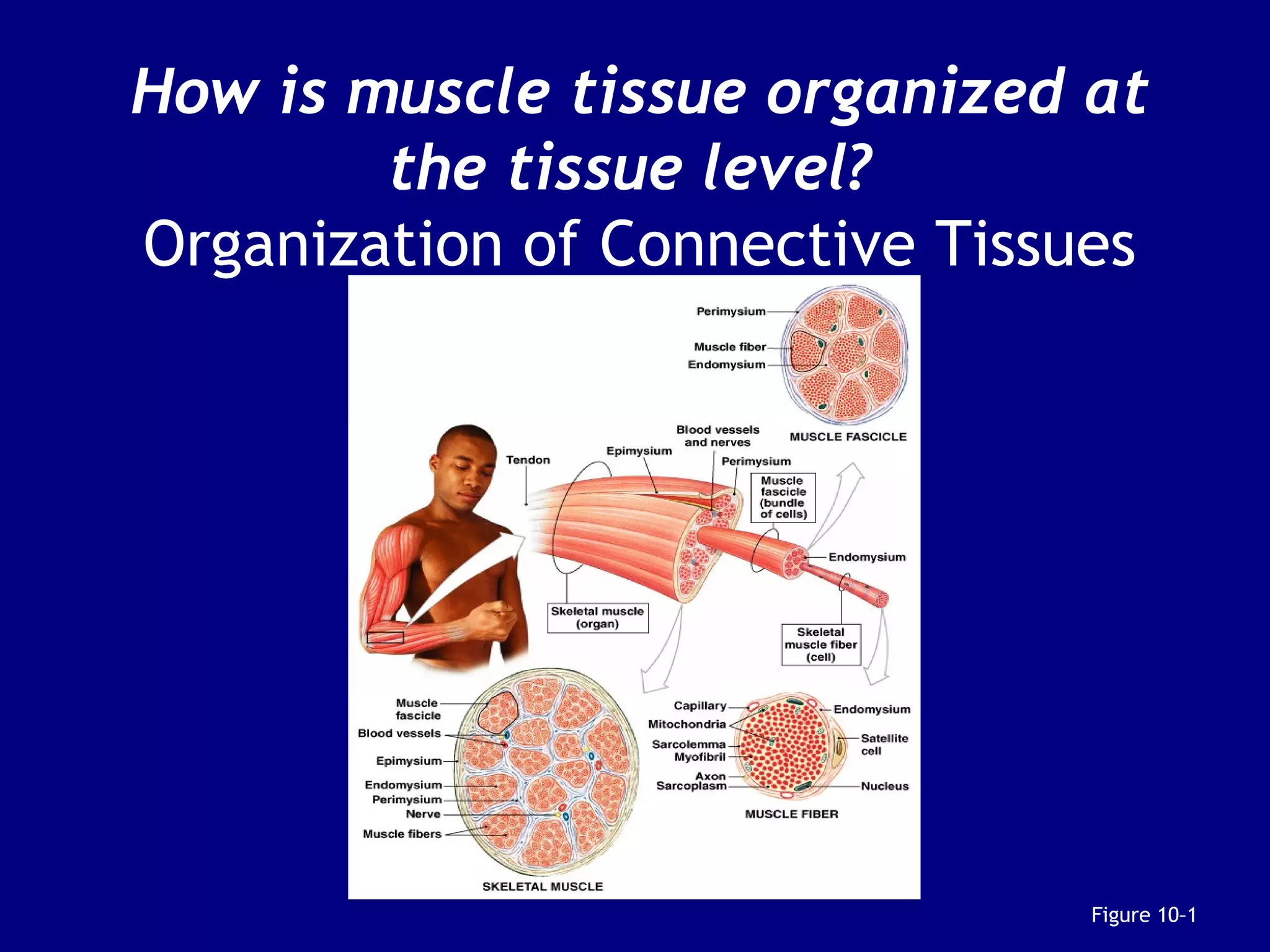
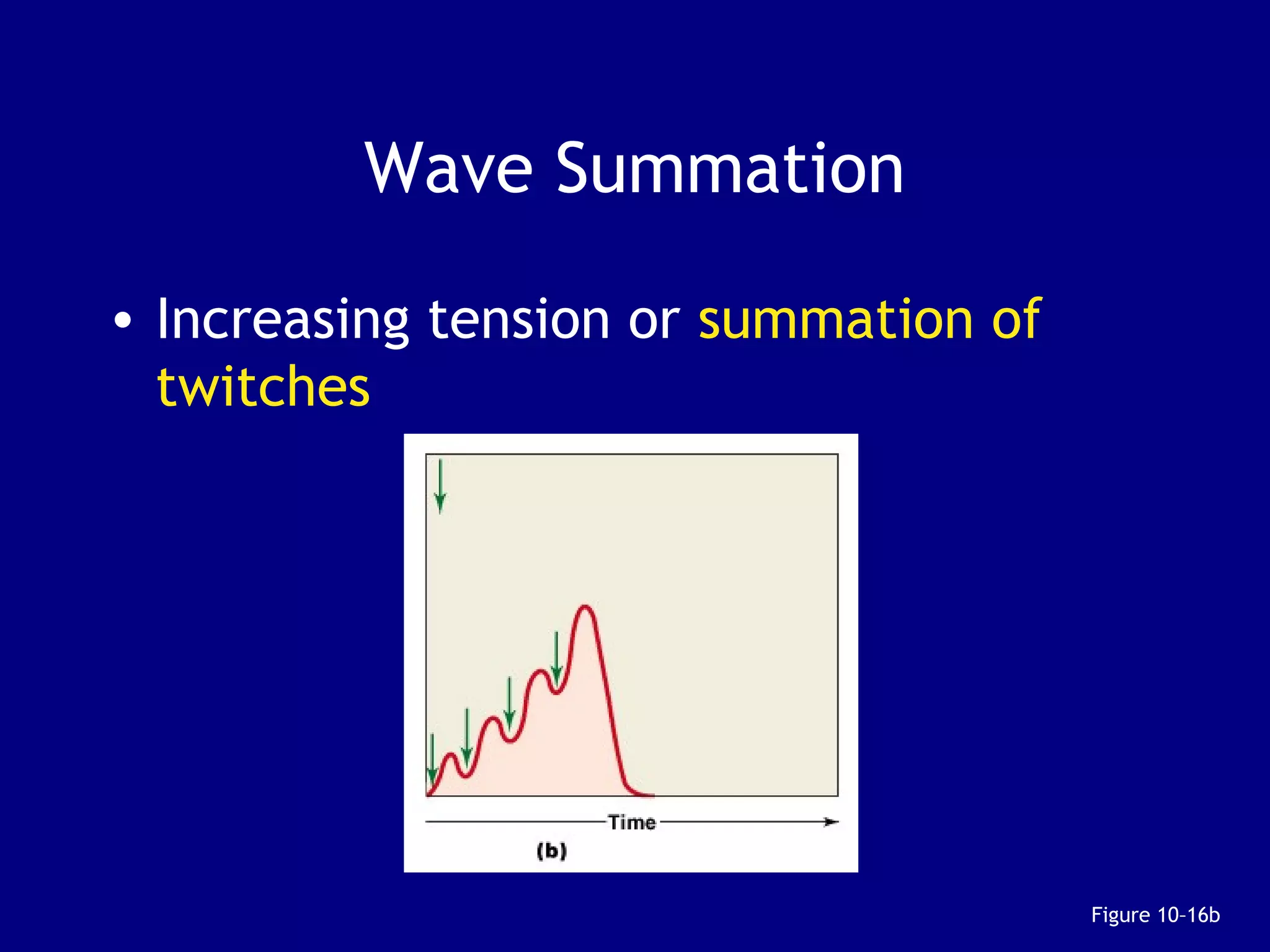
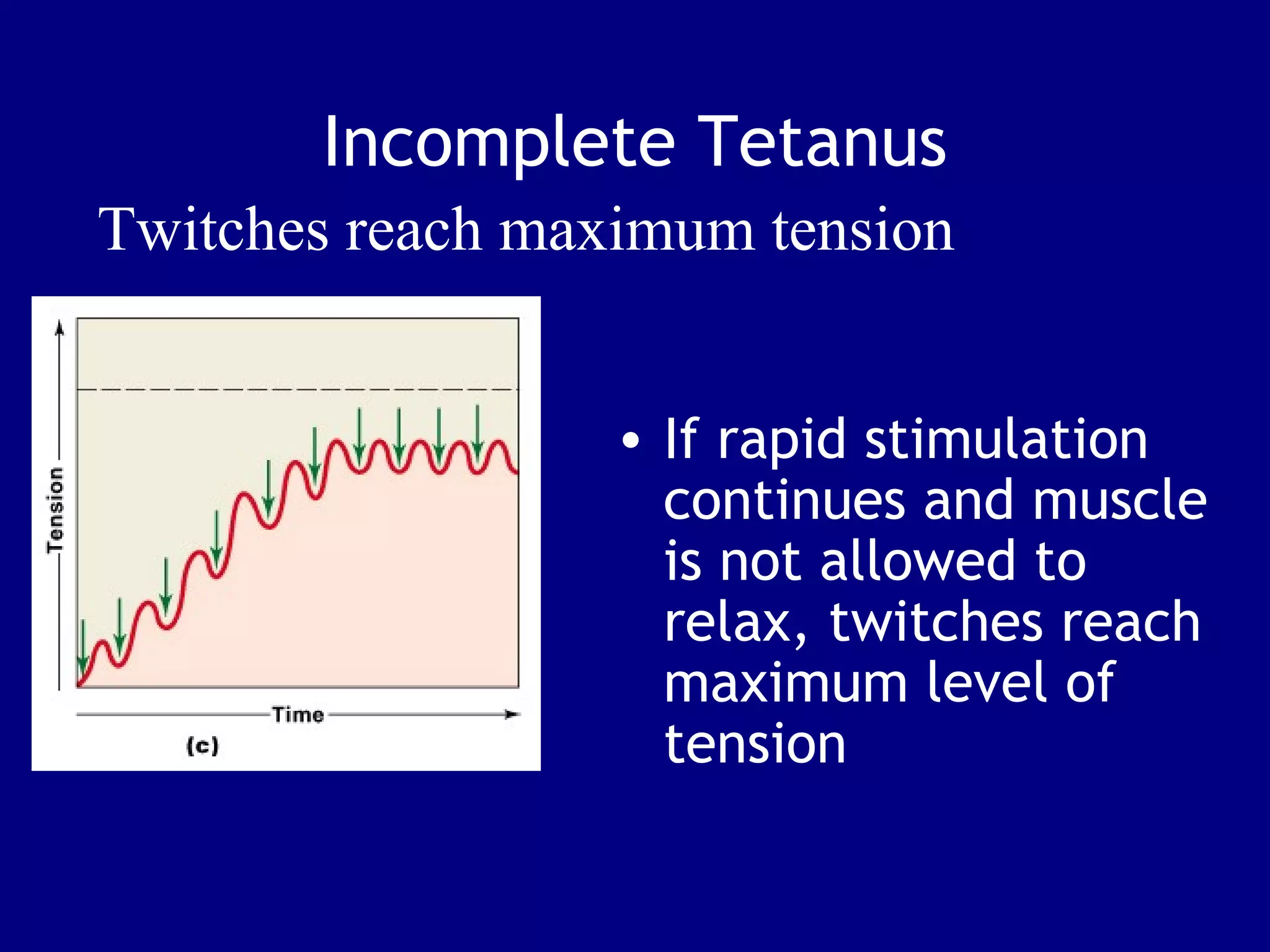
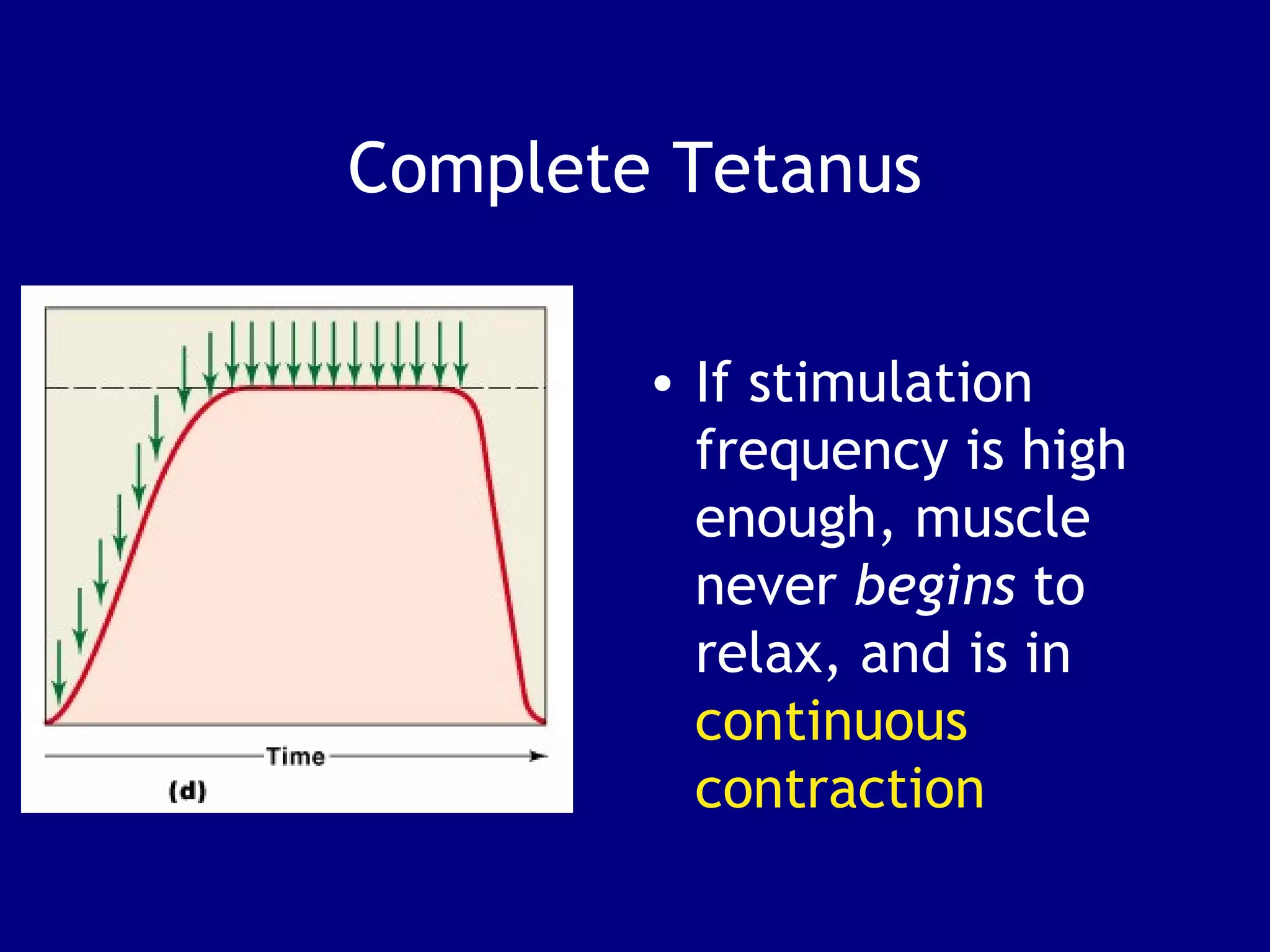
1. Muscle tissue is one of four primary tissue types and is divided into three main categories: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and allows voluntary movement.
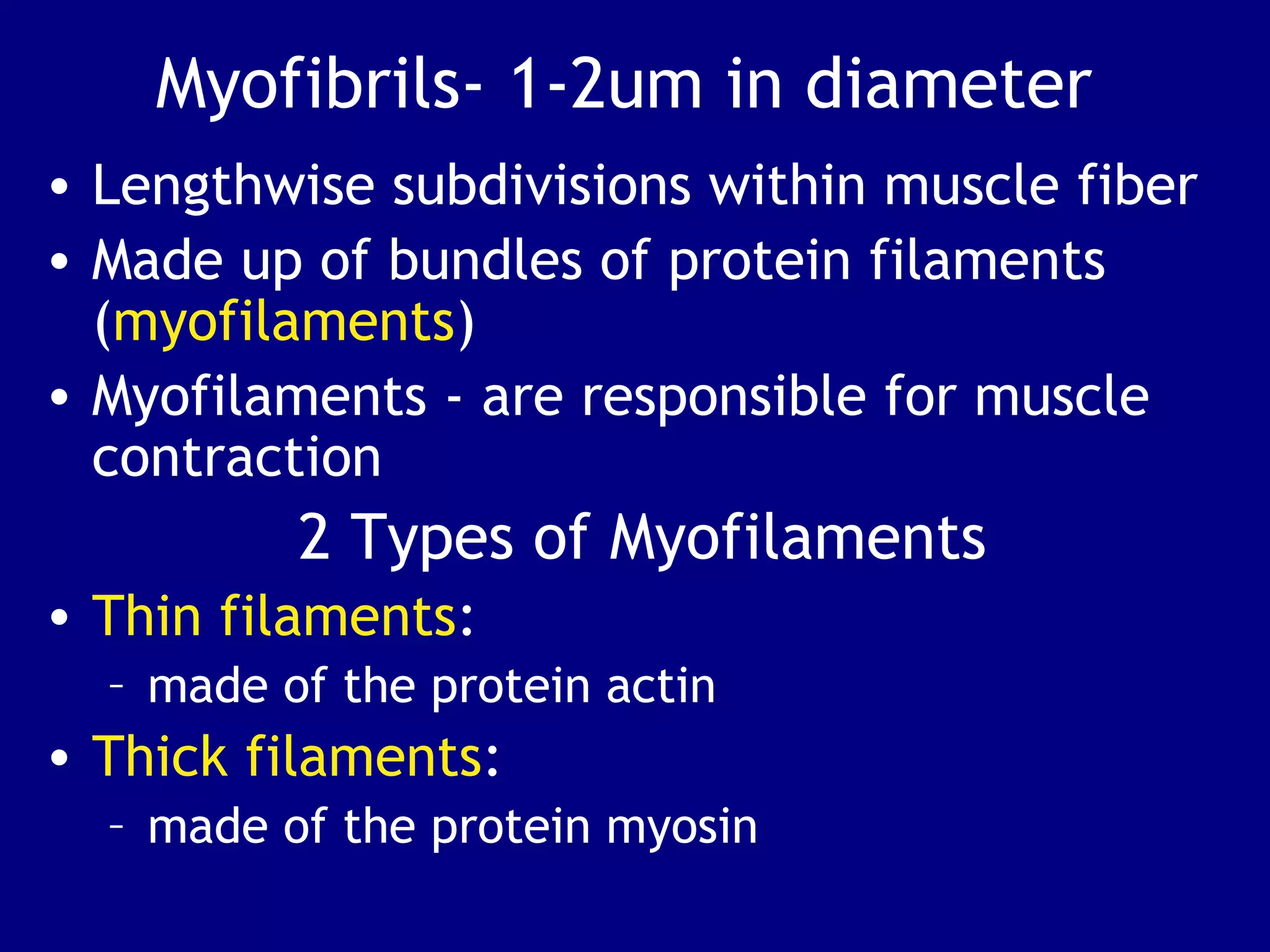
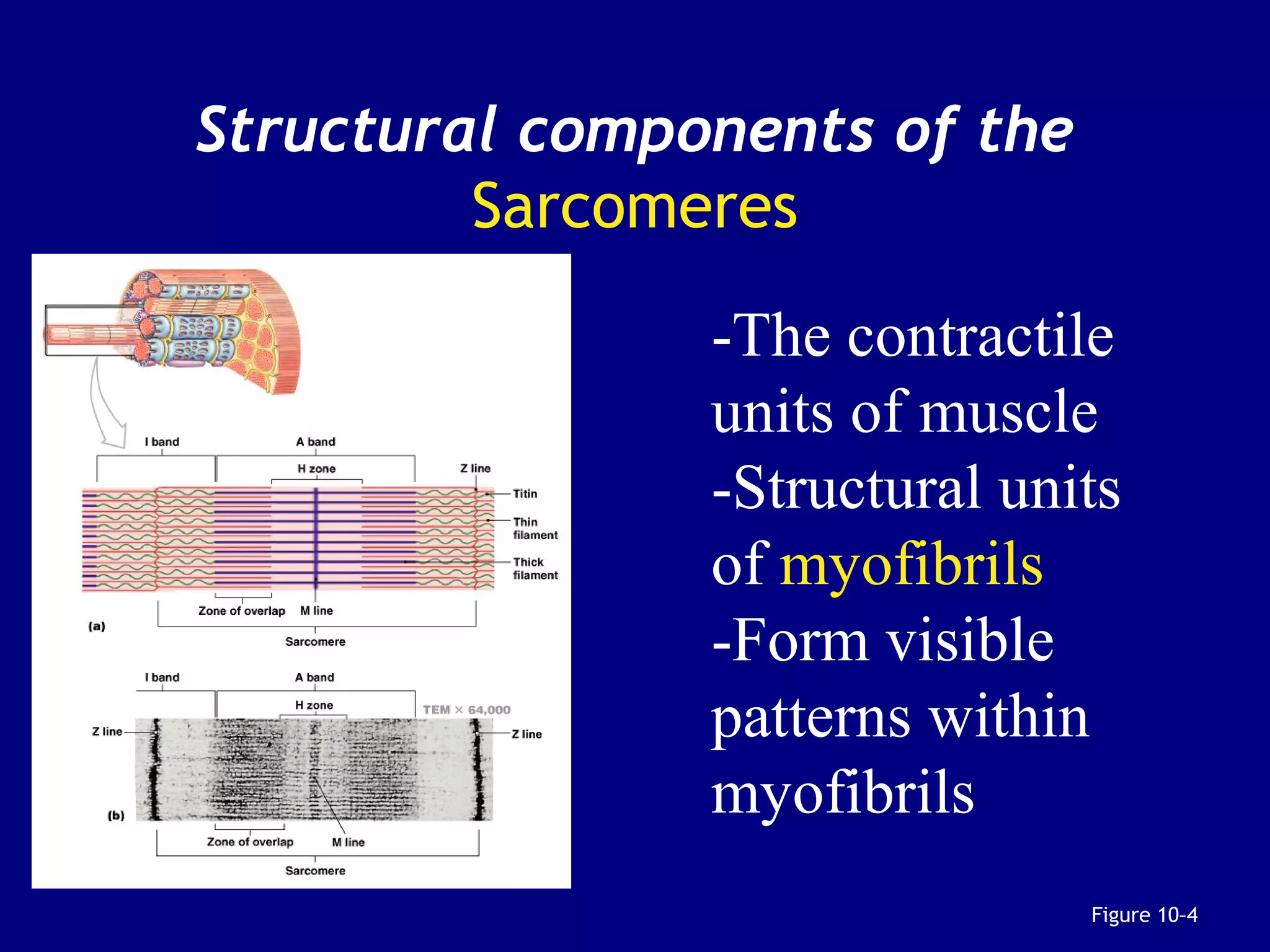
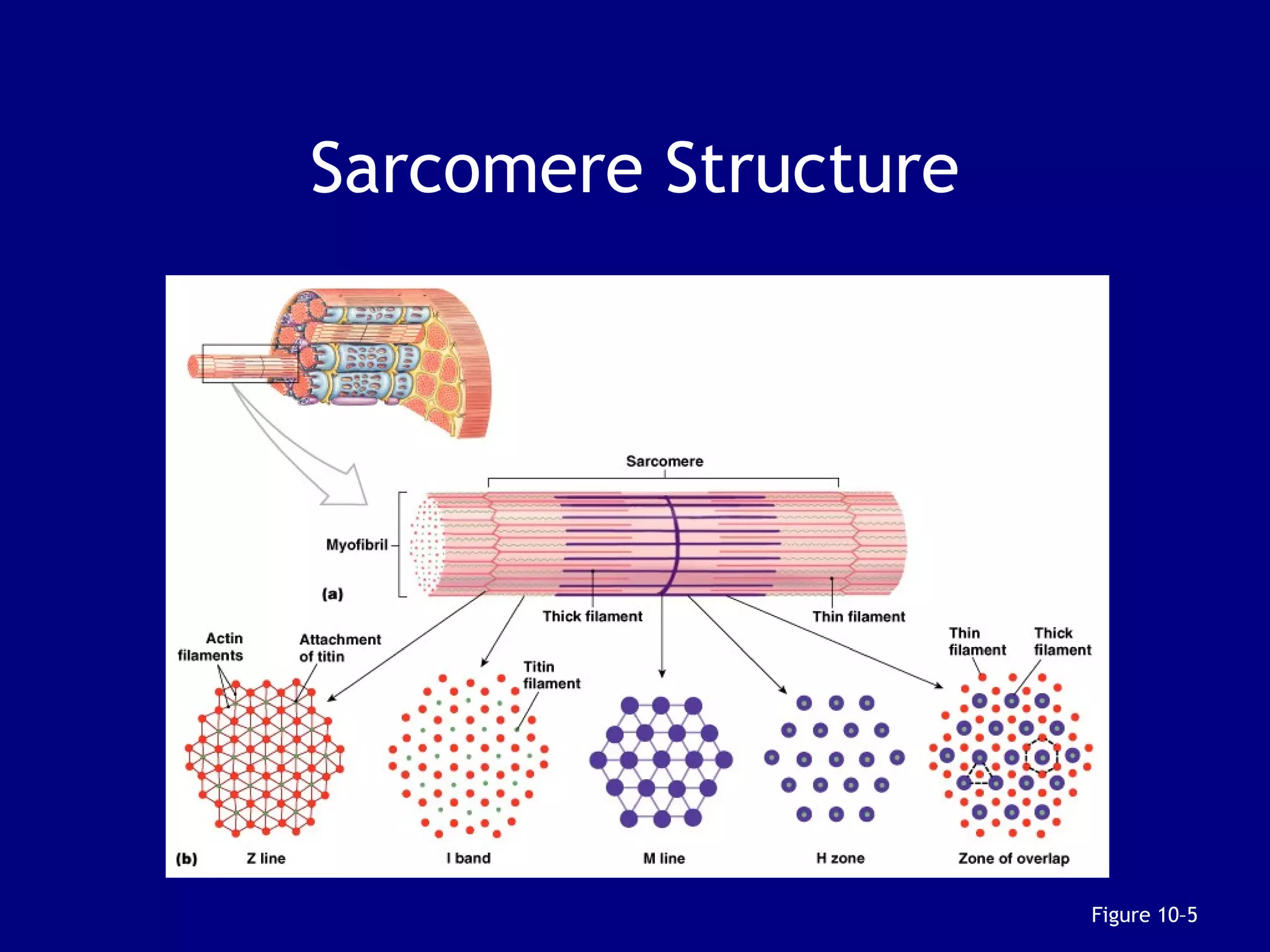
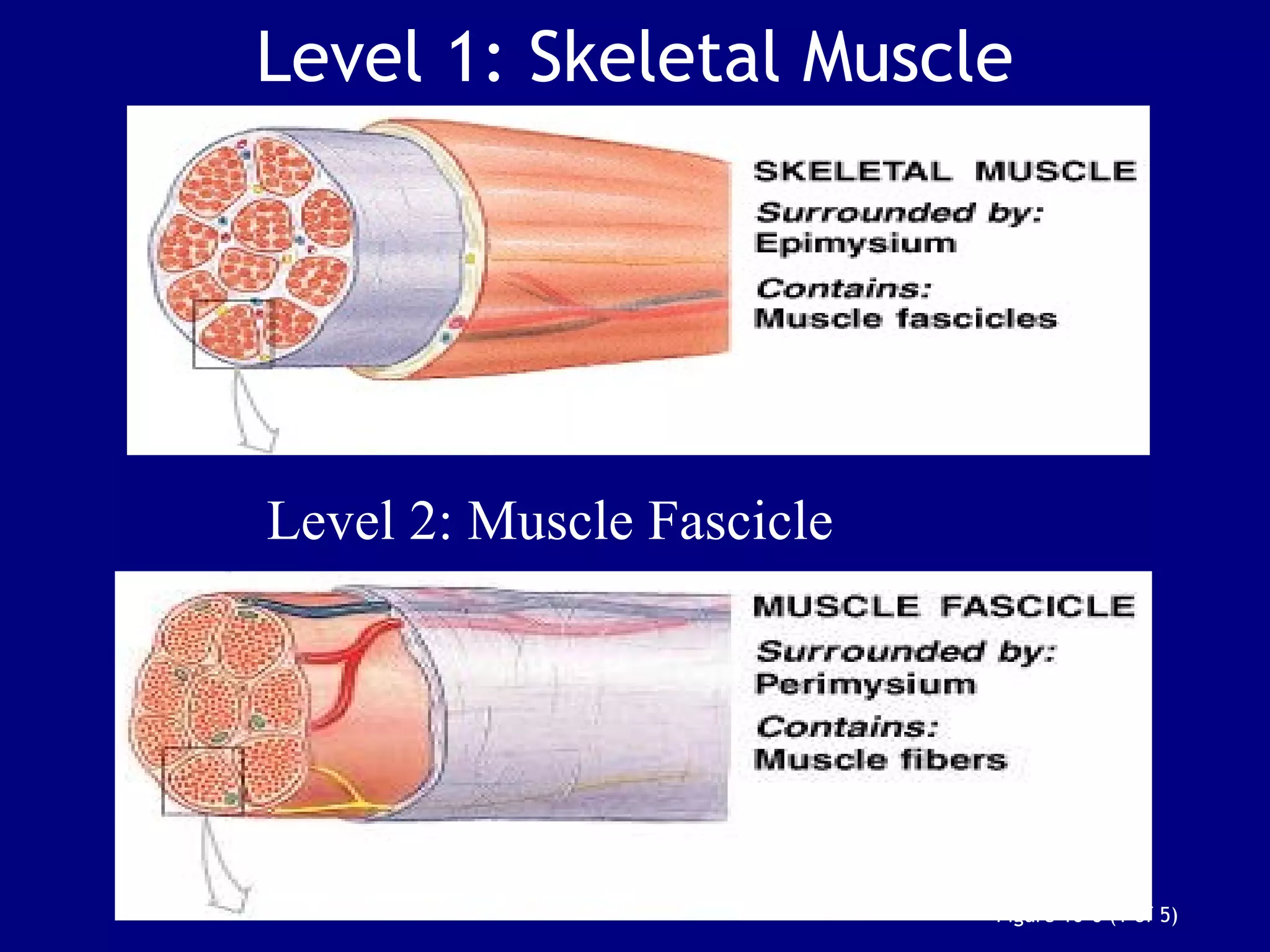
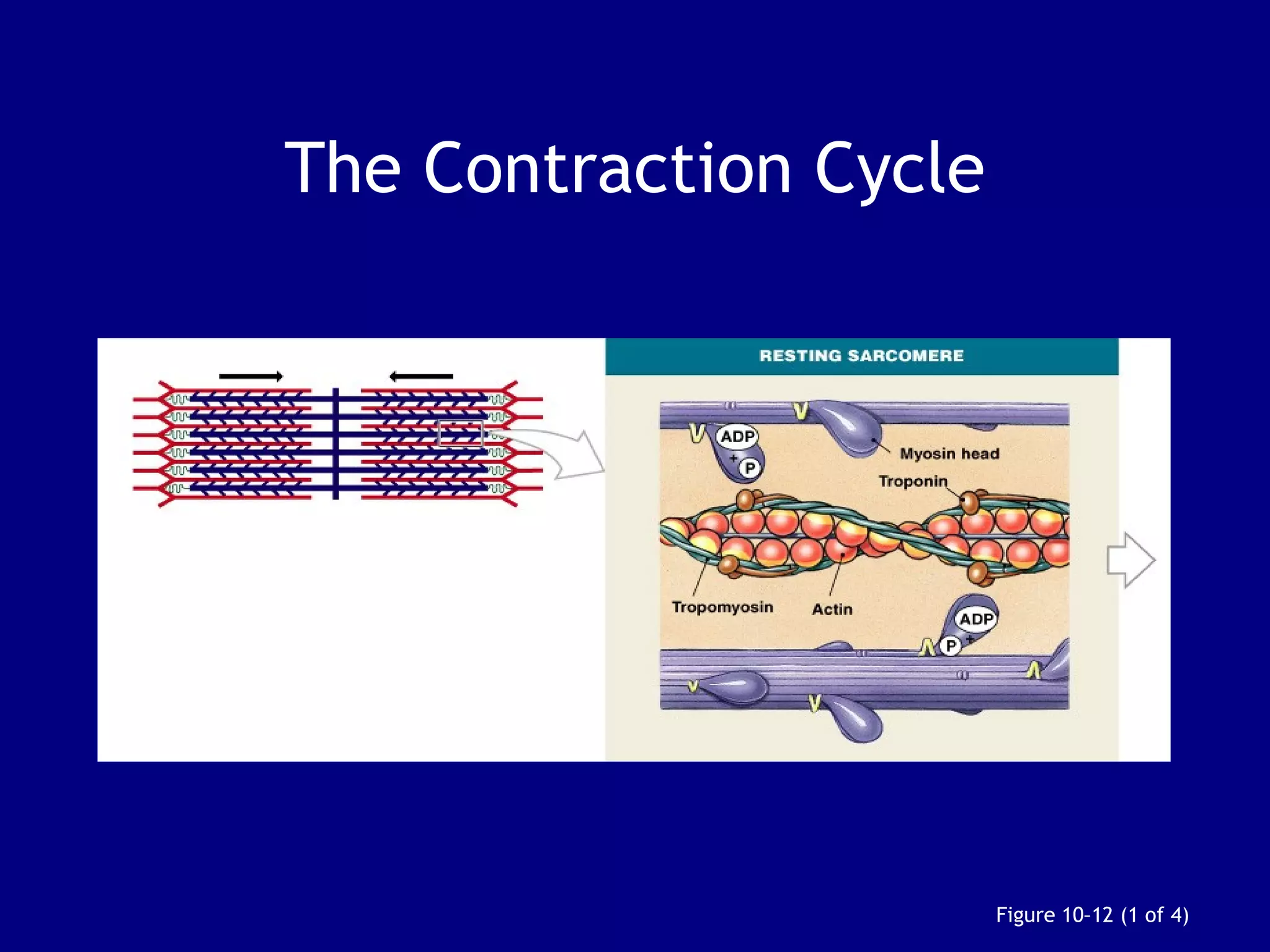
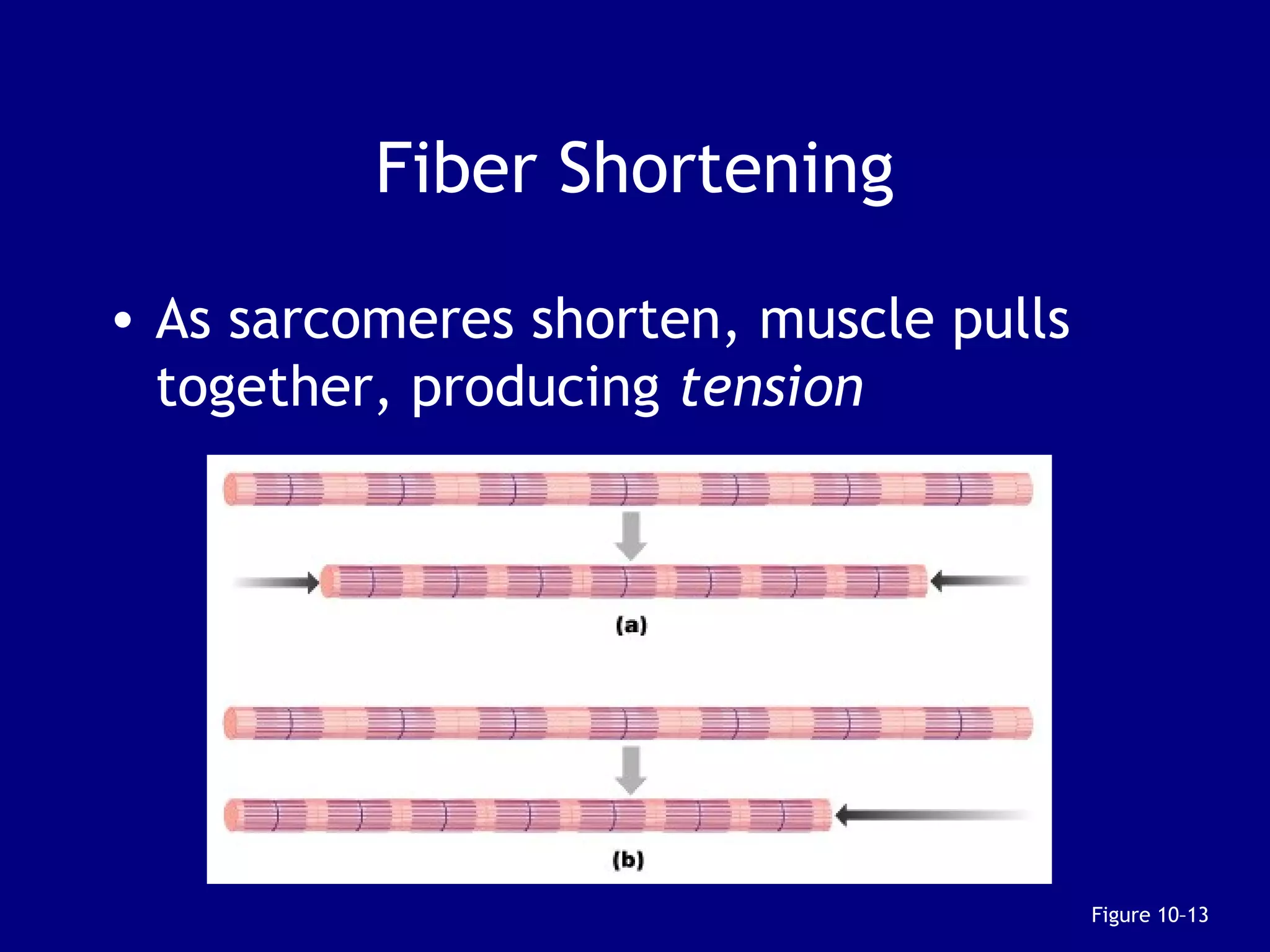
2. Skeletal muscle contains bundles of fibers surrounded by connective tissues. Within the fibers are myofibrils composed of thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments that slide past each other to cause muscle contraction.
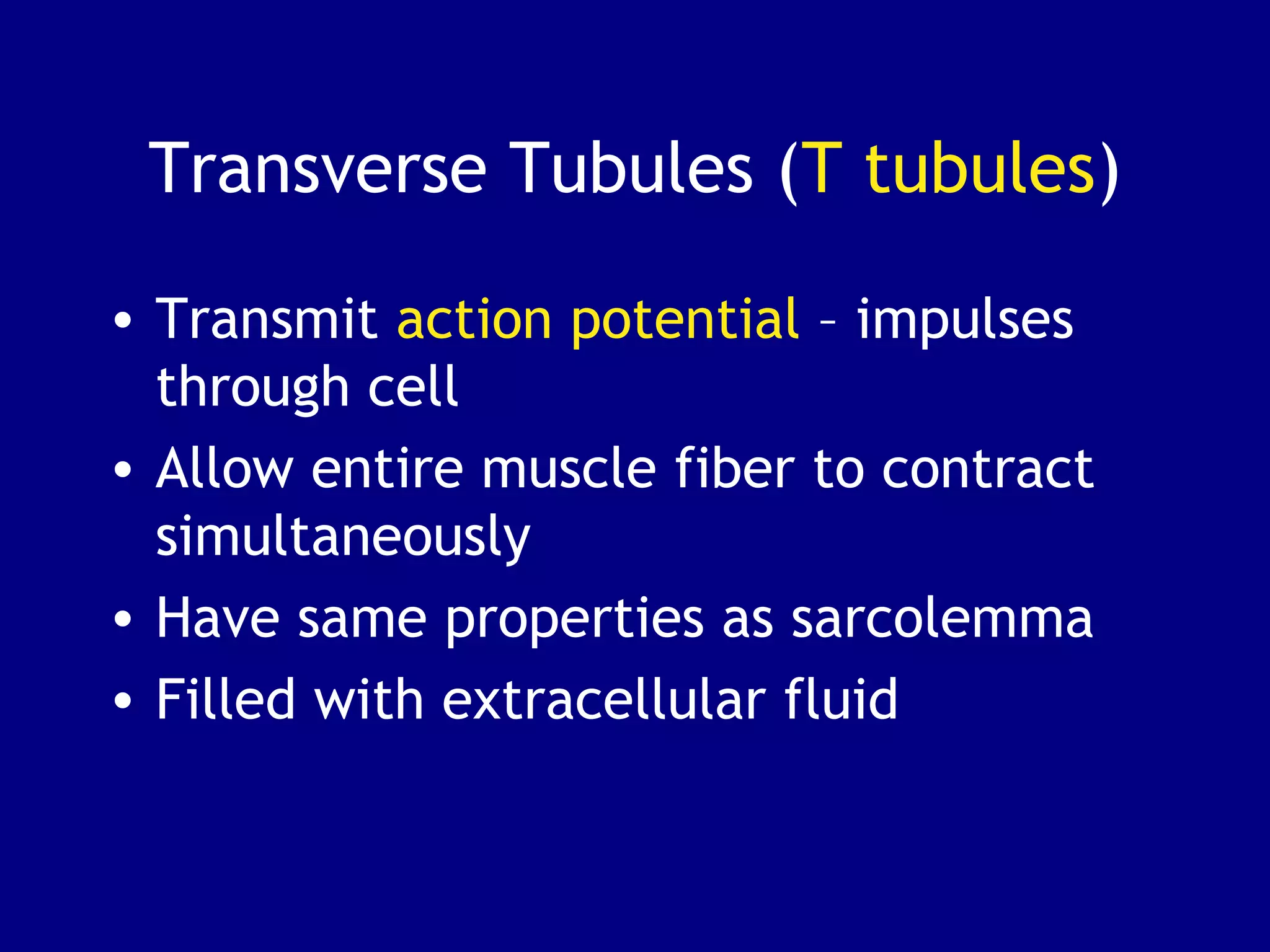
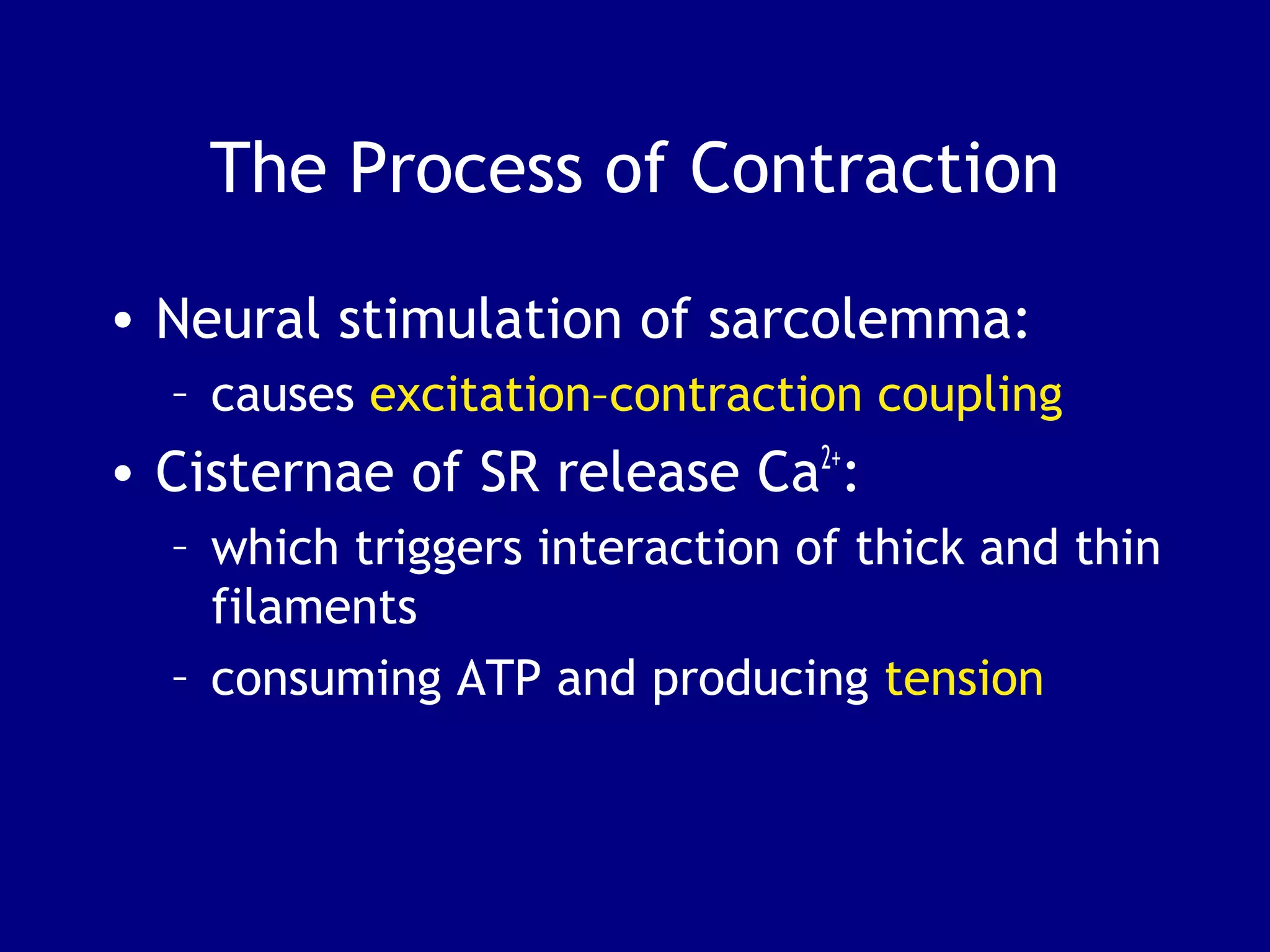
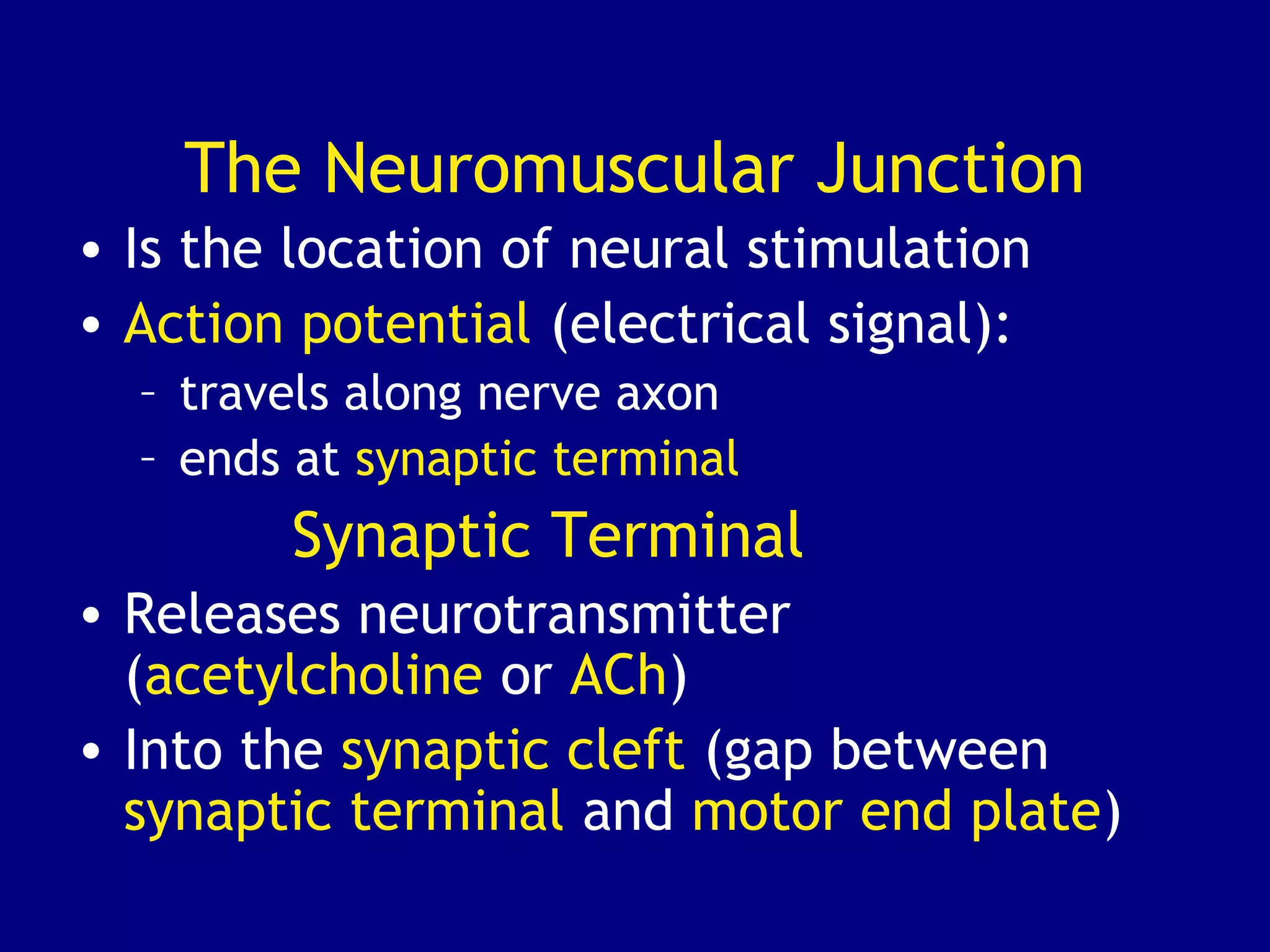
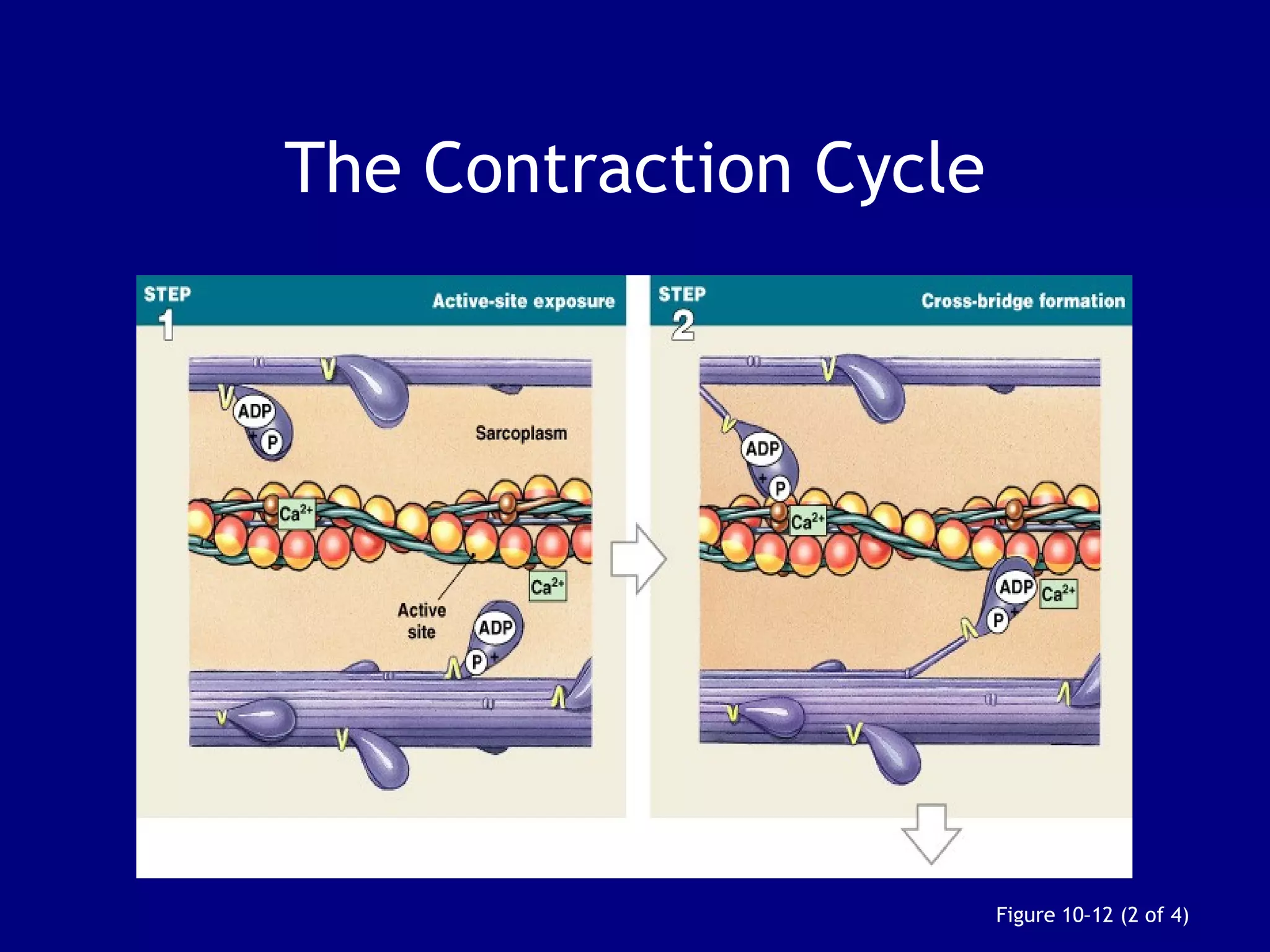
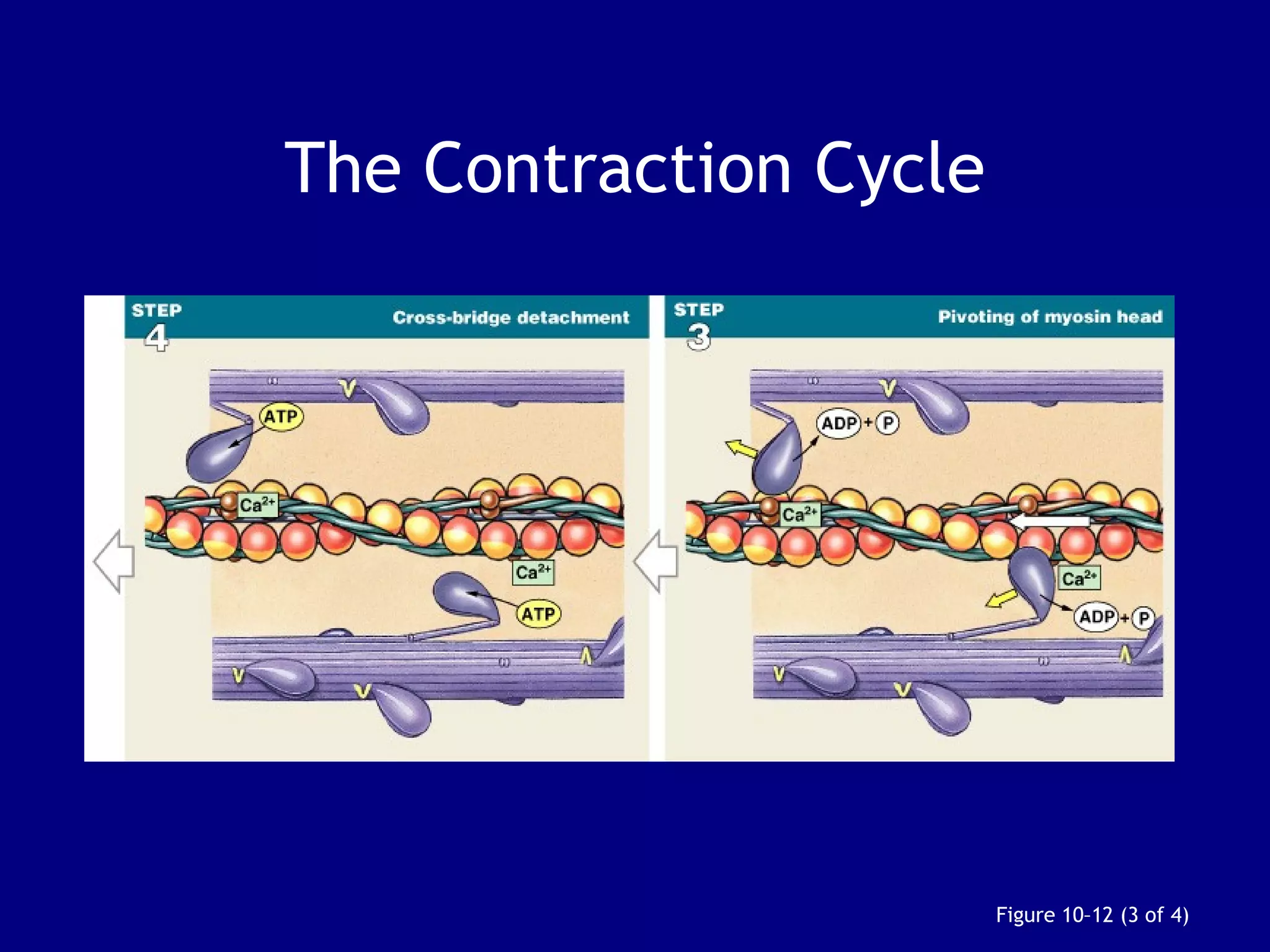
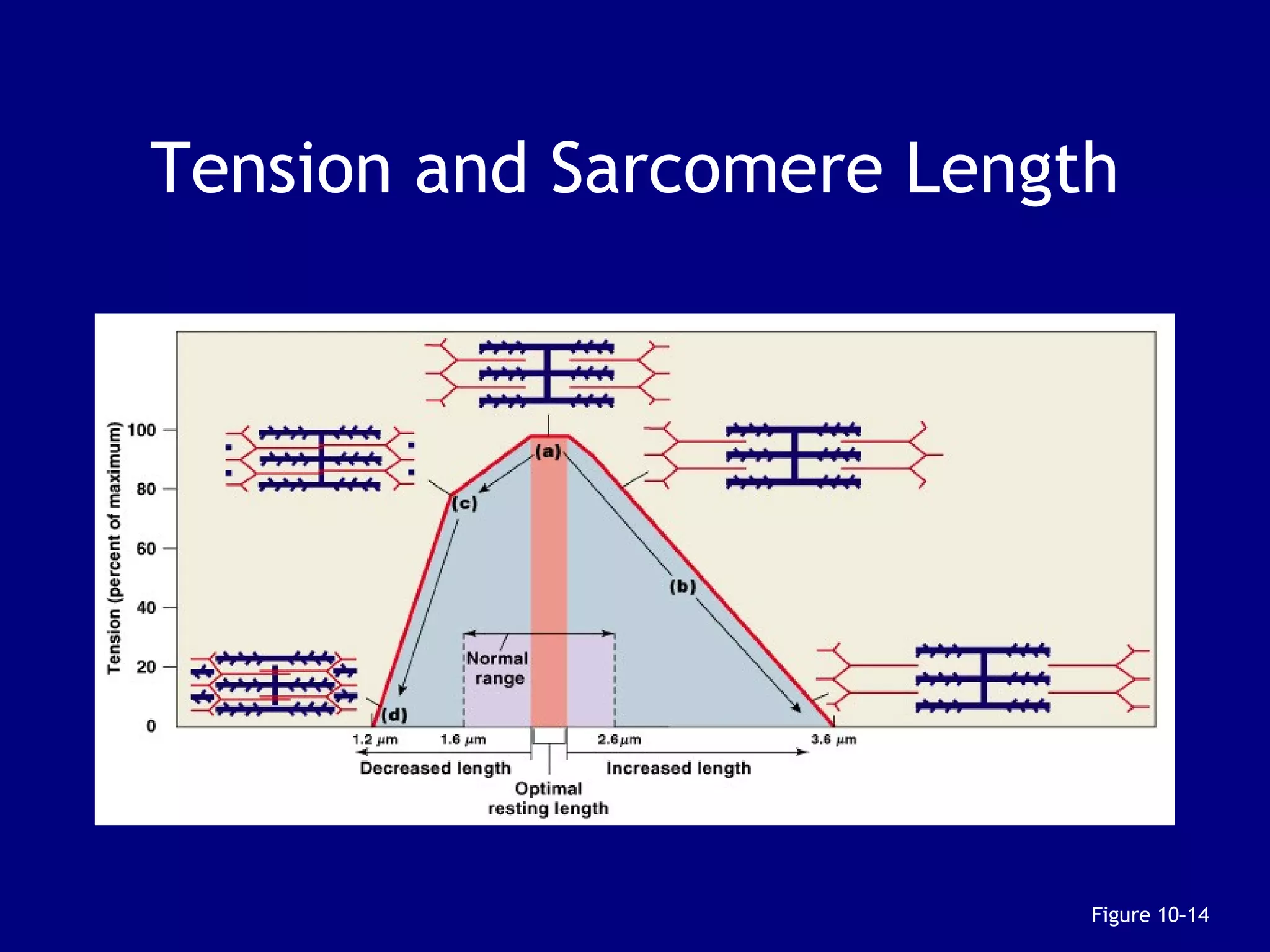
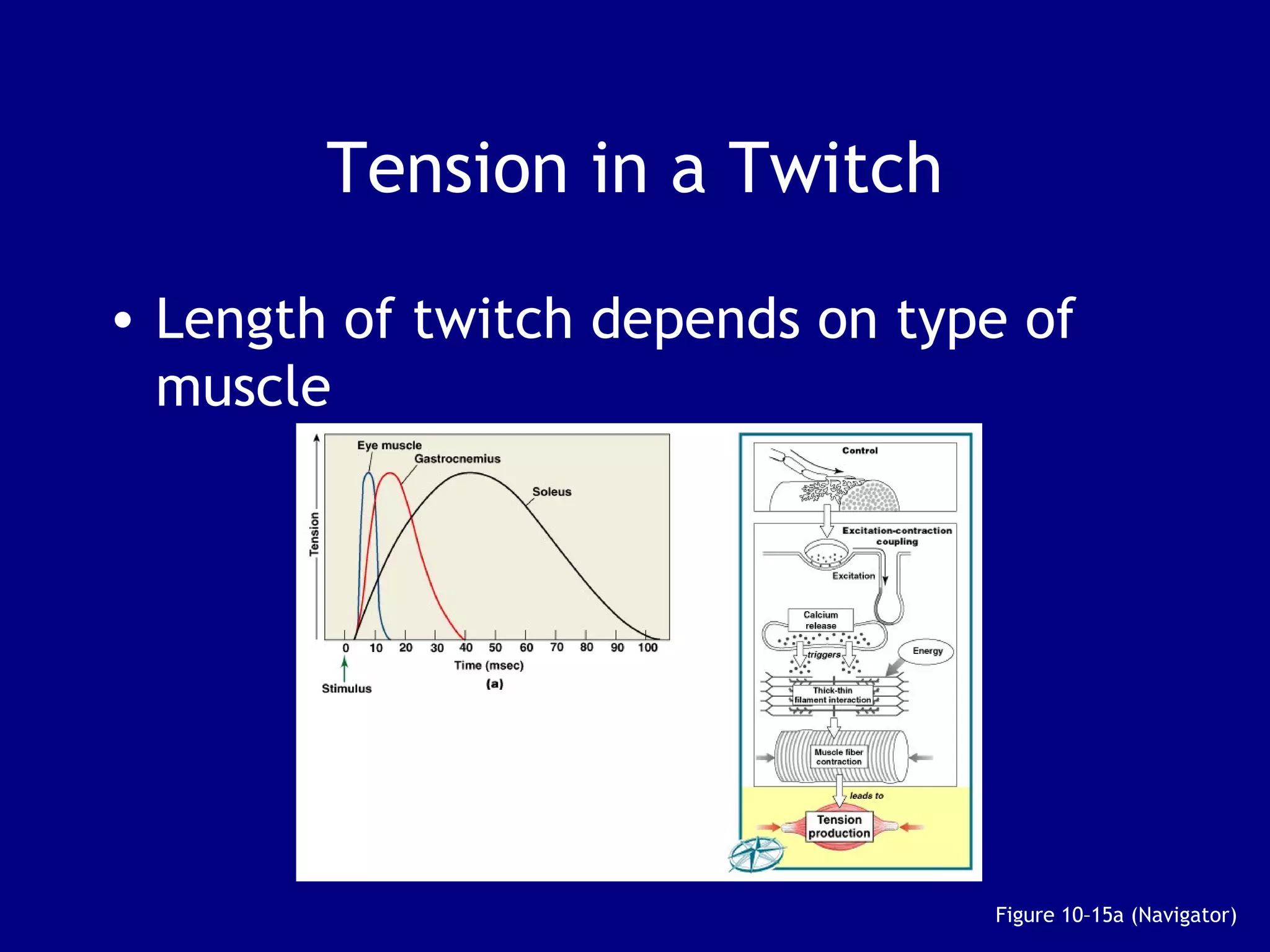
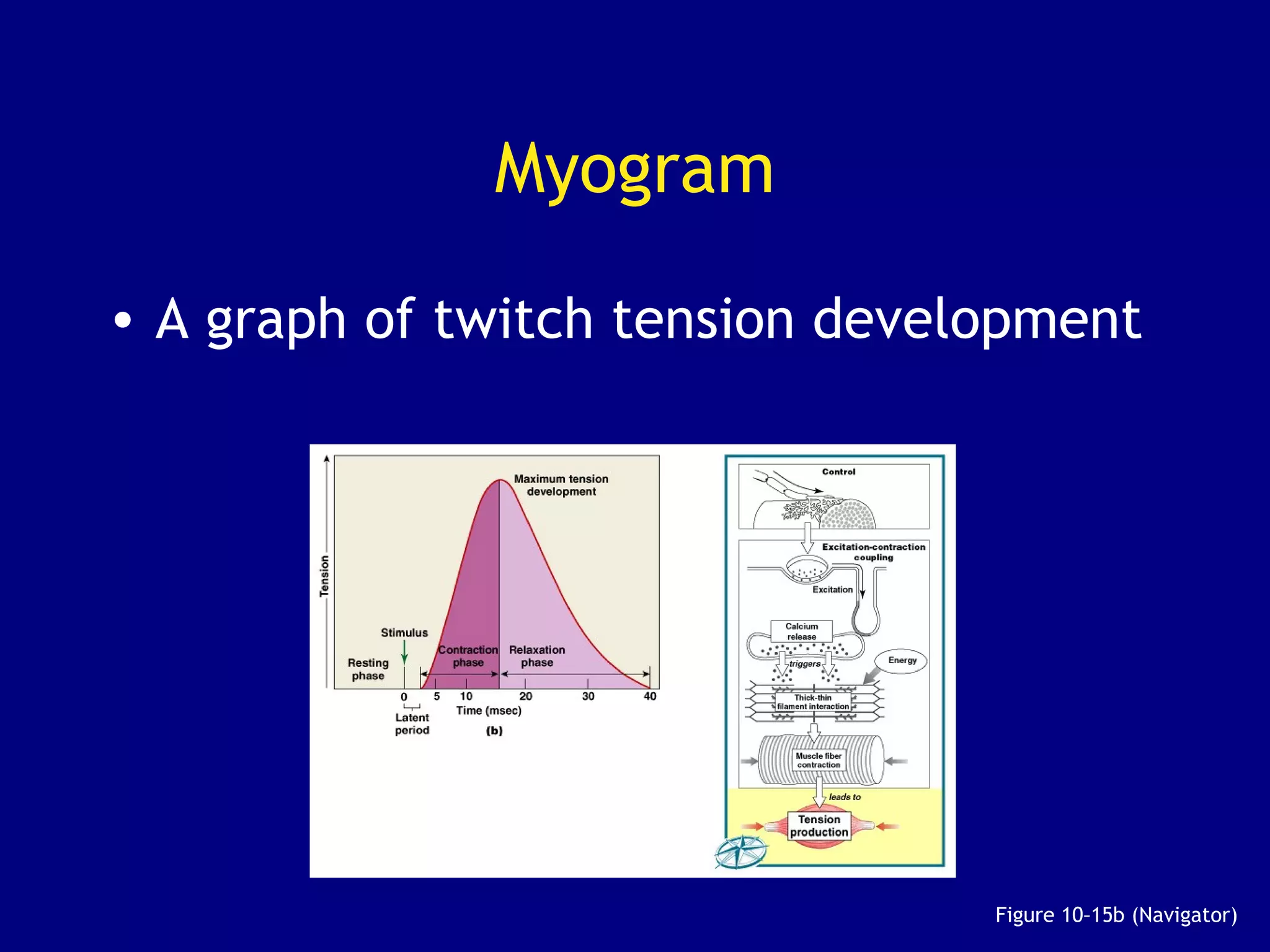
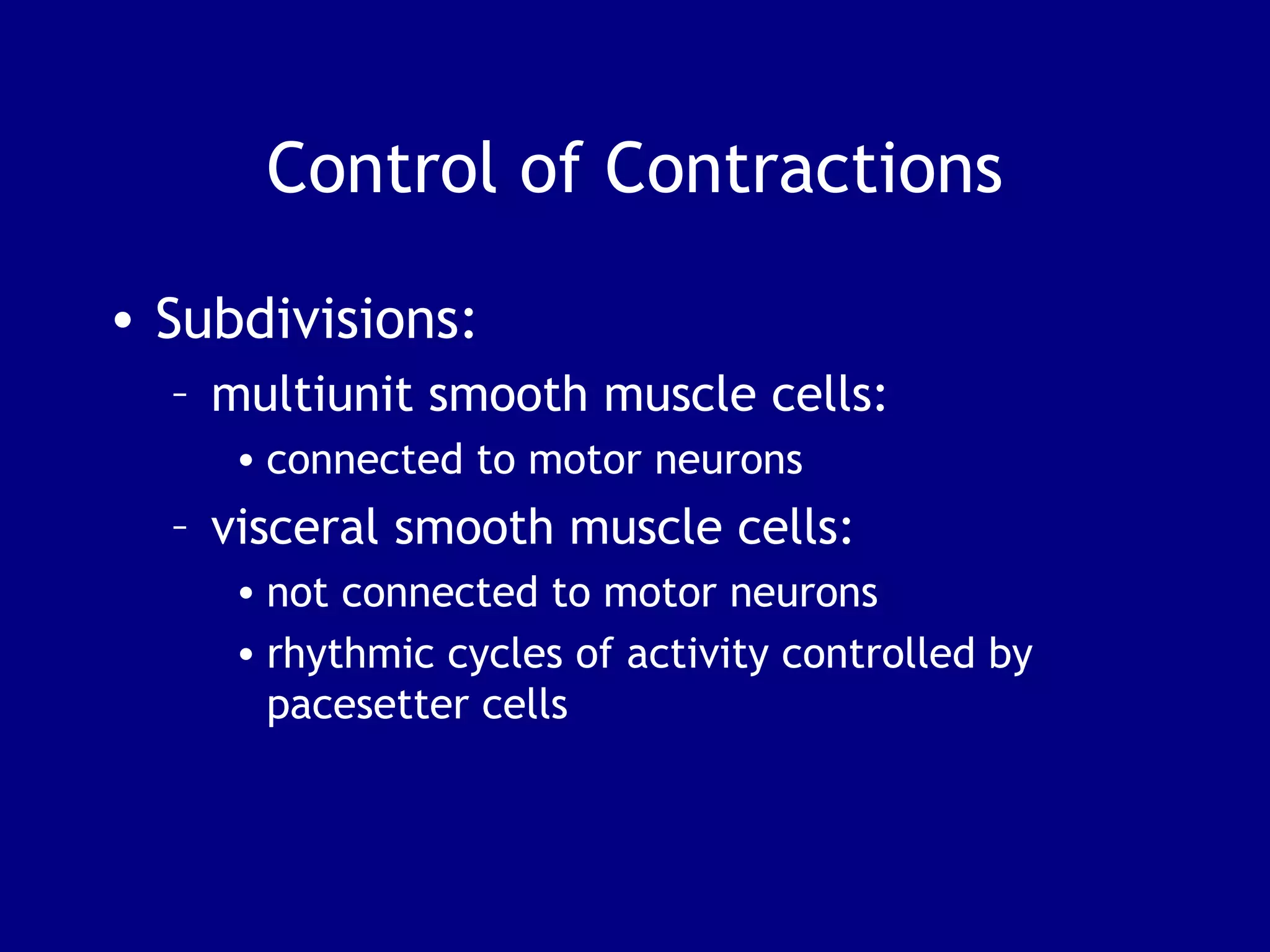
3. Contraction is triggered when a motor neuron stimulates the neuromuscular junction, causing calcium release and the myosin heads to interact with and pull on the actin filaments. The strength of contraction depends on factors like overlap of filaments and stimulation frequency.