, bending them towards light sources.