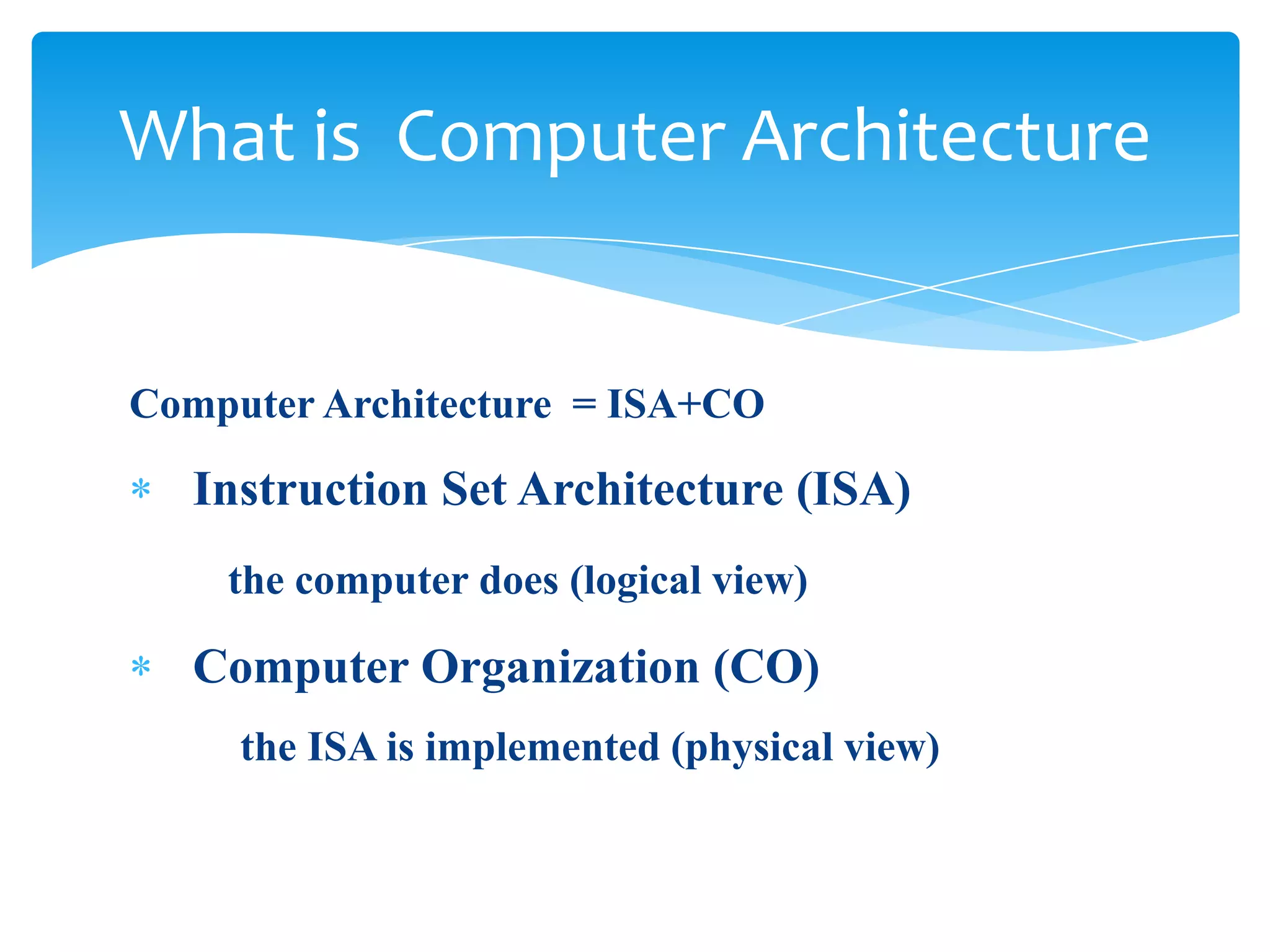
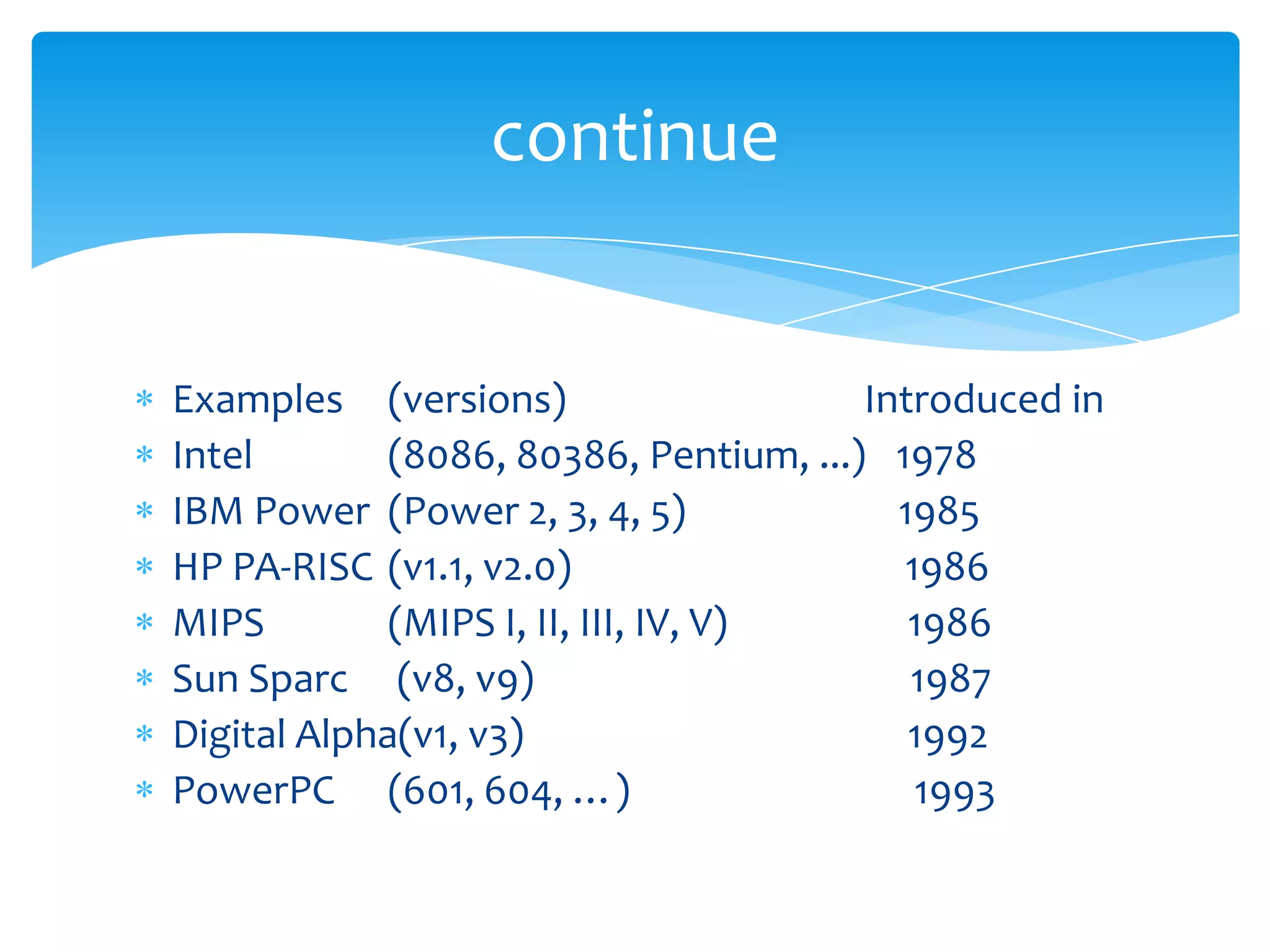
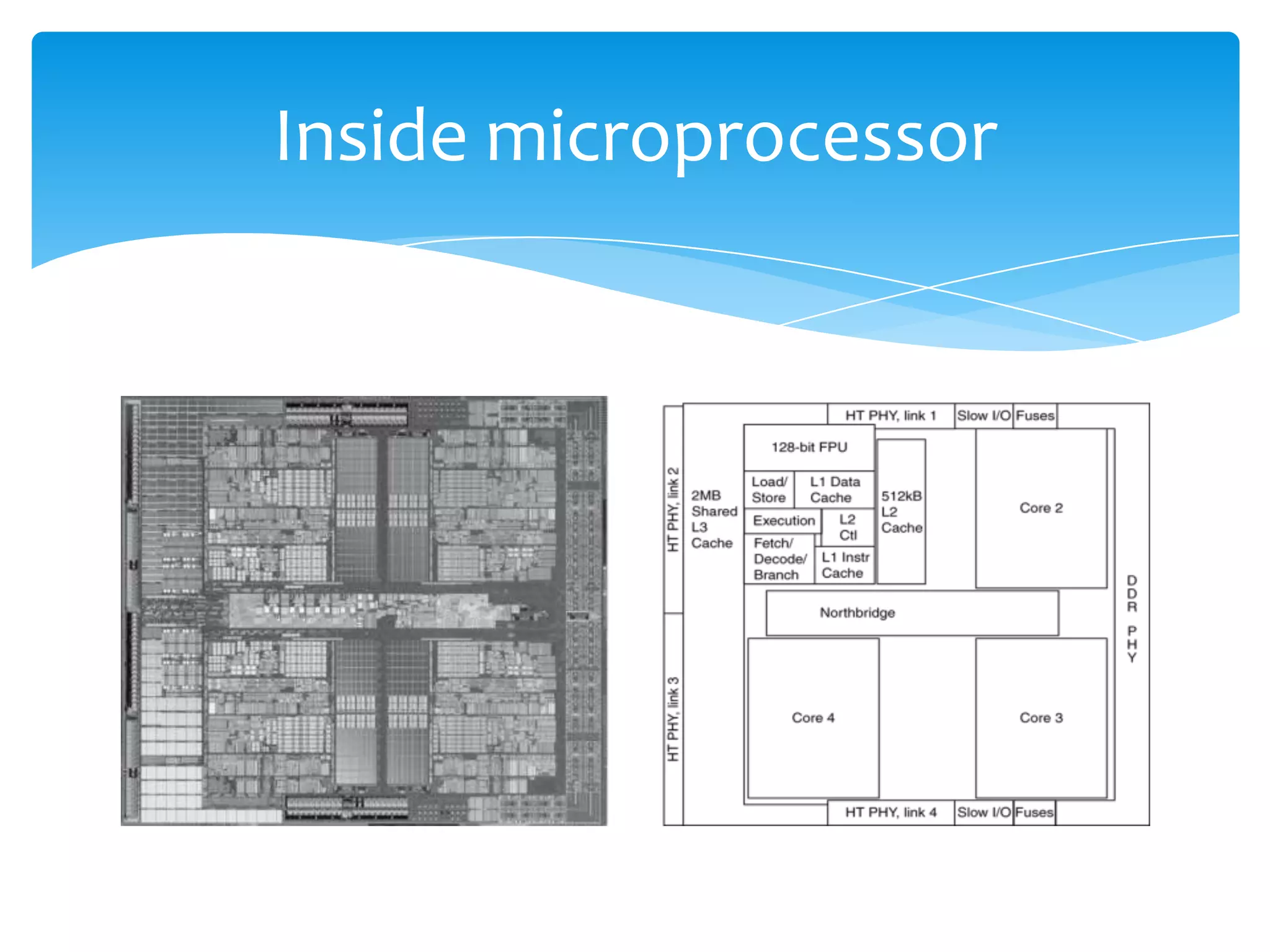
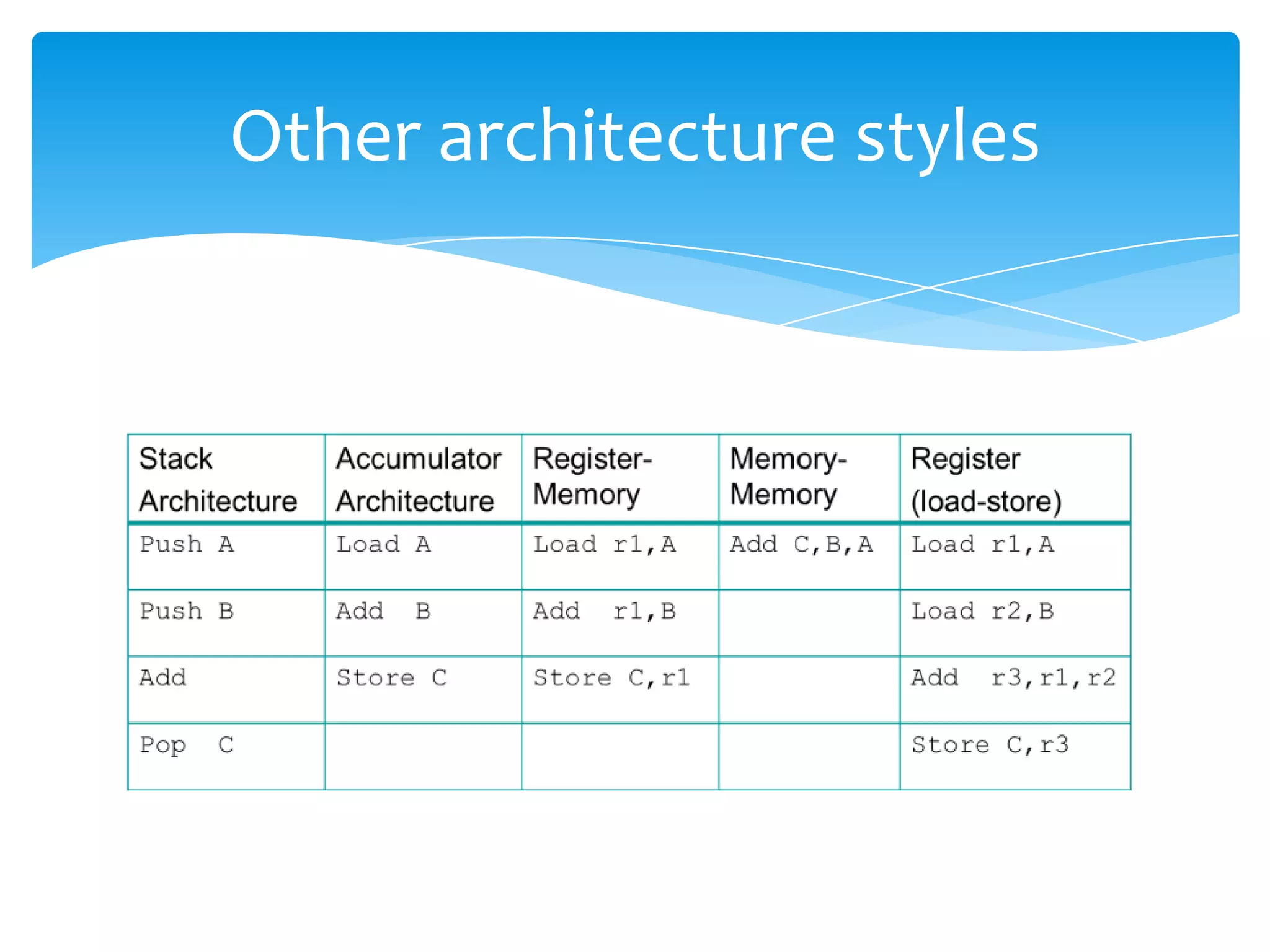
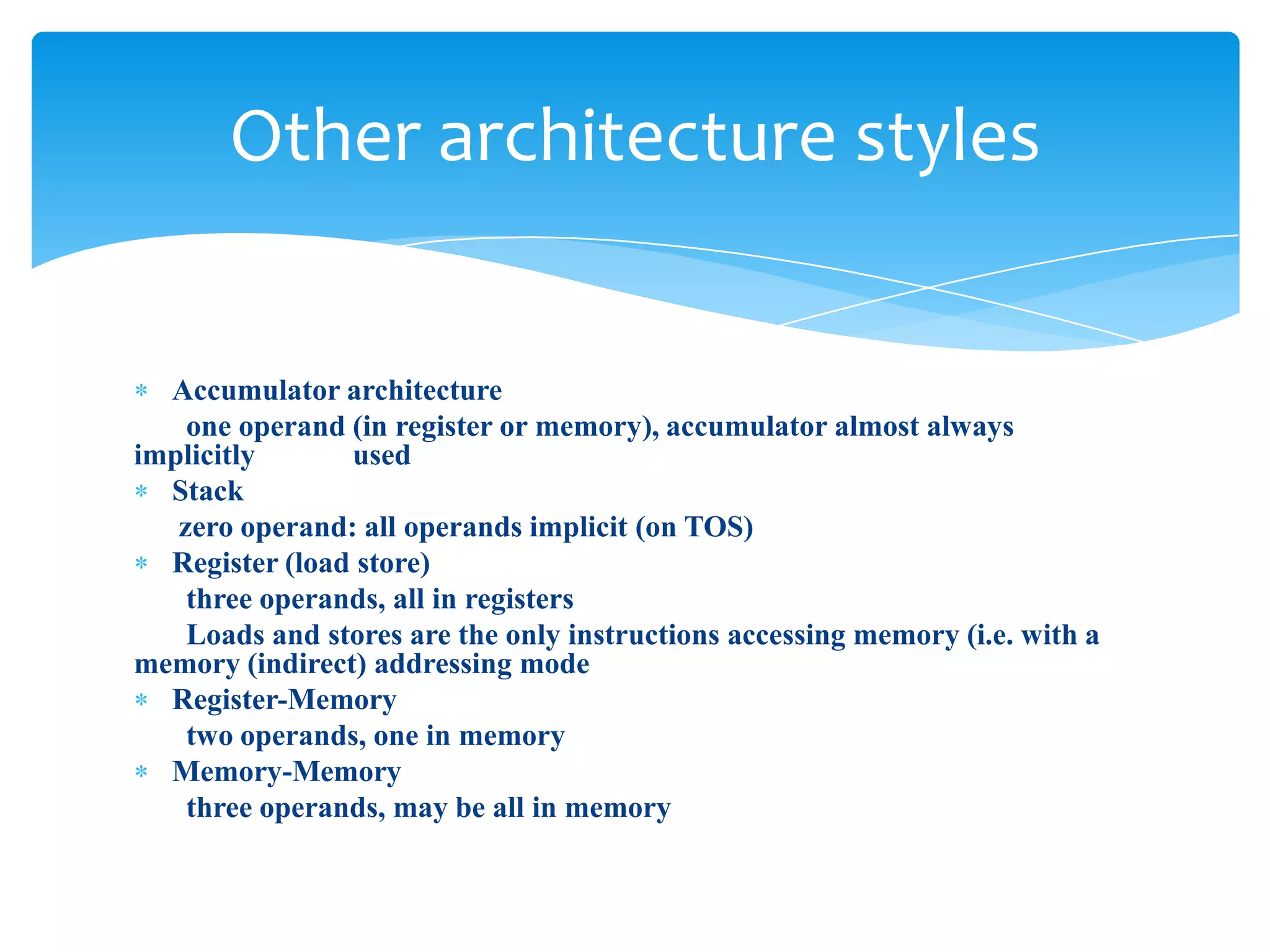
The document introduces computer architecture and organization. Computer architecture deals with the functional behavior of a computer as viewed by a programmer, such as instruction sets and data types. Computer organization deals with the physical and structural aspects not visible to programmers, such as memory types and control signals. Studying computer architecture and organization helps design better programs, optimize performance, and understand tradeoffs. Computer architecture (ISA) defines what a computer can do, while computer organization (CO) is how the ISA is physically implemented. Examples of instruction set architectures include Intel, IBM Power, HP PA-RISC, MIPS, and Sun SPARC.