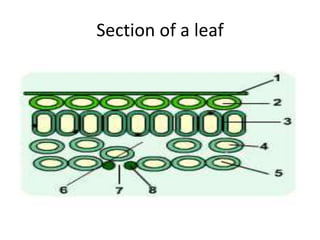
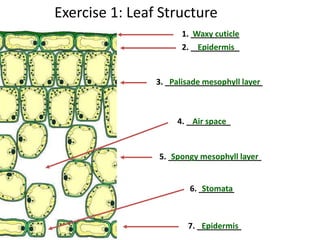
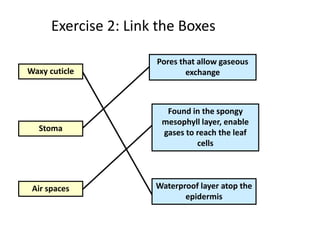
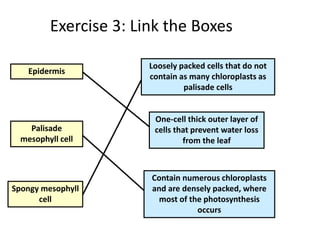
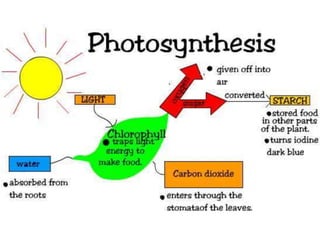
The document discusses plant nutrition and photosynthesis. It defines photosynthesis as the process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates from carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight using chlorophyll. The key organelle that contains chlorophyll and allows this process is the chloroplast. The document then provides exercises about leaf structure, the process of photosynthesis, and factors that can affect photosynthesis rates.