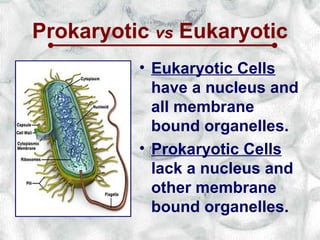
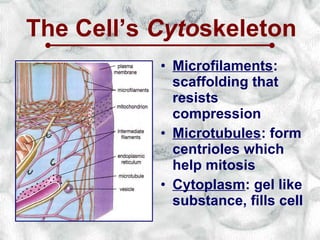
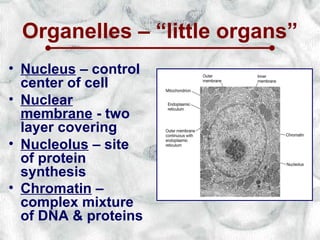
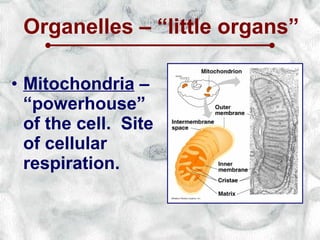
This document introduces cells and their structures. It outlines the cell theory that all living things are made of cells, which are the basic unit of life that only come from existing cells. It describes the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and introduces the major cell organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus and their functions. It also highlights unique plant cell structures like the cell wall and chloroplasts.