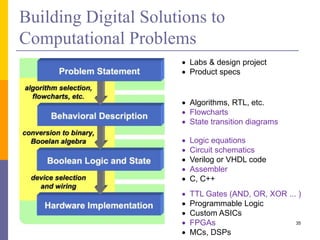
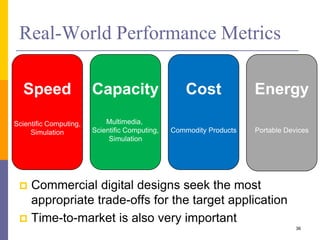
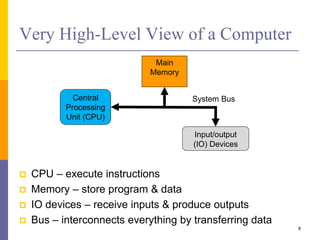
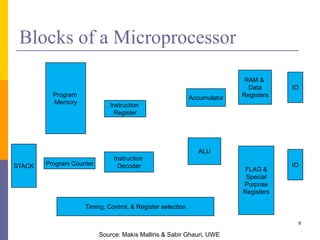
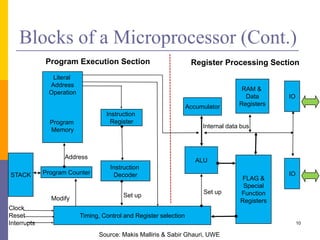
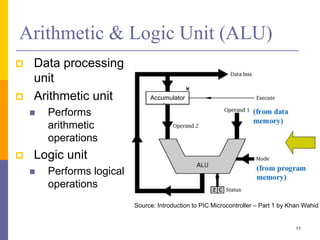
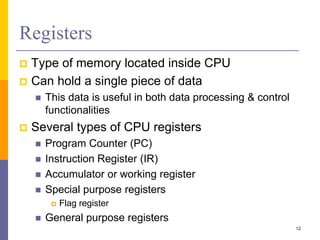
The document is an introduction to computer architecture, detailing the internal and external components of computers, their functions, and programming fundamentals. It covers the structure of microprocessors, the roles of the CPU, memory, and input/output devices, along with an overview of programming languages used in assembly and high-level coding. The document also highlights the differences between microprocessors and microcontrollers and discusses factors affecting architectural performance.








![18
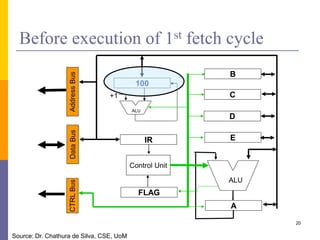
Sample Program
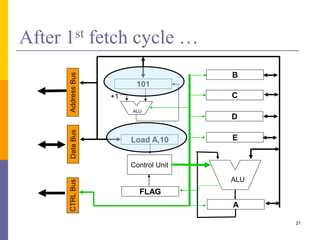
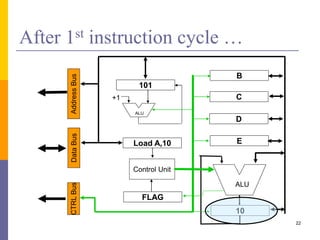
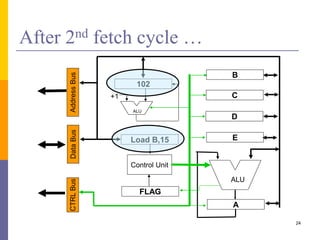
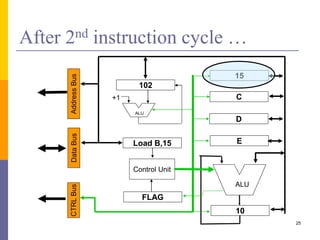
100: Load A,10
101: Load B,15
102: Add A,B
103: STORE A,[20]
Load A,10
Load B,15
ADD A,B
STORE A,[20]
100
101
102
103
104
105
Program memory
18
19
20
21
00
00
00
00
Data memory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01-introduction-141023192914-conversion-gate02/85/Computer-Architecture-An-Introduction-18-320.jpg)



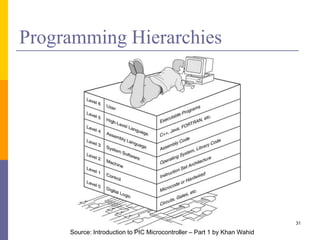

![Programming Language Levels (Cont.)
Assembler
Machine code (60s-70s)
.define const = 6
num1: .byte [1]
num2: .byte [2]
move.b num1,d0
addq.b #const,d0
move.b d0,num2
High-level languages
C code fragment (70s-80s)
#define const 6
int num1, num2;
num2 = num1 + const; 33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01-introduction-141023192914-conversion-gate02/85/Computer-Architecture-An-Introduction-33-320.jpg)