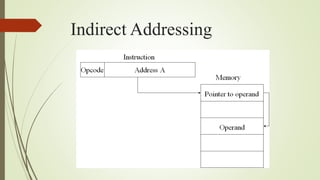
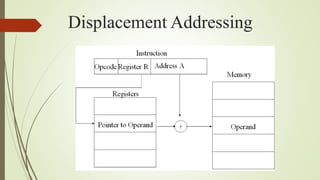
This document discusses various techniques for addressing locations in memory, including immediate, direct, indirect, register, register indirect, displacement, and stack addressing. Immediate addressing encodes the operand directly in the instruction, while direct addressing uses an address field to directly specify the memory location. Indirect addressing uses the address field to point to the location of the operand. Register addressing stores the operand in a register. Register indirect and displacement addressing combine aspects of register and direct/indirect addressing. Stack addressing implicitly operates on the top of the stack.