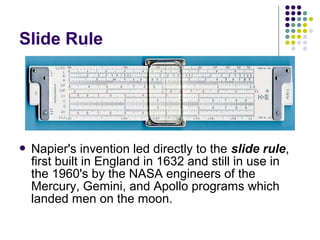
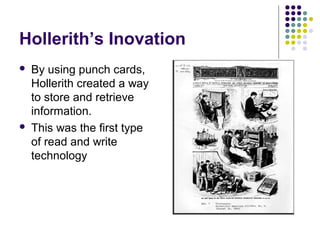
The document summarizes the history and generations of computers from the past to the future in 3 sentences:
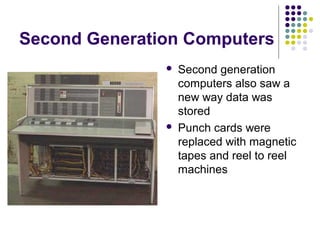
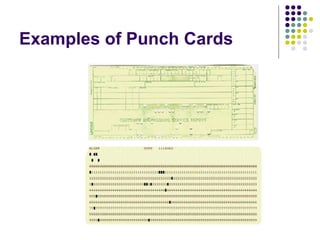
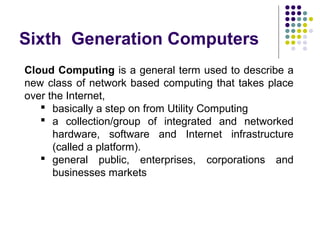
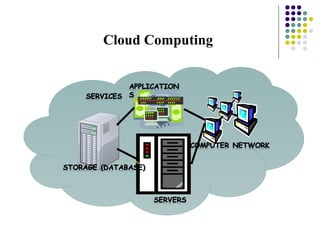
Past computers used early mechanical aids like the abacus and slide rule. The first electronic computers of the 1940s-1950s used vacuum tubes and were very large, expensive, and unreliable. Generations of computers since then have gotten smaller, cheaper, more powerful and efficient by transitioning to newer technologies like transistors, integrated circuits, personal computers, and future developments in areas like augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing.