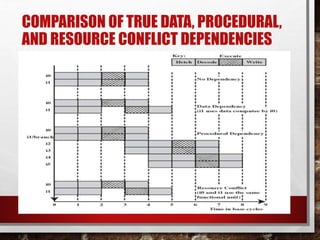
This document discusses different types of dependencies that can occur in programs:
- Data dependencies occur when an instruction refers to data from a previous instruction. There are three types: true data dependencies where an instruction depends on a previous result; output dependencies where two instructions write to the same register; and anti-dependencies where an instruction depends on data that could be overwritten.
- Control dependencies occur when the execution of one instruction depends on the outcome of another instruction, such as in an if-then statement.
- Resource conflicts occur when two instructions need the same hardware resource at the same time, such as a functional unit or register, stalling execution even if the instructions do not have a data or control dependency.






![CONTINUE . . .
MOV r1,[mem]
MOV r3,r1
MOV r2,5
(Load r1 from memory)
(r3 = r1;)
(r2 = 5;)
The superscalar machine would execute the first and
third instructions in parallel, yet have to wait anyway for
the first instruction to finish before executing the second
This holds up MULTIPLE pipelines](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cacaca-140303053553-phpapp01/85/Dependencies-7-320.jpg)