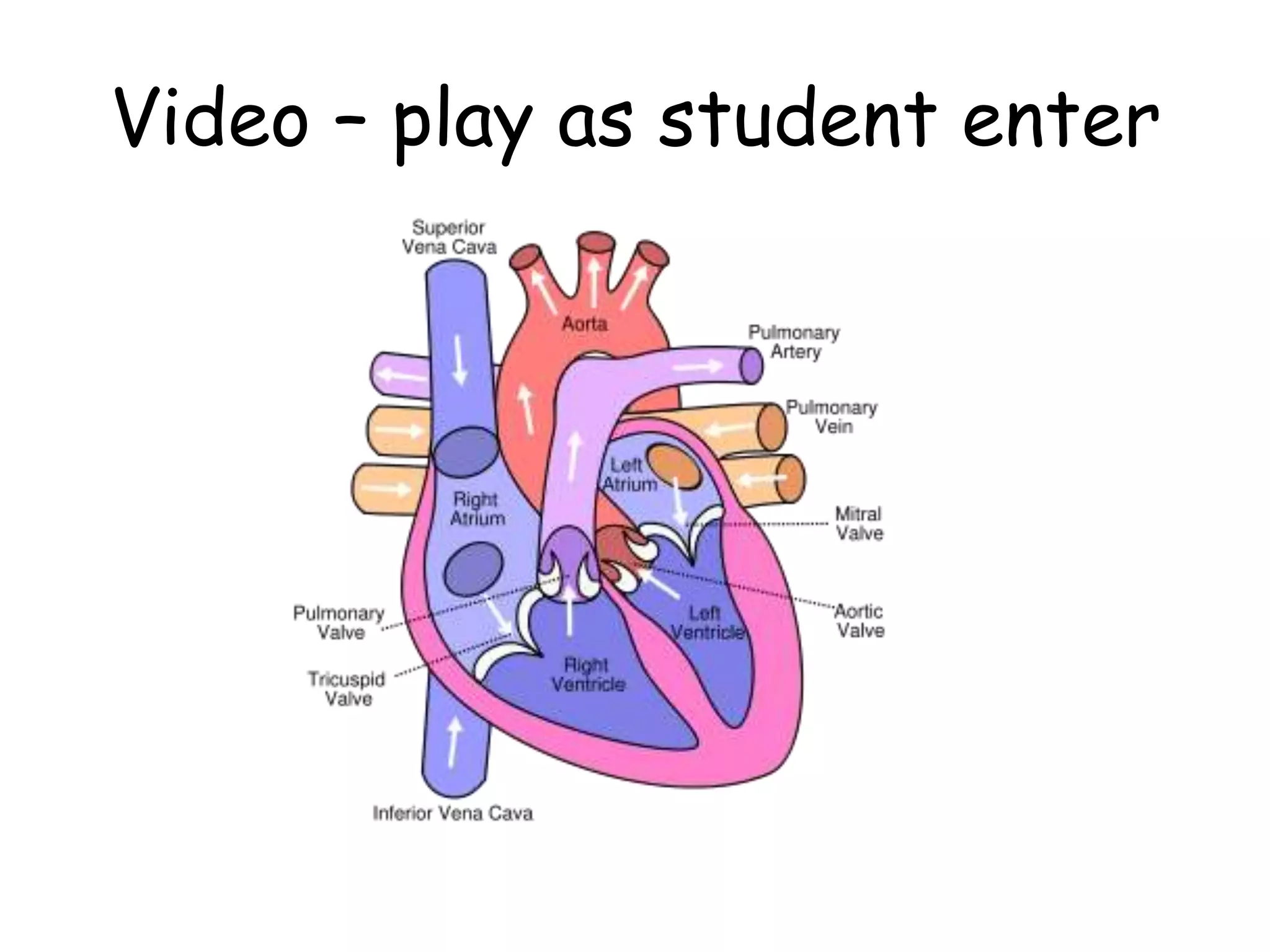
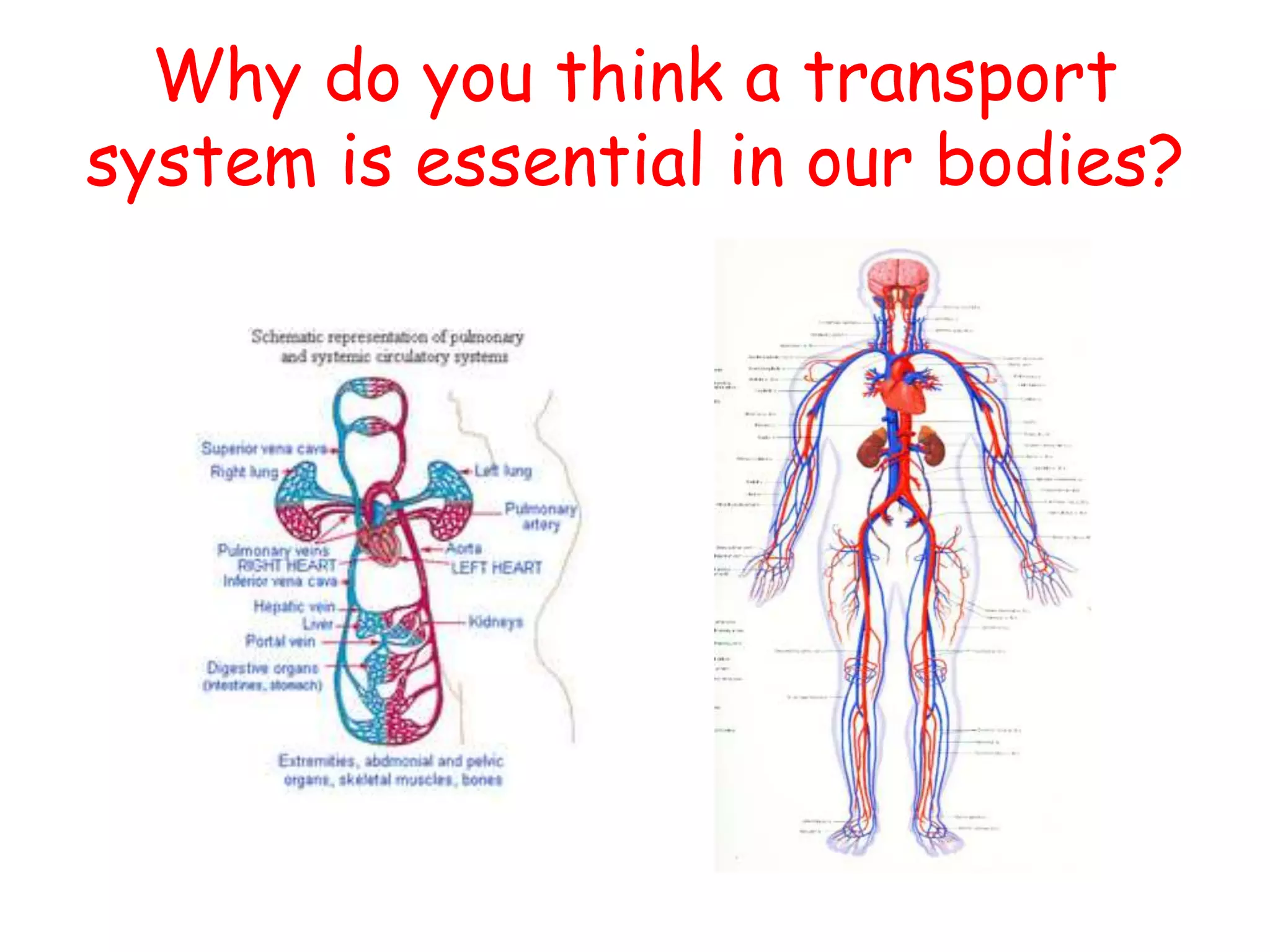
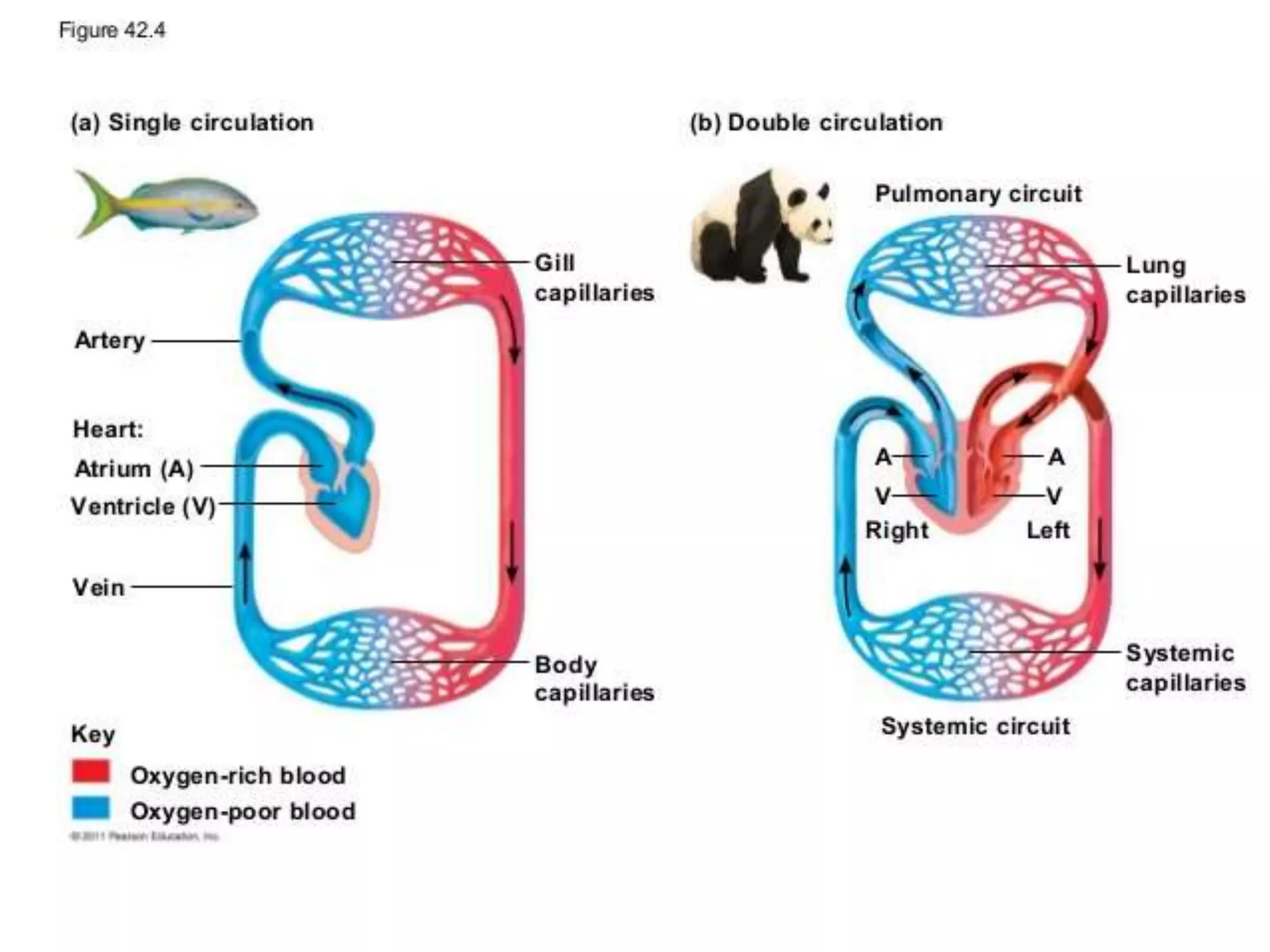
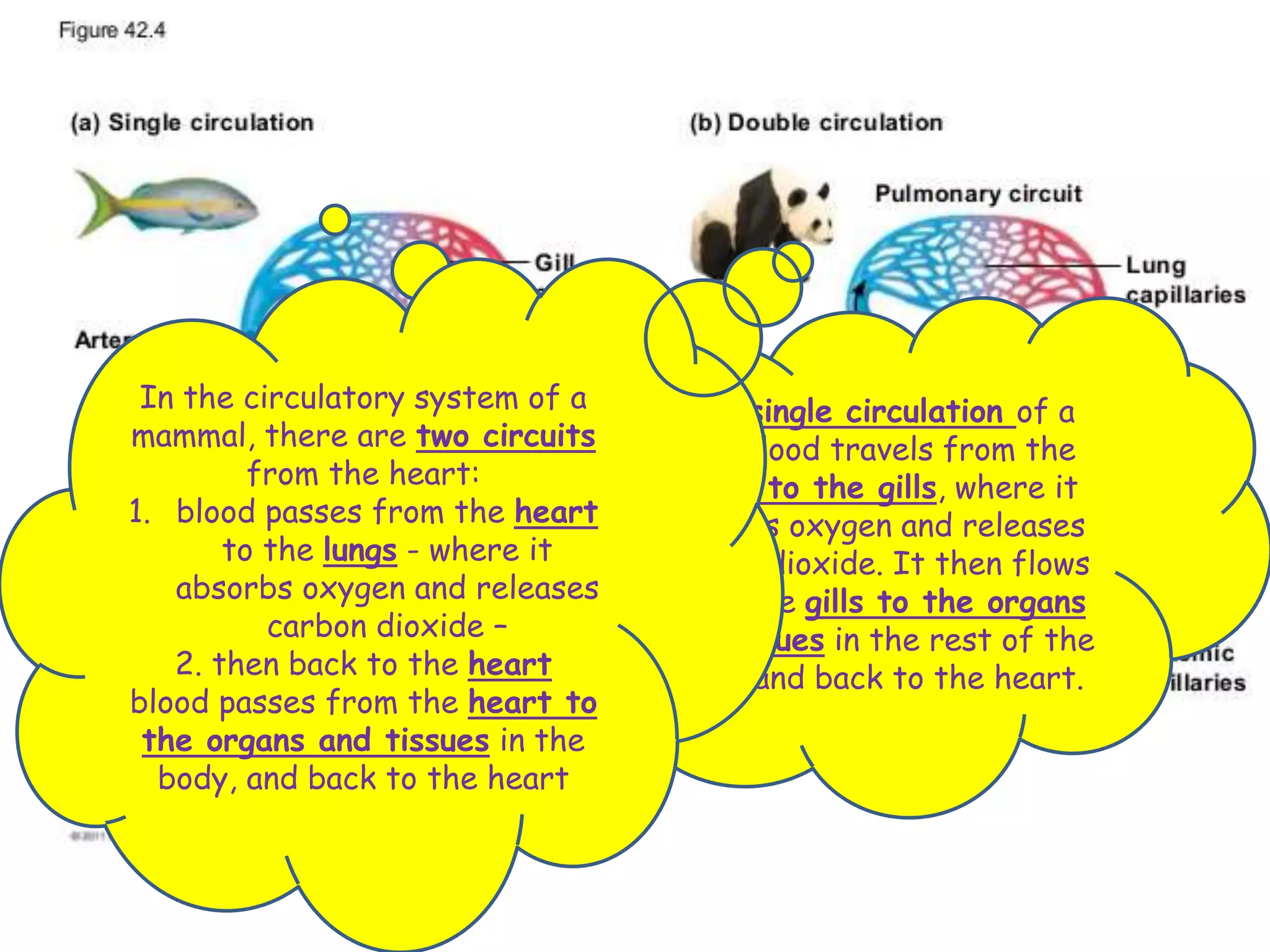
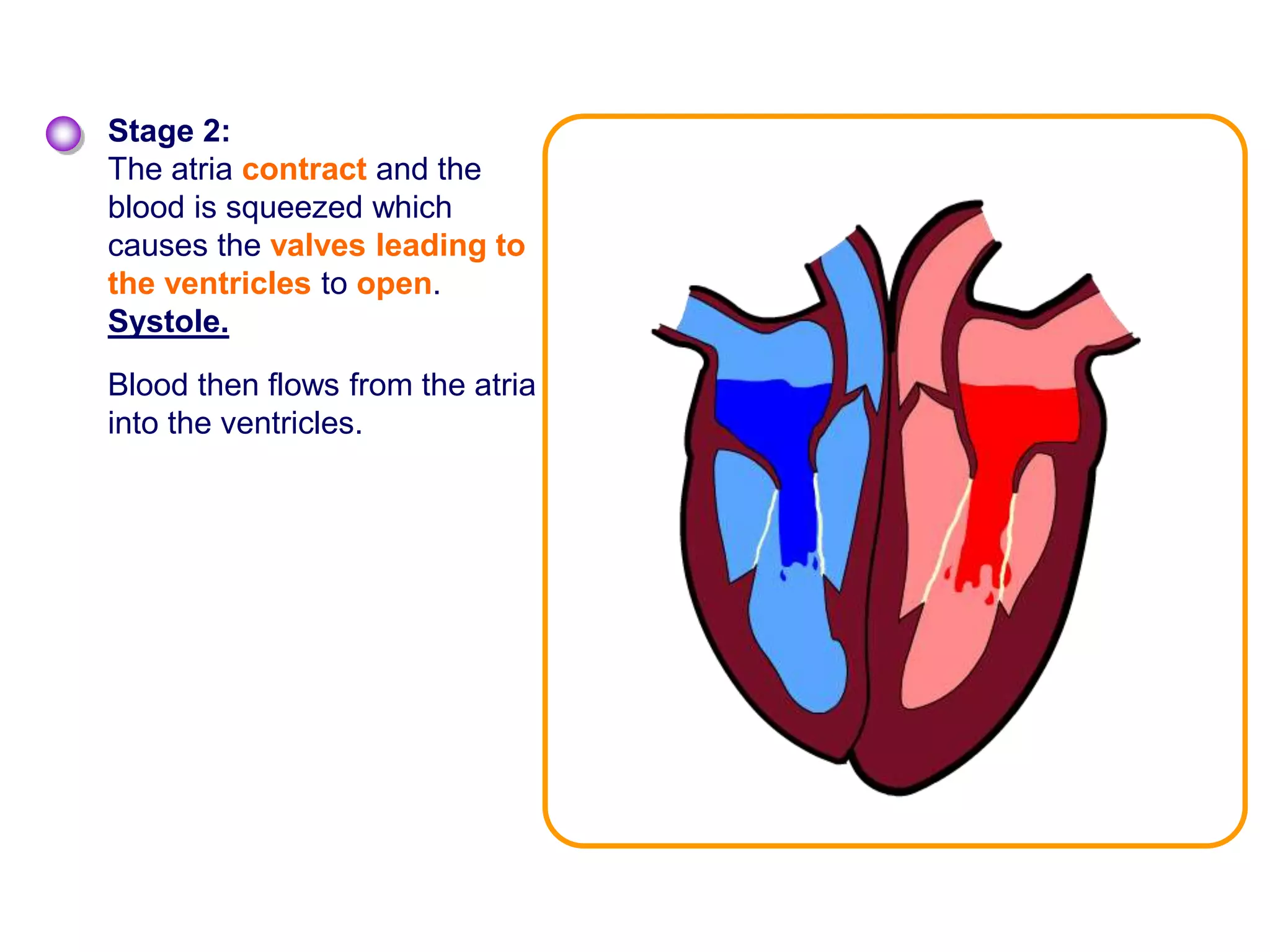
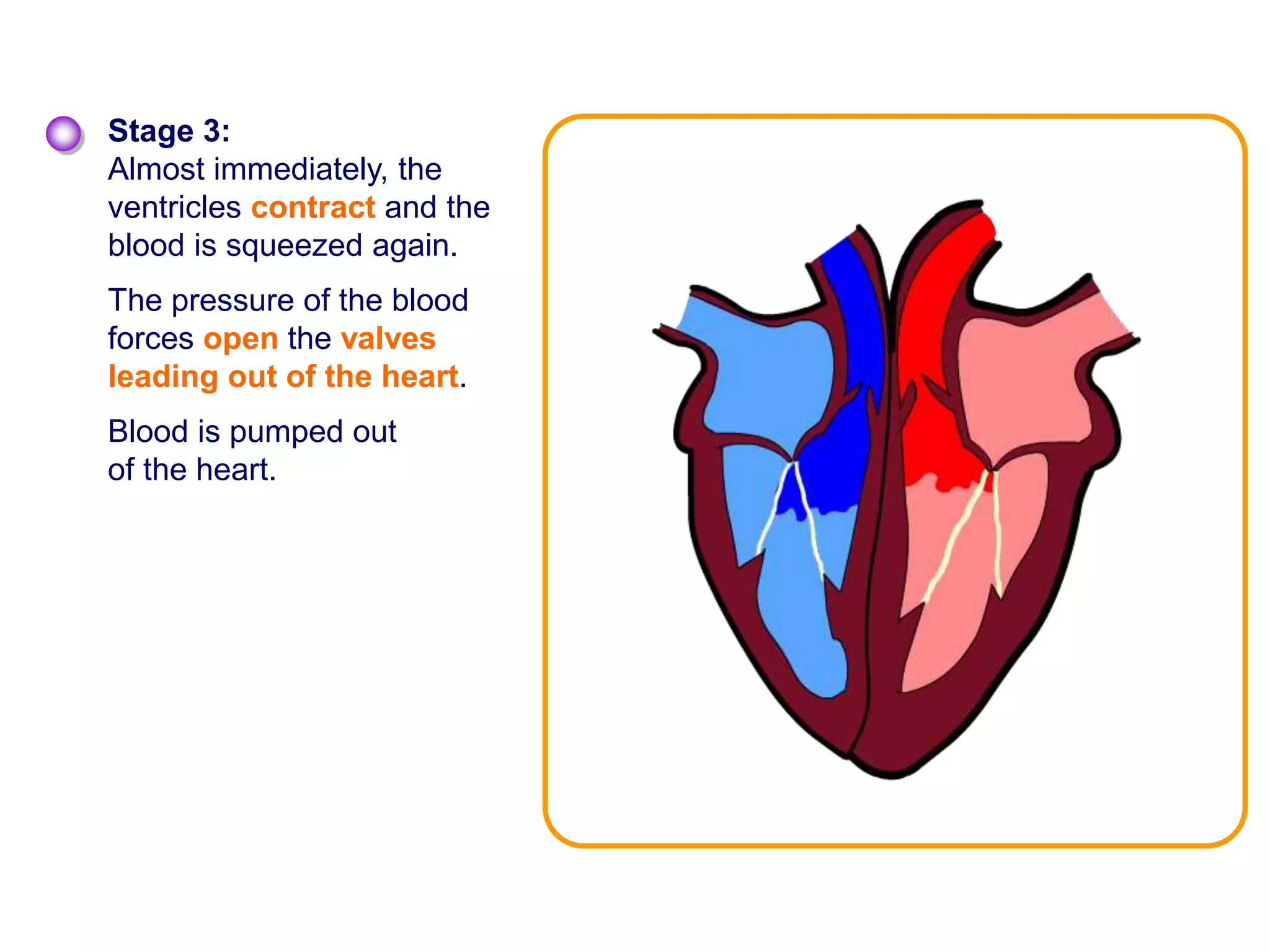
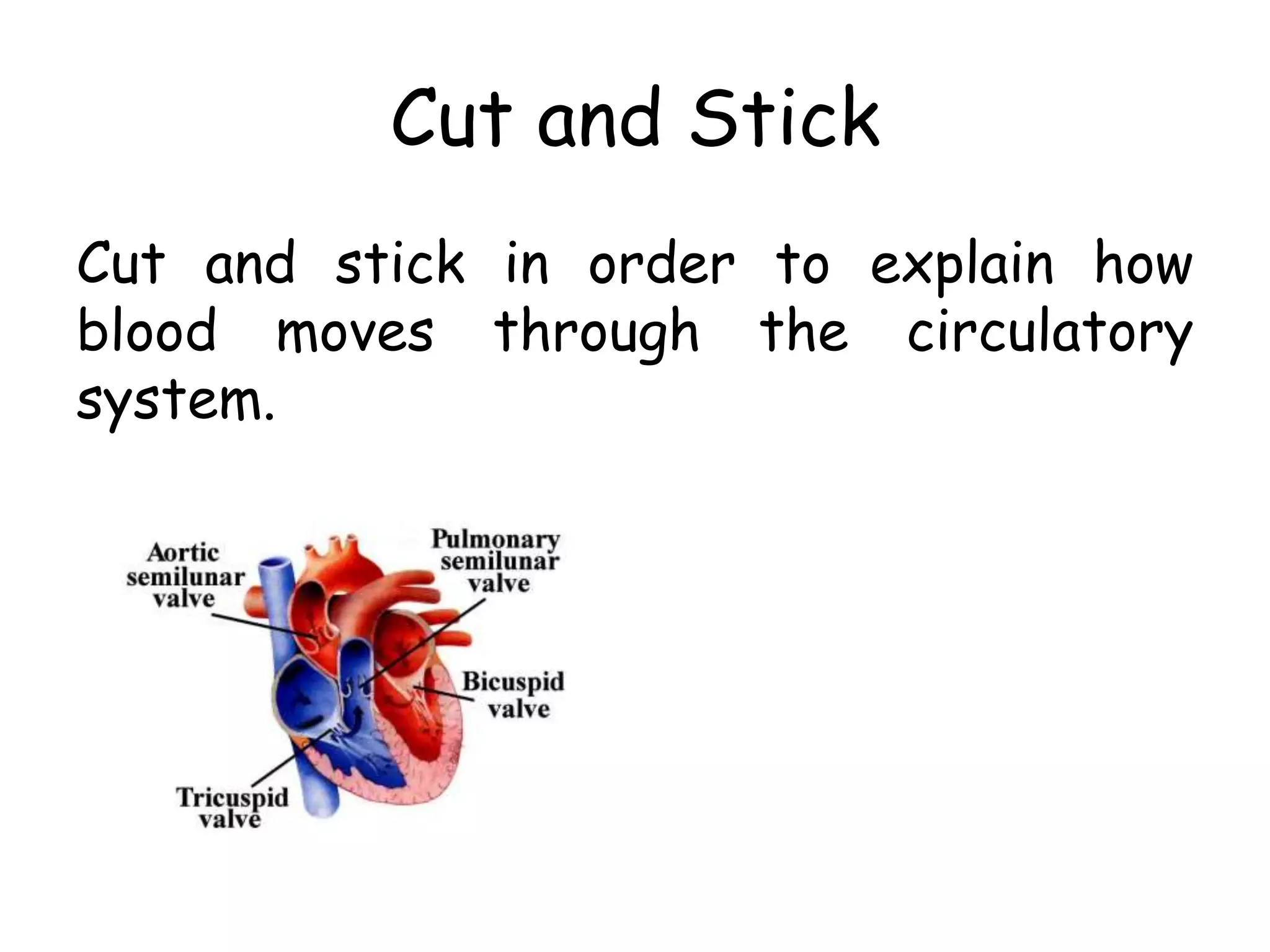
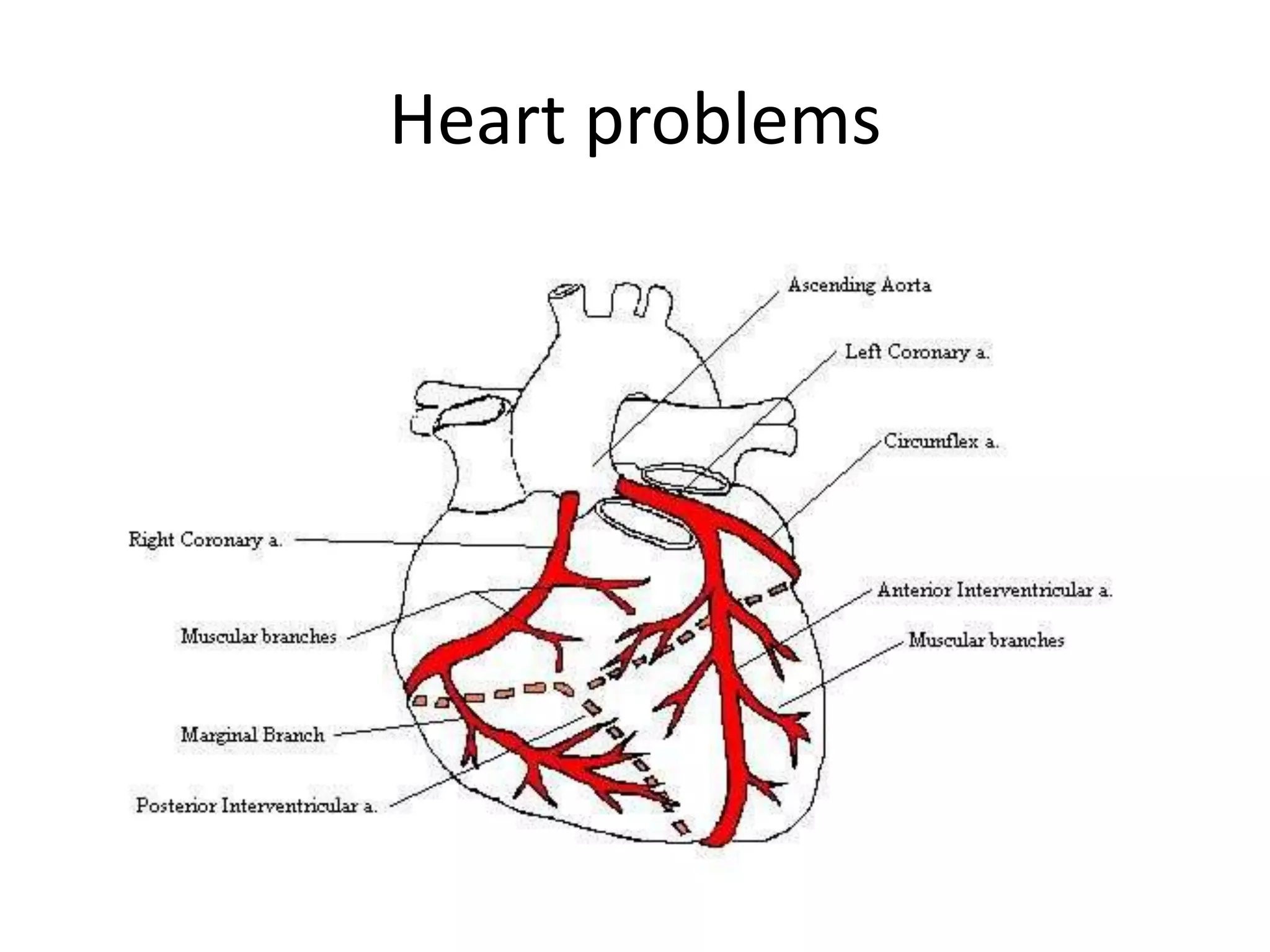
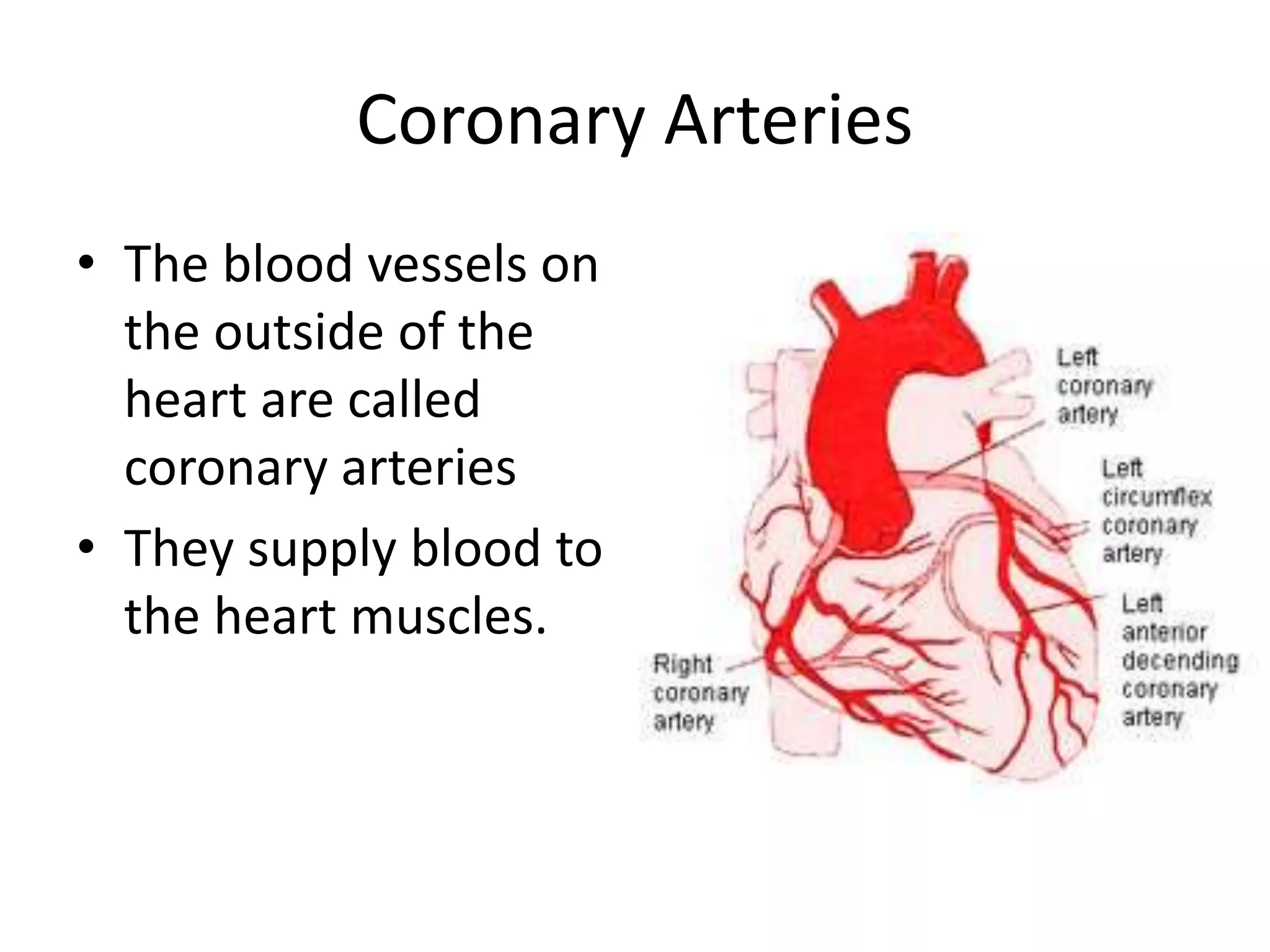
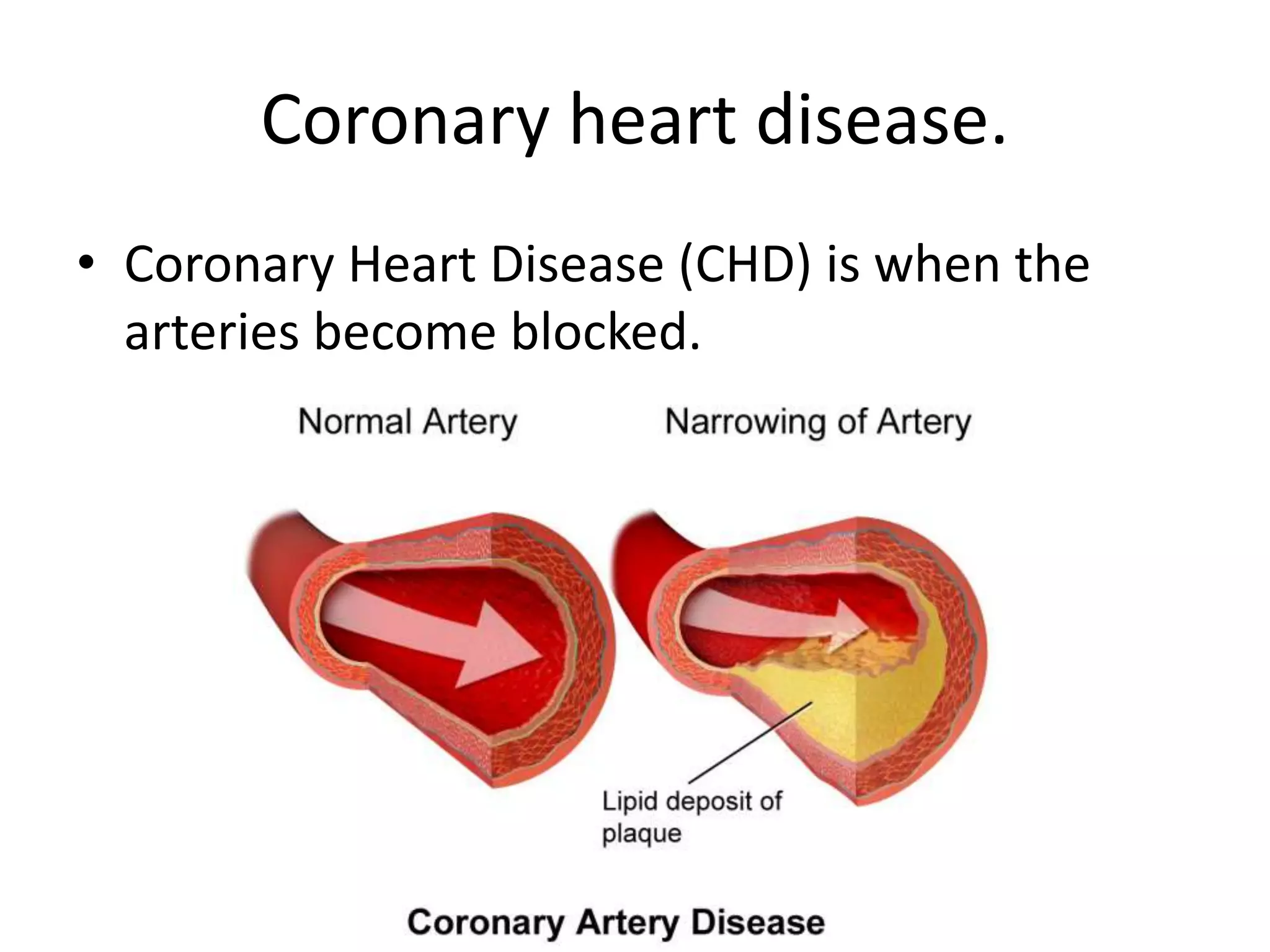
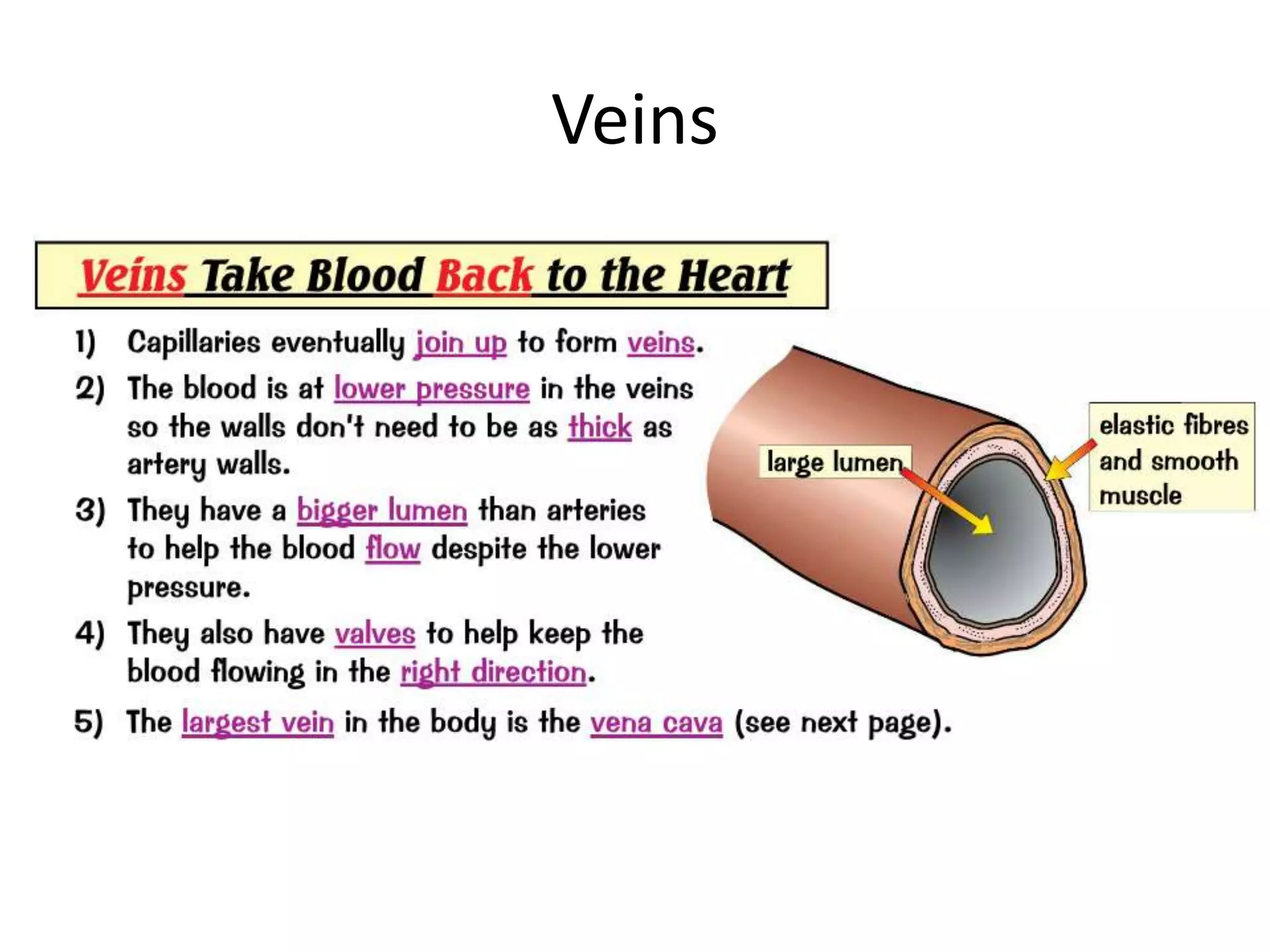
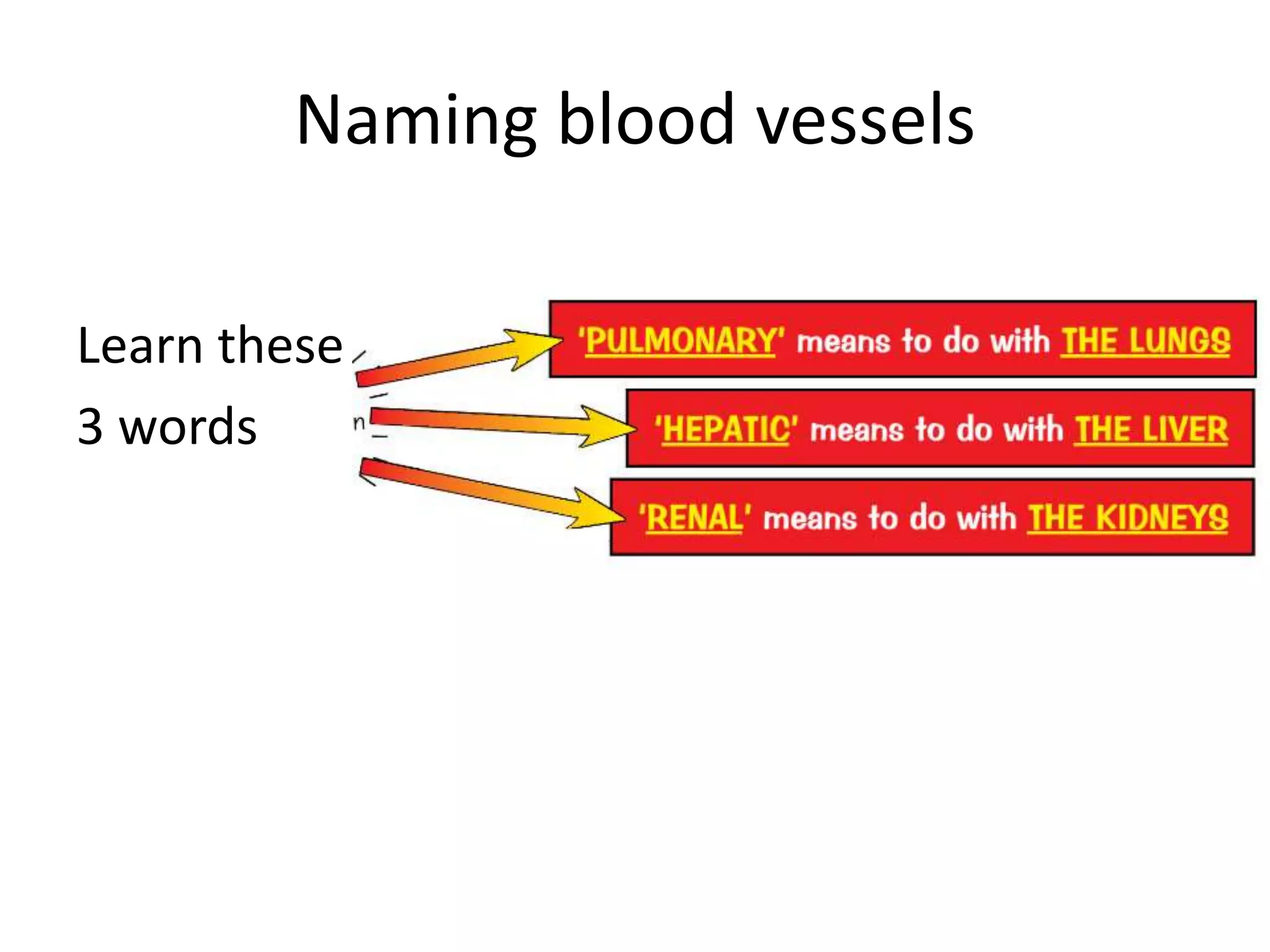
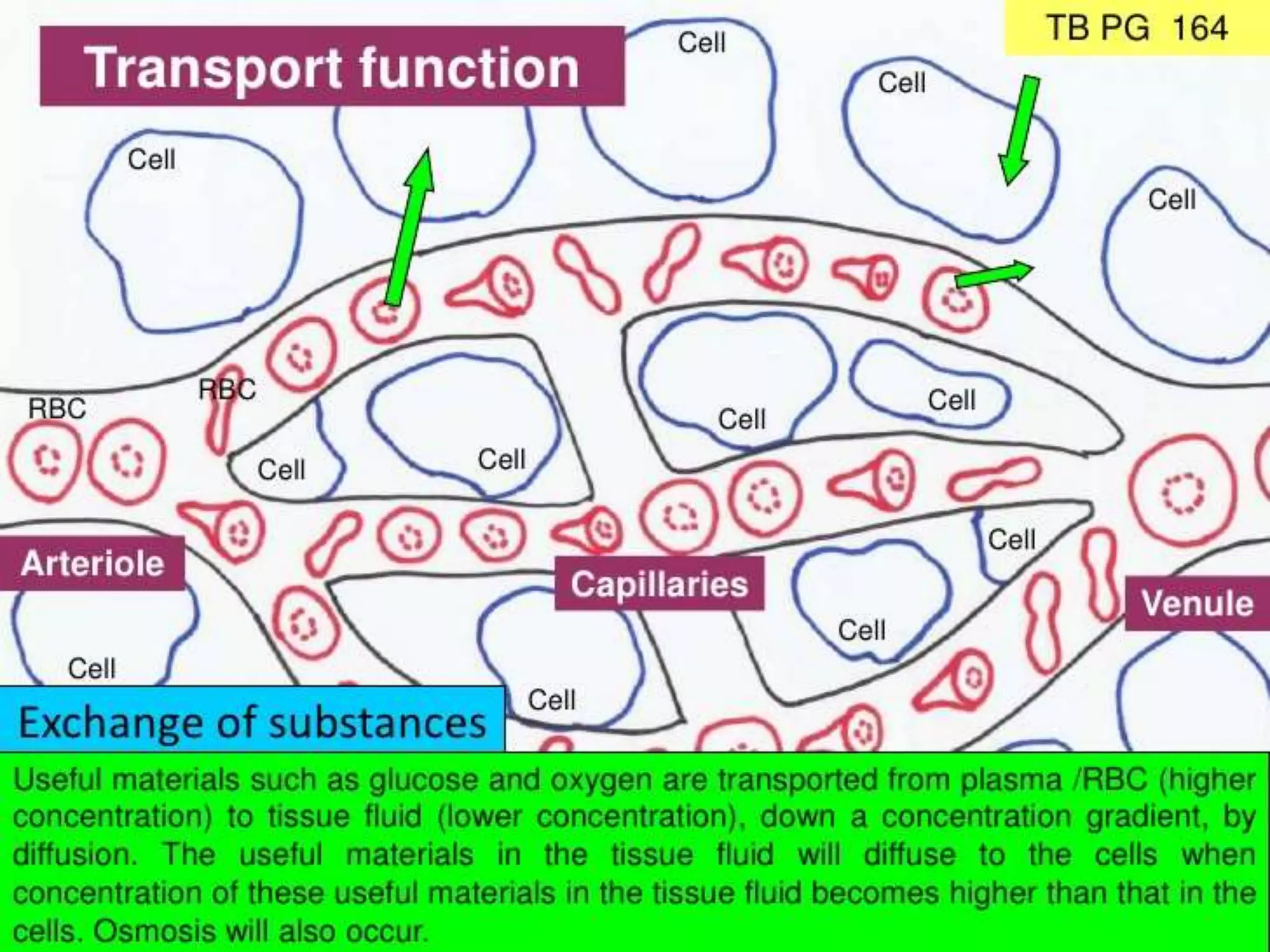
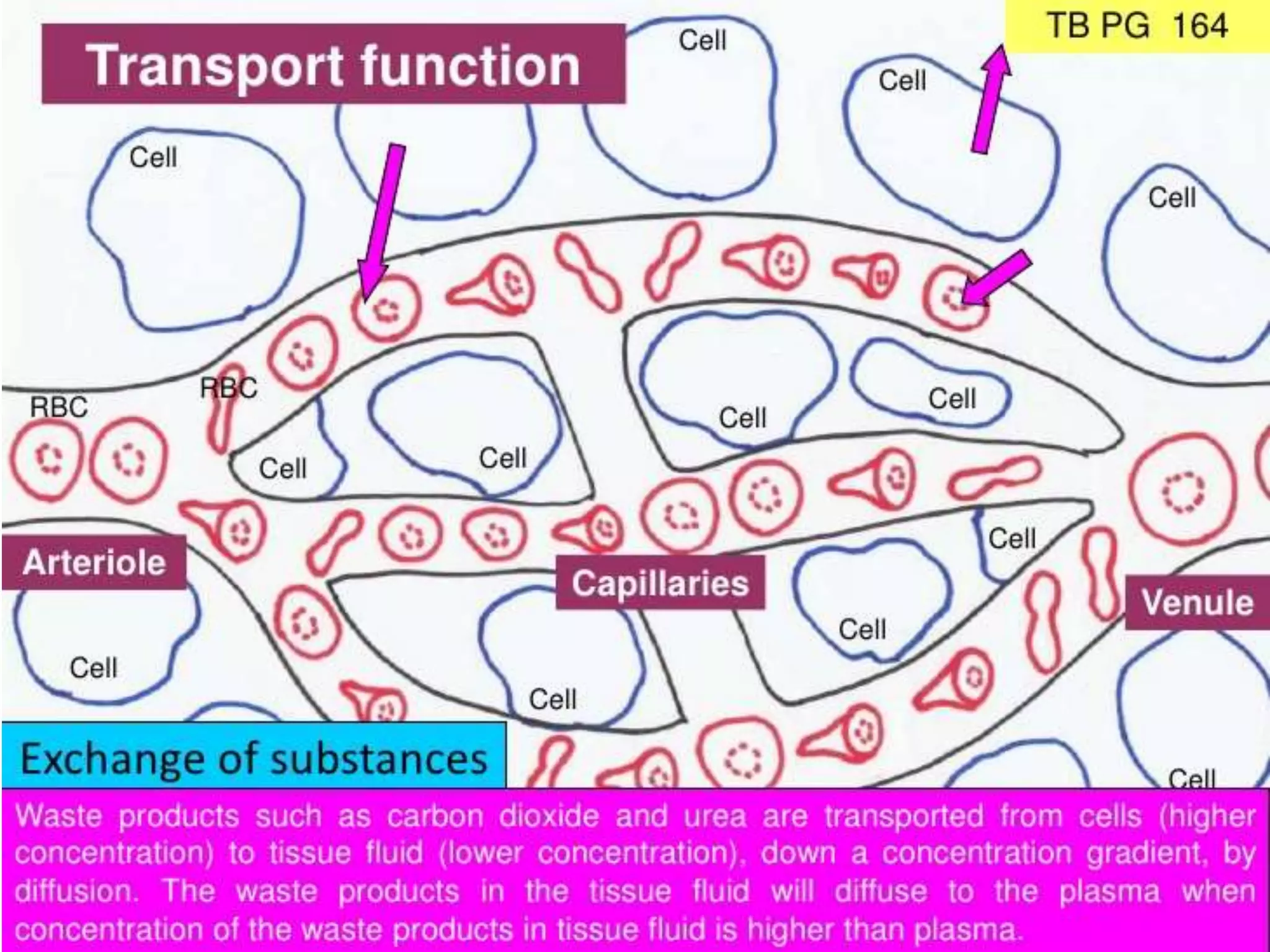
The document discusses the circulatory system and blood transport in animals. It describes single and double circulatory systems. In a single circulation, blood travels from the heart to the gills to absorb oxygen and then to the organs before returning to the heart. In a double circulation, there are two circuits - one where blood passes from the heart to the lungs to absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide, and another where blood passes from the heart to the organs and tissues to deliver oxygen before returning to the heart. A double circulation has evolved to create more pressure to pump blood around the system and separate oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood.