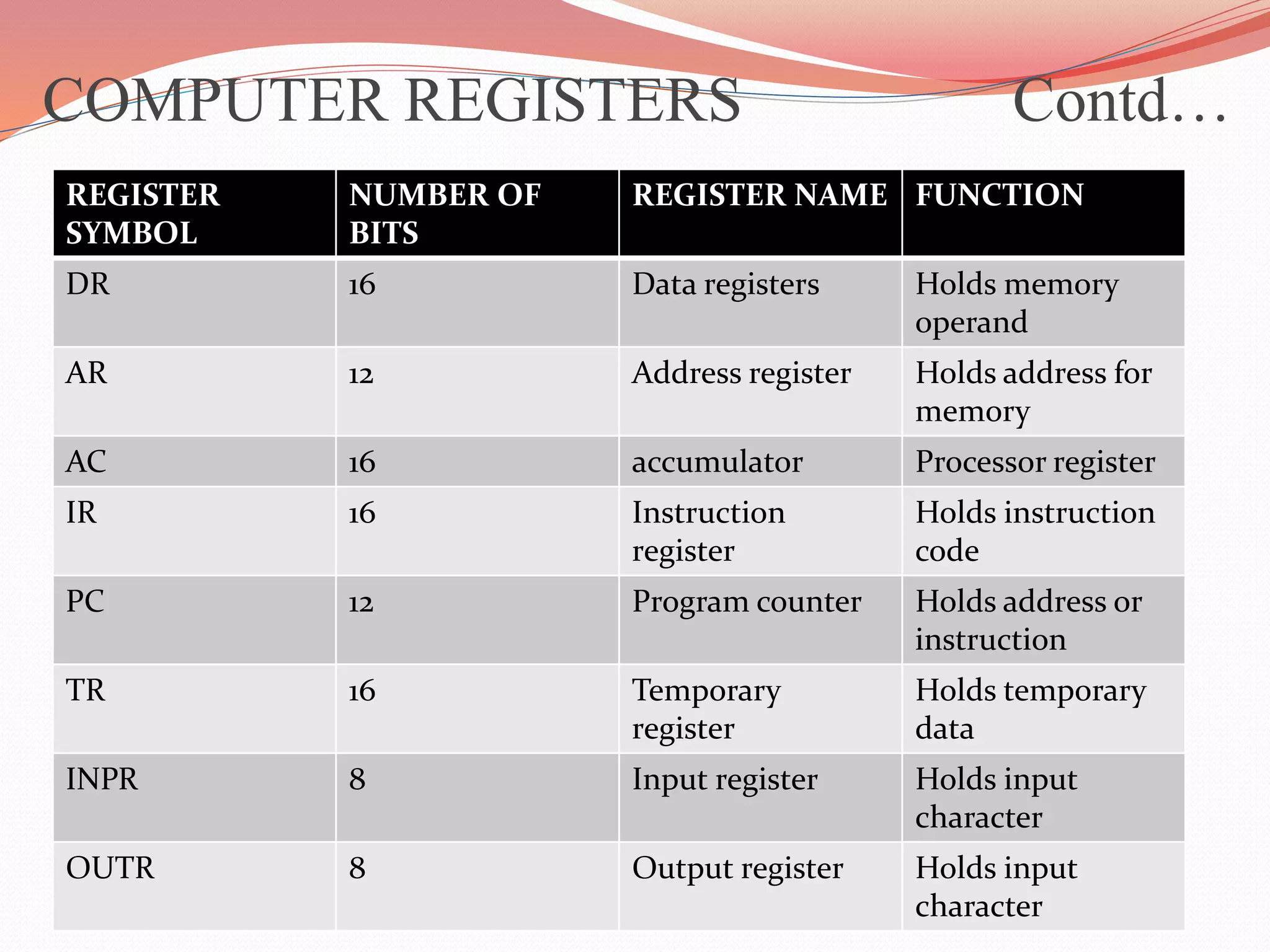
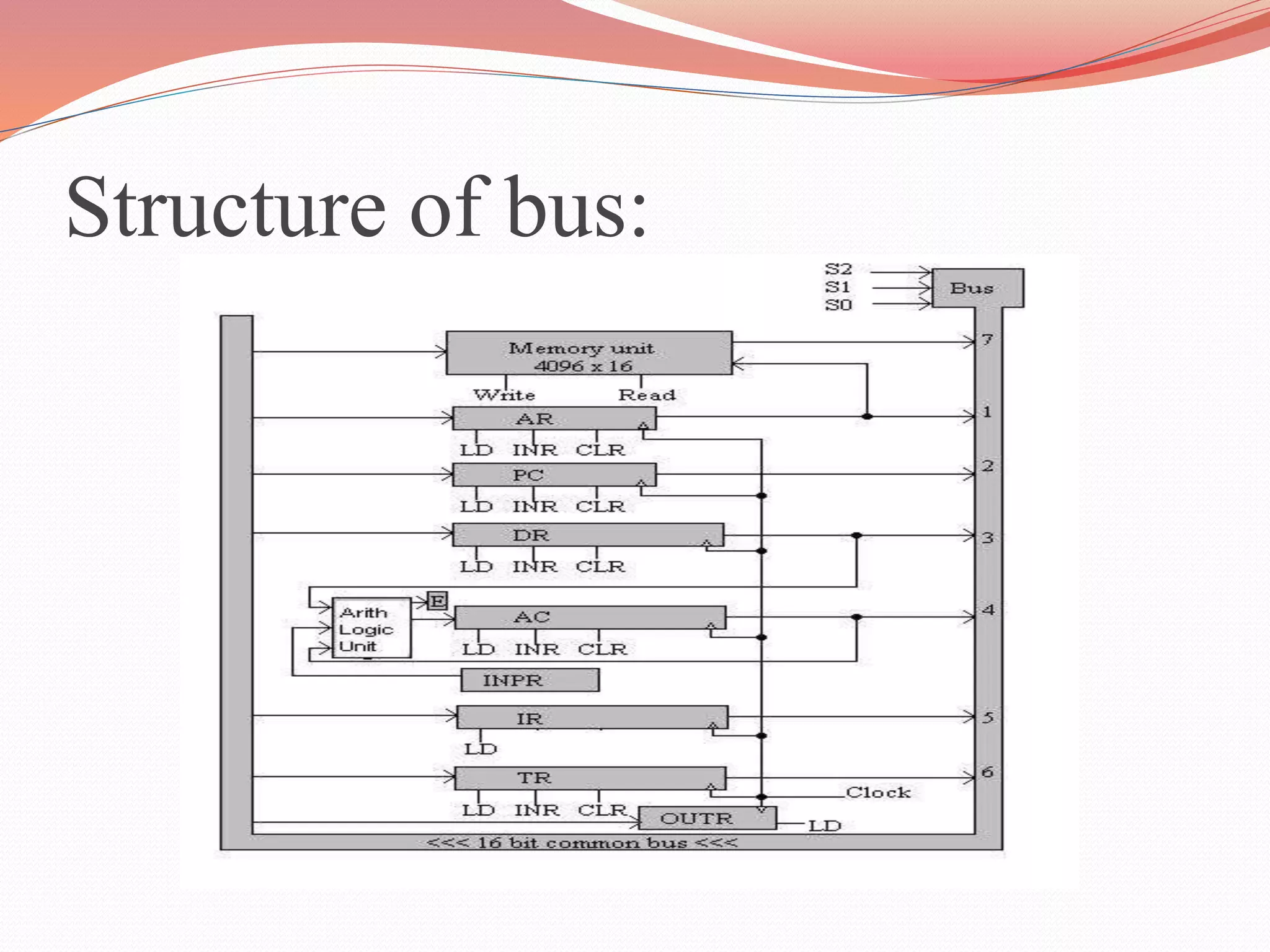
This document discusses computer registers and their functions. It describes 8 key registers - Data Register, Address Register, Accumulator, Instruction Register, Program Counter, Temporary Register, Input Register and Output Register. It explains what each register stores and its role. For example, the Program Counter holds the address of the next instruction to be executed, while the Accumulator is used for general processing. The registers are connected via a common bus to transfer information between memory and registers for processing instructions.